Mississippi Today
Work begins on Tippah highway project 20 years after being made priority

Tippah County, population about 20,500 in northeast Mississippi, was the state’s center of political power for one day this past week.
State Rep. Jody Steverson, a Republican who represents Tippah County, posted on social media, “I would like to personally invite every Tippah County citizen to this historic event… Never in our county’s history have the governor, lieutenant governor, and House speaker of Mississippi ever assembled in Tippah County simultaneously.”
Gov. Tate Reeves, Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann, House Speaker Jason White, as well as former Speaker Philip Gunn, were on hand for the ground-breaking of a project to four-lane about a 10-mile section of U.S. Highway 15 from the Tippah and Union counties line to about a mile north of Ripley, the county seat and largest city in Tippah County.
The ground-breaking was a big deal in Tippah County. The project has been on the drawing board since 2002 when the Legislature passed a bill called Vison 21 that established a method to four-lane highways in Mississippi based on needs and available money.
The section of U.S. 15 was on the initial Vison 21 map as an “immediate need.” More than two decades later, the state’s political leadership traveled to near the Tennessee state line to celebrate the ground-breaking.
Progress, finally.
Highway 15 has been in need of four-laning for decades, especially the section between New Albany in Union County and Ripley. Traffic on the two-lane road moves at a snail’s pace thanks in part to the big trucks at a furniture factory in the area and other businesses.
The ground-breaking more than two decades after U.S 15 was made a priority highlights the lack of funding the Department of Transportation has had for new highway construction projects. For more than a decade, the Department of Transportation has lacked enough money to maintain existing roads, much less construct new highways.
Thanks in large part to national economic conditions and federal funds, including the 2021 federal infrastructure bill, Mississippi currently has more money for roads and bridges. Mississippi has surplus funds that are being used, in part, on road and bridge needs. Work will begin soon on a few other highway projects.
But the surplus state money is not likely to last. The three Transportation commissioners and their executive director, Brad White, are still talking about the need for a source of new, sustained money to fund the state’s transportation needs on an ongoing basis. Central District Transportation Commissioner Willie Simmons focused on the need of a new source of revenue recently during the political stumping at the Neshoba County Fair.
Many also would argue that the lack of funding has been exacerbated at times by the Legislature passing bills to place projects above those cited as priorities by the process spelled out in Vision 21.
Gov. Reeves, who was no doubt the star in Tippah County at the ground-breaking, was blamed by some for bypassing the Vison 21 projects as lieutenant governor.
In 2014, the House voted to kill the Department of Transportation budget because of what House leaders described as the Senate leadership’s insistence on placing “pet projects” in the bill.
Those projects included the six laning of Lakeland Drive in suburban Jackson near where then-Lt. Gov. Reeves, who presided over the Senate, lived.
The issue of Lakeland Drive was a major one during Reeves’ successful 2019 gubernatorial bid as it came to light that part of the Lakeland Project included building a $2 million frontage road to make it easier for people in the gated neighborhood where Reeves lived to gain access to Lakeland Drive.
The access road was scrapped by the Transportation Commission after it made news. The addition of the extra lanes on Lakeland Drive was completed.
Reeves took credit for the six-laning of Lakeland, but said he had no input on the frontage road. But emails at the time indicated that members of his staff were in discussions with MDOT officials about the project.
Then-MDOT Executive Director Melinda McGrath said in correspondence with Reeves that the Legislature in budgeting money for projects such as Lakeland Drive was ignoring the Vison 21 priorities.
Work is finally beginning on Highway 15 in Tippah County and the governor said he is happy about it.
On social media he posted, “Stopped in Tippah County to break ground on a nearly $200 million Highway 15 expansion project. This massive investment will help further solidify Mississippi as a transportation hub for the country. Together, we’re making our infrastructure bigger and better than ever before.”
Slowly, that might be finally happening.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Crooked Letter Sports Podcast
Podcast: Ohio State won it all, but where would Ole Miss have been with Quinshon Jundkins?

Lots to talk about on the days after the national championship game, but in Mississippi, especially in Oxford, much of the talk is about what might have been had Judkins stayed at Ole Miss. Also, the Clevelands discuss Egg Bowl basketball, the grueling SEC schedule, the NFL playoffs, and John Wade’s saga at Southern Miss.
Stream all episodes here.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Mississippi Today
With EPA support, the Corps is moving forward with the Yazoo Pumps

Barring any legal challenge, it appears the South Delta is finally getting its pumps.
The U.S Army Corps of Engineers announced last Friday it’s moving forward with an altered version of the Yazoo Pumps, a flood relief project that the agency has touted for decades. The project now also has the backing of the Environmental Protection Agency, whose veto killed a previous iteration in 2008 because of the pumps’ potential to harm 67,000 acres of valuable wetland habitat.
In a Jan. 8 letter, the EPA wrote that proposed mitigation components — such as cutting off the pumps at different points depending on the time of year, as well as maintaining certain water levels for aquatic species during low-flow periods — are “expected to reduce adverse effects to an acceptable level.”
South Delta residents have called for the project to be built for years, especially after the record-setting backwater flood in 2019. State lawmakers from the area rejoiced over last week’s news.
“It’s been a long time coming,” said Sen. Joseph Thomas, D-Yazoo City, explaining that most in his district support the pumps. “I’m sure there are some minuses and pluses (to the project), but by and large I think it needs to happen.”
Sen. Briggs Hopson, R-Vicksburg, recalled that almost half of his district was underwater in 2019.

“I’m very pleased that the Corps has issued this (decision),” Hopson told Mississippi Today on Tuesday.
Before the Corps’ latest proposal, the future of the pumps was in limbo for several years. Under President Trump’s first administration, the EPA in 2020 said the 2008 veto no longer applied to the proposal because of Corps research suggesting that the wetlands mainly relied on water during the winter months — a less critical period for the agriculture-dependent South Delta — to survive, and that using the pumps during the rest of the year would still allow the wetlands to exist.
The EPA then restored the veto under President Biden’s administration. But in 2023, the Corps agreed to work with the EPA on flood-control solutions which, as it turned out, still included the pumps.
While the public comment period is over and the project appears to be moving forward, the Corps has yet to provide a cost estimate for the pumps, which are likely to cost at least hundreds of millions of dollars. A 19,000 cubic-feet-per second, or cfs, pumping station in Louisiana cost roughly $1 billion to build over a decade ago, and the Corps is proposing a 25,000 cfs station for the South Delta.
Corps spokesperson Christi Kilroy told Mississippi Today that the project will move onto the engineering and design phase, during which the agency will come up with a price estimate. Mississippi Today asked multiple times if it’s unusual to wait until after the public has had a chance to comment to provide an estimate, but the agency did not respond.

Under the project’s new design, the pumps will turn on when backwater reaches the 90-foot elevation mark anytime during the designated “crop season” from March 25 to Oct. 15. During the rest of the year, the Corps will allow the backwater to reach 93 feet before pumping.
In last Friday’s decision, the Corps wrote that the project would have “less than significant effects (on wetlands) due to mitigation.” The project’s mitigation includes acquiring and reforesting 5,700 acres of “frequently flooded” farmland to compensate for wetland impacts.
In a statement sent to Mississippi Today, the EPA said that the “higher pumping elevations” — the Corps’ previous proposal started the pumps at 87 feet — and the “seasonal approach” to pumping will reduce the wetlands impact.
However conservationists, including a group of former EPA employees, are not convinced. The Environmental Protection Network, a nonprofit of over 650 former EPA employees, wrote in August that the latest proposed pumping station “has the potential to drain the same or similar wetlands identified in the 2008 (veto) and potentially more.”
“Similar to concerns EPA identified in the 2008 (veto)… EPN’s concerns with the potential adverse impacts of this version of the project remain,” the group wrote.
A coalition of other groups — including Audubon Delta, Earthjustice, Healthy Gulf and Mississippi Sierra Club — remain opposed to the project, arguing that hundreds of species rely on the wetlands during the “crop season” for migration, breeding and rearing.

“This action is a massive stain on the Biden Administration’s environmental legacy and undermines EPA’s own authority to protect our nation’s most important waters,” the coalition said in a statement last Friday.
When asked about potential legal challenges to the Corps’ decision, Audubon Delta’s policy director Jill Mastrototaro told Mississippi Today via email: “This project clearly violates the veto as we’ve documented in our comments. We’re carefully reviewing the details of the announcement and all options are on the table.”
In addition to the pumps, the project includes voluntary buyouts for those whose properties flood below the 93-foot mark, which includes 152 homes.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1906


Jan. 22, 1906

Pioneer aviator and civil rights activist Willa Beatrice Brown was born in Glasgow, Kentucky.
While working in Chicago, she learned how to fly and became the first Black female to earn a commercial pilot’s license. A journalist said that when she entered the newsroom, “she made such a stunning appearance that all the typewriters suddenly went silent. … She had a confident bearing and there was an undercurrent of determination in her husky voice as she announced, not asked, that she wanted to see me.”
In 1939, she married her former flight instructor, Cornelius Coffey, and they co-founded the Cornelius Coffey School of Aeronautics, the first Black-owned private flight training academy in the U.S.
She succeeded in convincing the U.S. Army Air Corps to let them train Black pilots. Hundreds of men and women trained under them, including nearly 200 future Tuskegee Airmen.
In 1942, she became the first Black officer in the U.S. Civil Air Patrol. After World War II ended, she became the first Black woman to run for Congress. Although she lost, she remained politically active and worked in Chicago, teaching business and aeronautics.
After she retired, she served on an advisory board to the Federal Aviation Administration. She died in 1992. A historical marker in her hometown now recognizes her as the first Black woman to earn a pilot’s license in the U.S., and Women in Aviation International named her one of the 100 most influential women in aviation and space.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days agoGeorgia senator arrested for trying to defy ban on entering House chamber
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days agoU-Haul: South Carolina the fastest growing state in the country
-
 News from the South - Tennessee News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed4 days ago‘Don’t lose hope’: More than 100 Tennesseans protest incoming Trump administration
-
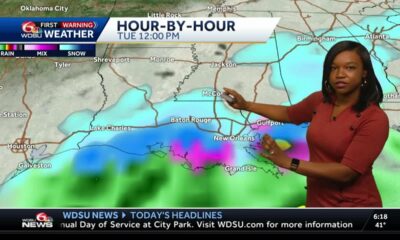
 News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days agoTracking weekend rain and chances for wintry weather
-
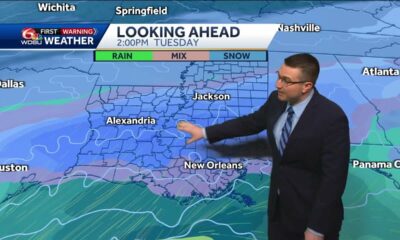
 News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days agoTracking wintry weather potential
-

 News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed5 days agoSoutheast Louisiana officials brace for freezing temperatures
-

 News from the South - Tennessee News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed5 days agoSpeed limit reduced on State Route 109 in Wilson County
-
 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed5 days agoFalling Saturday temperatures
































