Marmots were the perfect test species for a wildlife adversity index. Xochitl Ortiz Ross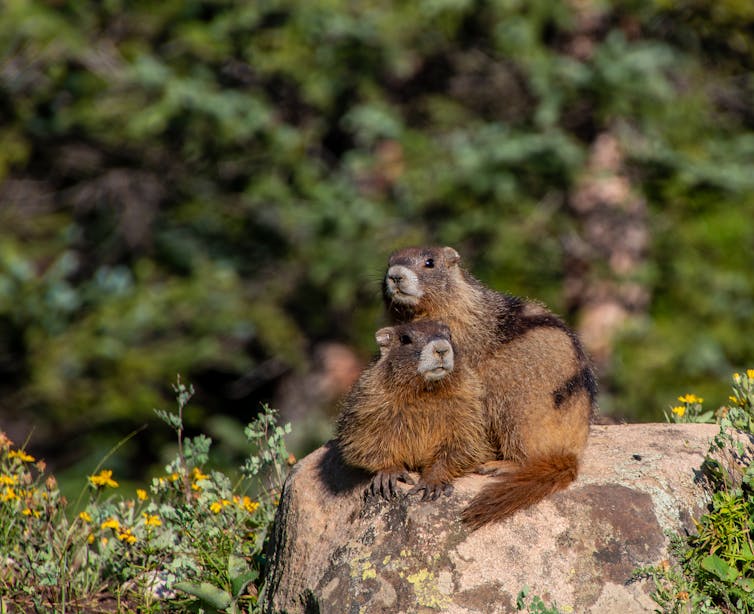
Xochitl Ortiz Ross, University of California, Los Angeles
Psychologists know that childhood trauma, or the experience of harmful or adverse events, can have lasting repercussions on the health and well-being of people well into adulthood. But while the consequences of early adversity have been well researched in humans, people aren’t the only ones who can experience adversity.
If you have a rescue dog, you probably have witnessed how the abuse or neglect it may have experienced earlier in life now influence its behavior – these pets tend to be more skittish or reactive. Wild animals also experience adversity. Although their negative experiences are easy to dismiss as part of life in the wild, they still have lifelong repercussions – just like traumatic events in people and pets.
As behavioral ecologists, we are interested in how adverse experiences early in life can affect animals’ behavior, including the kinds of decisions they make and the way they interact with the world around them. In other words, we want to see how these experience affect the way they behave and survive in the wild.
Many studies in humans and other animals have shown the importance of early life experiences in shaping how individuals develop. But researchers know less about how multiple, different instances of adversity or stressors can accumulate within the body and what their overall impact is on an animal’s well-being.
Wild populations face many kinds of stressors. They compete for food, risk getting eaten by a predator, suffer illness and must contend with extreme weather conditions. And as if life in the wild wasn’t hard enough, humans are now adding additional stressors such as chemical, light and sound pollution, as well as habitat destruction.
Given the widespread loss of biodiversity, understanding how animals react to and are harmed by these stressors can help conservation groups better protect them. But accounting for such a diversity of stressors is no easy feat. To address this need and demonstrate the cumulative impact of multiple stressors, our research team decided to develop an index for wild animals based on psychological research on human childhood trauma.
A cumulative adversity index
Developmental psychologists began to develop what psychologists now call the adverse childhood experiences score, which describes the amount of adversity a person experienced as a child. Briefly, this index adds up all the adverse events – including forms of neglect, abuse or other household dysfunction – an individual experienced during childhood into a single cumulative score.
This score can then be used to predict later-life health risks such as chronic health conditions, mental illness or even economic status. This approach has revolutionized many human health intervention programs by identifying at-risk children and adults, which allows for more targeted interventions and preventive efforts.
So, what about wild animals? Can we use a similar type of score or index to predict negative survival outcomes and identify at-risk individuals and populations?
These are the questions we were interested in answering in our latest research paper. We developed a framework on how to create a cumulative adversity index – similar to the adverse childhood experiences score, but for populations of wild animals. We then used this index to gain insights about the survival and longevity of yellow-bellied marmots. In other words, we wanted to see whether we could use this index to estimate how long a marmot would live.
A marmot case study
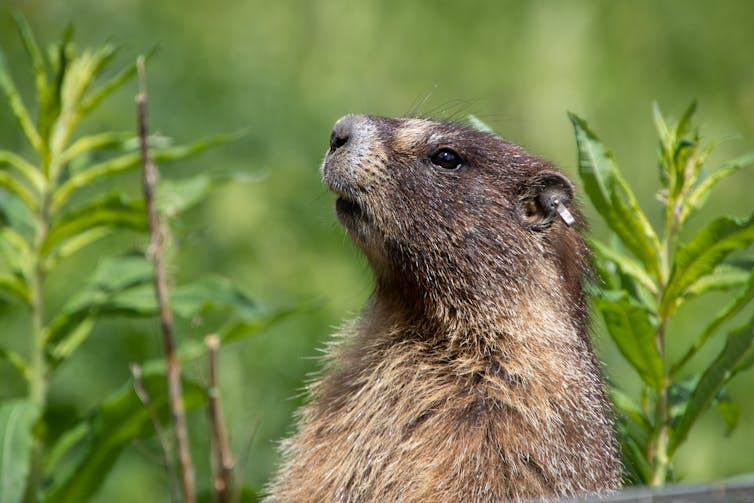
Yellow-bellied marmots are a large ground squirrel closely related to groundhogs. Our research group has been studying these marmots in Colorado at the Rocky Mountain Biological Laboratory since 1962.
Yellow-bellied marmots are an excellent study system because they are diurnal, or active during the day, and they have an address. They live in burrows scattered across a small, defined geographical area called a colony. The size of the colony and the number of individuals that reside within varies greatly from year to year, but they are normally composed of matrilines, which means related females tend to remain within the natal colony, while male relatives move away to find a new colony.
Yellow-bellied marmots hibernate for most of the year, but they become active between April and September. During this active period, we observe each colony daily and regularly trap each individual in the population – that’s over 200 unique individuals just in 2023. We then mark their backs with a distinct symbol and give them uniquely numbered ear tags so they can be later identified.
Although they can live up to 15 years, we have detailed information about the life experiences of individual marmots spanning almost 30 generations. They were the perfect test population for our cumulative adversity index.
Among the sources of adversity, we included ecological measures such as a late spring, a summer drought and high predator presence. We also included parental measures such as having an underweight or stressed mother, being born or weaned late, and losing their mother. The model also included demographic measures such as being born in a large litter or having many male siblings.
Importantly, we looked only at females, since they are the ones who tend to stay home. Therefore, some of the adversities listed are only applicable to females. For example, females born in litters with many males become masculinized, likely from the high testosterone levels in the mother’s uterus. The females behave more like males, but this also reduces their life span and reproductive output. Therefore, having many male siblings is harmful to females, but maybe not to males.

So, does our index, or the number of adverse events a marmot experienced early on, explain differences in marmot survival? We found that, yes, it does.
Experiencing even just one adversity event before age 2 nearly halved an adult marmot’s odds of survival, regardless of the type of adversity they experienced. This is the first record of lasting negative consequences from losing a mother in this species.
So what?
Our study isn’t the only one of its kind. A few other studies have used an index similar to the human adverse childhood experiences score with wild primates and hyenas, with largely similar results. We are interested in broadening this framework so that other researchers can adopt it for the species they study.
A better understanding of how animals can or cannot cope with multiple sources of adversity can inform wildlife conservation and management practices. For example, an index like ours could help identify at-risk populations that require a more immediate conservation action.
Instead of tackling the one stressor that seems to have the greatest effect on a species, this approach could help managers consider how best to reduce the total number of stressors a species experiences.
For example, changing weather patterns driven by global heating trends may create new stressors that a wildlife manager can’t address. But it might be possible to reduce how many times these animals have to interact with people during key times of the year by closing trails, or providing extra food to replace the food they lose from harsh weather.
While this index is still in early development, it could one day help researchers ask new questions about how animals adapt to stress in the wild.![]()
Xochitl Ortiz Ross, Ph.D. Candidate in Ecology & Evolutionary Biology, University of California, Los Angeles
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.