Chuck Fishman/Getty Images
Narcisa Pricope, Mississippi State University
Valentine’s Day often conjures images of chocolates and romance. But the crop behind this indulgence faces an existential threat.
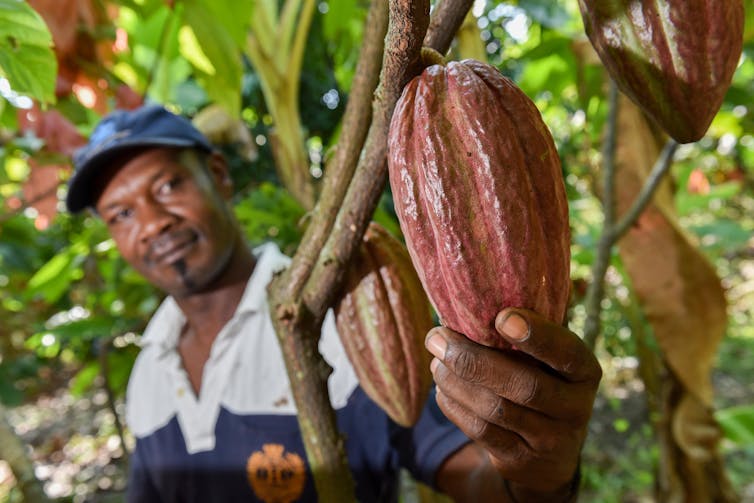
Regions like northeastern Brazil, one of the world’s notable cocoa-producing areas, are grappling with increasing aridity – a slow, yet unrelenting drying of the land. Cocoa is made from the beans of the cacao tree, which thrives in humid climates. The crop is struggling in these drying regions, and so are the farmers who grow it.
This is not just Brazil’s story. Across West Africa, where 70% of the world’s cacao is grown, and in the Americas and Southeast Asia, shifting moisture levels threaten the delicate balance required for production. These regions, home to vibrant ecosystems and global breadbaskets that feed the world, are on the frontlines of aridity’s slow but relentless advance.

©2017CIAT/NeilPalmer, CC BY-NC-SA
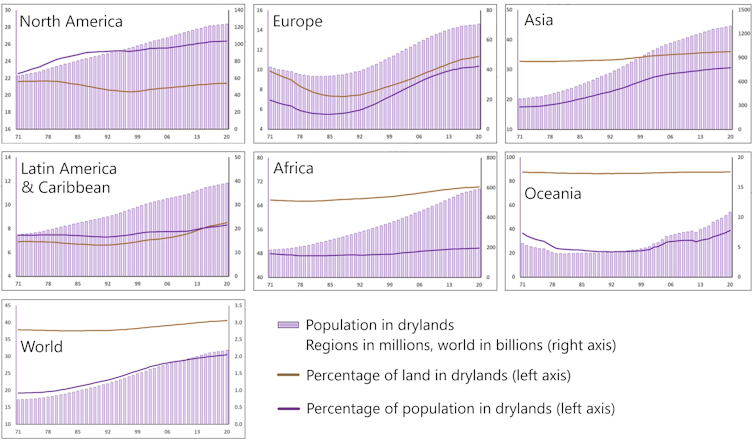
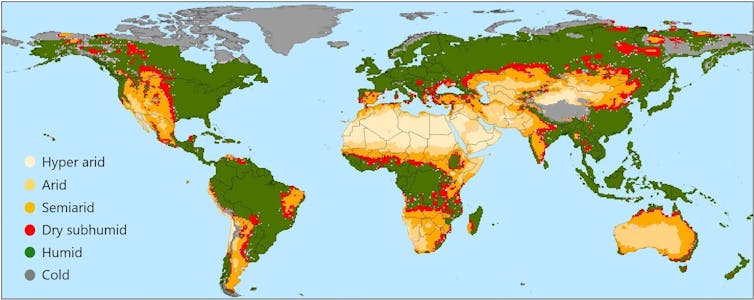
Over the past 30 years, more than three-quarters of the Earth’s landmass has become drier. A recent report I helped coordinate for the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification found that drylands now cover 41% of global land, an area that expanded by nearly 1.7 million square miles (4.3 million square kilometers) over those three decades — about half the size of Australia.
This creeping dryness is not just a climate phenomenon. It’s a long-term transformation that may be irreversible and that carries devastating consequences for ecosystems, agriculture and livelihoods worldwide.
What causes aridity?
Aridity, while often thought of as purely a climate phenomenon, is the result of a complex interplay among human-driven factors. These include greenhouse gas emissions, land use practices and the degradation of critical natural resources, such as soil and biodiversity.
These interconnected forces have been accelerating the transformation of once-productive landscapes into increasingly arid regions, with consequences that ripple across ecosystems and economies.
Greenhouse gas emissions: A global catalyst
Human-induced climate change is the primary driver of rising aridity.
Greenhouse gas emissions, particularly from fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, increase global temperatures. Rising temperatures, in turn, cause moisture to evaporate at a faster rate. This heightened evaporation reduces soil and plant moisture, exacerbating water scarcity – even in regions with moderate rainfall.
Aridity began accelerating globally in the 1950s, and the world has seen a pronounced shift over the past three decades.
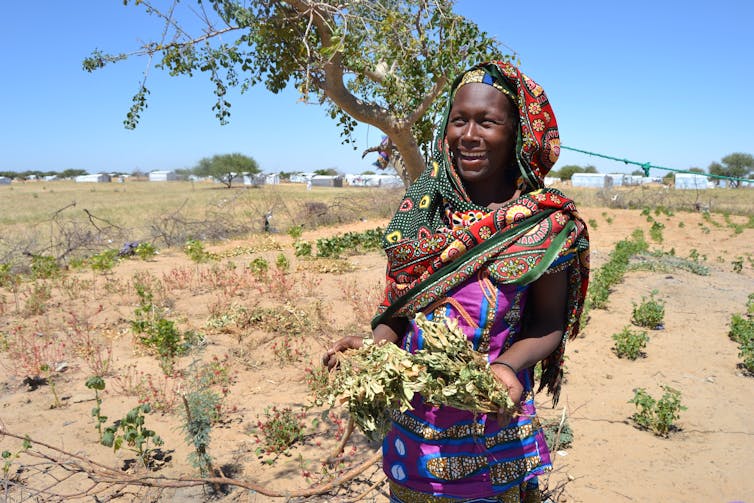
This process is particularly stark in regions already prone to dryness, such as Africa’s Sahel region and the Mediterranean. In these areas, reduced precipitation – combined with increased evaporation – creates a feedback loop: Drier soils absorb less heat, leaving the atmosphere warmer and intensifying arid conditions.
UNCCD
Unsustainable land use practices: A hidden accelerator
Aridity is also affected by how people use and manage land.
Unsustainable agricultural practices, overgrazing and deforestation strip soils of their protective vegetation cover, leaving them vulnerable to erosion. Industrial farming techniques often prioritize short-term yields over long-term sustainability, depleting nutrients and organic matter essential for healthy soils.
For example, in cocoa-producing regions like northeastern Brazil, deforestation to make room for agriculture disrupts local water cycles and exposes soils to degradation. Without vegetation to anchor it, topsoil – critical for plant growth – washes away during rainfall or is blown away by winds, taking with it vital nutrients.
These changes create a vicious cycle: Degraded soils also hold less water and lead to more runoff, reducing the land’s ability to recover.

United Nations Chad, CC BY-NC-SA
The soil-biodiversity connection
Soil, often overlooked in discussions of climate resilience, plays a critical role in mitigating aridity.
Healthy soils act as reservoirs, storing water and nutrients that plants depend on. They also support biodiversity below and above ground. A single teaspoon of soil contains billions of microorganisms that help cycle nutrients and maintain ecological balance.
However, as soils degrade under aridity and mismanagement, this biodiversity diminishes. Microbial communities, essential for nutrient cycling and plant health, decline. When soils become compacted and lose organic matter, the land’s ability to retain water diminishes, making it even more susceptible to drying out.
In short, the loss of soil health creates cascading effects that undermine ecosystems, agricultural productivity and food security.
Global hot spots: Looming food security crises
Cocoa is just one crop affected by the encroachment of rising aridity.
Other key agricultural zones, including the breadbaskets of the world, are also at risk. In the Mediterranean, Africa’s Sahel and parts of the U.S. West, aridity already undermines farming and biodiversity.
By 2100, up to 5 billion people could live in drylands – nearly double the current population in these areas, due to both population growth and expansion of drylands as the planet warms. This puts immense pressure on food systems. It can also accelerate migration as declining agricultural productivity, water scarcity and worsening living conditions force rural populations to move in search of opportunities.
UNCCD
Aridity’s ripple effects also extend far beyond agriculture. Ecosystems, already strained by deforestation and pollution, are stressed as water resources dwindle. Wildlife migrates or dies, and plant species adapted to moister conditions can’t survive. The Sahel’s delicate grasslands, for instance, are rapidly giving way to desert shrubs.
On a global scale, economic losses linked to aridification are staggering. In Africa, rising aridity contributed to a 12% drop in gross domestic product from 1990 to 2015. Sandstorms and dust storms, wildfires and water scarcity further burden governments, exacerbating poverty and health crises in the most affected regions.
The path forward
Aridity is not inevitable, nor are its effects completely irreversible. But coordinated global efforts are essential to curb its progression.
Countries can work together to restore degraded lands by protecting and restoring ecosystems, improving soil health and encouraging sustainable farming methods.
Communities can manage water more efficiently through rainwater harvesting and advanced irrigation systems that optimize water use. Governments can reduce the drivers of climate change by investing in renewable energy.
Continued international collaboration, including working with businesses, can help share technologies to make these actions more effective and available worldwide.
So, as you savor chocolate this Valentine’s Day, remember the fragile ecosystems behind it. The price of cocoa in early 2025 was near its all-time high, due in part to dry conditions in Africa. Without urgent action to address aridity, this scenario may become more common, and cocoa – and the sweet concoctions derived from it – may well become a rare luxury.
Collective action against aridity isn’t just about saving chocolate – it’s about preserving the planet’s capacity to sustain life.![]()
Narcisa Pricope, Professor of Geography and Land Systems Science and Associate Vice President for Research, Mississippi State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.