Mississippi Today
Why the CDC has recommended new COVID boosters for all
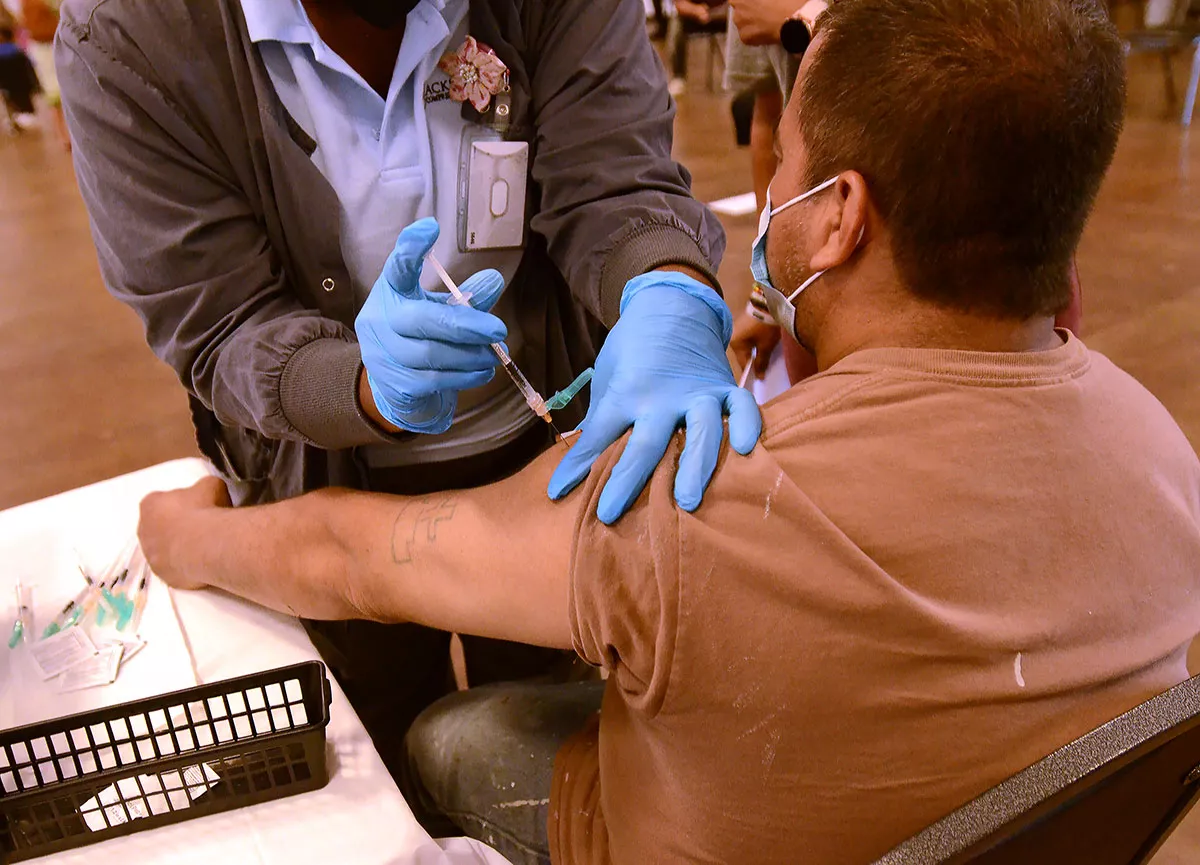
Everyone over the age of 6 months should get the latest COVID-19 booster, a federal expert panel recommended Tuesday after hearing an estimate that universal vaccination could prevent 100,000 more hospitalizations each year than if only the elderly were vaccinated.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 13-1 for the motion after months of debate about whether to limit its recommendation to high-risk groups. A day earlier, the FDA approved the new booster, stating it was safe and effective at protecting against the COVID variants currently circulating in the U.S.
After the last booster was released, in 2022, only 17% of the U.S. population got it — compared with the roughly half of the nation who got the first booster after it became available in fall 2021. Broader uptake was hurt by pandemic weariness and evidence the shots don’t always prevent COVID infections. But those who did get the shot were far less likely to get very sick or die, according to data presented at Tuesday’s meeting.
The virus sometimes causes severe illness even in those without underlying conditions, causing more deaths in children than other vaccine-preventable diseases, as chickenpox did before vaccines against those pathogens were universally recommended.
The number of hospitalized patients with COVID has ticked up modestly in recent weeks, CDC data shows, and infectious disease experts anticipate a surge in the late fall and winter.
The shots are made by Moderna and by Pfizer and its German partner, BioNTech, which have decided to charge up to $130 a shot. They have launched national marketing campaigns to encourage vaccination. The advisory committee deferred a decision on a third booster, produced by Novavax, because the FDA hasn’t yet approved it. Here’s what to know:
Who should get the COVID booster?
The CDC advises that everyone over 6 months old should, for the broader benefit of all. Those at highest risk of serious disease include babies and toddlers, the elderly, pregnant women, and people with chronic health conditions including obesity. The risks are lower — though not zero — for everyone else. The vaccines, we’ve learned, tend to prevent infection in most people for only a few months. But they do a good job of preventing hospitalization and death, and by at least diminishing infections they may slow spread of the disease to the vulnerable, whose immune systems may be too weak to generate a good response to the vaccine.
Pablo Sánchez, a pediatrics professor at The Ohio State University who was the lone dissenter on the CDC panel, said he was worried the boosters hadn’t been tested enough, especially in kids. The vaccine strain in the new boosters was approved only in June, so nearly all the tests were done in mice or monkeys. However, nearly identical vaccines have been given safely to billions of people worldwide.
When should you get it?
The vaccine makers say they’ll begin rolling out the vaccine this week. If you’re in a high-risk group and haven’t been vaccinated or been sick with COVID in the past two months, you could get it right away, says John Moore, an immunology expert at Weill Cornell Medical College. If you plan to travel this holiday season, as he does, Moore said, it would make sense to push your shot to late October or early November, to maximize the period in which protection induced by the vaccine is still high.
Who will pay for it?
When the ACIP recommends a vaccine for children, the government is legally obligated to guarantee kids free coverage, and the same holds for commercial insurance coverage of adult vaccines. For the 25 to 30 million uninsured adults, the federal government created the Bridge Access Program. It will pay for rural and community health centers, as well as Walgreens, CVS, and some independent pharmacies, to provide COVID shots for free. Manufacturers have agreed to donate some of the doses, CDC officials said.
Will this new booster work against the current variants of COVID?
It should. More than 90% of currently circulating strains are closely related to the variant selected for the booster earlier this year, and studies showed the vaccines produced ample antibodies against most of them. The shots also appeared to produce a good immune response against a divergent strain that initially worried people, called BA.2.86. That strain represents fewer than 1% of cases currently. Moore calls it a “nothingburger.”
Why are some doctors not gung-ho about the booster?
Experience with the COVID vaccines has shown that their protection against hospitalization and death lasts longer than their protection against illness, which wanes relatively quickly, and this has created widespread skepticism. Most people in the U.S. have been ill with COVID and most have been vaccinated at least once, which together are generally enough to prevent grave illness, if not infection — in most people. Many doctors think the focus should be on vaccinating those truly at risk.
With new COVID boosters, plus flu and RSV vaccines, how many shots should I expect to get this fall?
People tend to get sick in the late fall because they’re inside more and may be traveling and gathering in large family groups. This fall, for the first time, there’s a vaccine — for older adults — against respiratory syncytial virus. Kathryn Edwards, a 75-year-old Vanderbilt University pediatrician, plans to get all three shots but “probably won’t get them all together,” she said. COVID “can have a punch” and some of the RSV vaccines and the flu shot that’s recommended for people 65 and older also can cause sore arms and, sometimes, fever or other symptoms. A hint emerged from data earlier this year that people who got flu and COVID shots together might be at slightly higher risk of stroke. That linkage seems to have faded after further study, but it still might be safer not to get them together.
Pfizer and Moderna are both testing combination vaccines, with the first flu-COVID shot to be available as early as next year.
Has this booster version been used elsewhere in the world?
Nope, although Pfizer’s shot has been approved in the European Union, Japan, and South Korea, and Moderna has won approval in Japan and Canada. Rollouts will start in the U.S. and other countries this week.
Unlike in earlier periods of the pandemic, mandates for the booster are unlikely. But “it’s important for people to have access to the vaccine if they want it,” said panel member Beth Bell, a professor of public health at the University of Washington.
“Having said that, it’s clear the risk is not equal, and the messaging needs to clarify that a lot of older people and people with underlying conditions are dying, and they really need to get a booster,” she said.
ACIP member Sarah Long, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, voted for a universal recommendation but said she worried it was not enough. “I think we’ll recommend it and nobody will get it,” she said. “The people who need it most won’t get it.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Did you miss our previous article…
https://www.biloxinewsevents.com/?p=287552
Mississippi Today
Speaker White wants Christmas tree projects bill included in special legislative session

House Speaker Jason White sent a terse letter to Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann on Thursday, saying House leaders are frustrated with Senate leaders refusing to discuss a “Christmas tree” bill spending millions on special projects across the state.
The letter signals the two Republican leaders remain far apart on setting an overall $7 billion state budget. Bickering between the GOP leaders led to a stalemate and lawmakers ending their regular 2025 session without setting a budget. Gov. Tate Reeves plans to call them back into special session before the new budget year starts July 1 to avoid a shutdown, but wants them to have a budget mostly worked out before he does so.
White’s letter to Hosemann, which contains words in all capital letters that are underlined and italicized, said that the House wants to spend cash reserves on projects for state agencies, local communities, universities, colleges, and the Mississippi Department of Transportation.
“We believe the Senate position to NOT fund any local infrastructure projects is unreasonable,” White wrote.
The speaker in his letter noted that he and Hosemann had a meeting with the governor on Tuesday. Reeves, according to the letter, advised the two legislative leaders that if they couldn’t reach an agreement on how to disburse the surplus money, referred to as capital expense money, they should not spend any of it on infrastructure.
A spokesperson for Hosemann said the lieutenant governor has not yet reviewed the letter, and he was out of the office on Thursday working with a state agency.
“He is attending Good Friday services today, and will address any correspondence after the celebration of Easter,” the spokesperson said.
Hosemann has recently said the Legislature should set an austere budget in light of federal spending cuts coming from the Trump administration, and because state lawmakers this year passed a measure to eliminate the state income tax, the source of nearly a third of the state’s operating revenue.
Lawmakers spend capital expense money for multiple purposes, but the bulk of it — typically $200 million to $400 million a year — goes toward local projects, known as the Christmas Tree bill. Lawmakers jockey for a share of the spending for their home districts, in a process that has been called a political spoils system — areas with the most powerful lawmakers often get the largest share, not areas with the most needs. Legislative leaders often use the projects bill as either a carrot or stick to garner votes from rank and file legislators on other issues.
A Mississippi Today investigation last year revealed House Ways and Means Chairman Trey Lamar, a Republican from Sentobia, has steered tens of millions of dollars in Christmas tree spending to his district, including money to rebuild a road that runs by his north Mississippi home, renovate a nearby private country club golf course and to rebuild a tiny cul-de-sac that runs by a home he has in Jackson.
There is little oversight on how these funds are spent, and there is no requirement that lawmakers disburse the money in an equal manner or based on communities’ needs.
In the past, lawmakers borrowed money for Christmas tree bills. But state coffers have been full in recent years largely from federal pandemic aid spending, so the state has been spending its excess cash. White in his letter said the state has “ample funds” for a special projects bill.
“We, in the House, would like to sit down and have an agreement with our Senate counterparts on state agency Capital Expenditure spending AND local projects spending,” White wrote. “It is extremely important to our agencies and local governments. The ball is in your court, and the House awaits your response.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Mississippi Today
Advocate: Election is the chance for Jackson to finally launch in the spirit of Blue Origin

Editor’s note: This essay is part of Mississippi Today Ideas, a platform for thoughtful Mississippians to share fact-based ideas about our state’s past, present and future. You can read more about the section here.
As the world recently watched the successful return of Blue Origin’s historic all-women crew from space, Jackson stands grounded. The city is still grappling with problems that no rocket can solve.
But the spirit of that mission — unity, courage and collective effort — can be applied right here in our capital city. Instead of launching away, it is time to launch together toward a more just, functioning and thriving Jackson.
The upcoming mayoral runoff election on April 22 provides such an opportunity, not just for a new administration, but for a new mindset. This isn’t about endorsements. It’s about engagement.
It’s a moment for the people of Jackson and Hinds County to take a long, honest look at ourselves and ask if we have shown up for our city and worked with elected officials, instead of remaining at odds with them.
It is time to vote again — this time with deeper understanding and shared responsibility. Jackson is in crisis — and crisis won’t wait.
According to the U.S. Census projections, Jackson is the fastest-shrinking city in the United States, losing nearly 4,000 residents in a single year. That kind of loss isn’t just about numbers. It’s about hope, resources, and people’s decision to give up rather than dig in.
Add to that the long-standing issues: a crippled water system, public safety concerns, economic decline and a sense of division that often pits neighbor against neighbor, party against party and race against race.
Mayor Chokwe Antar Lumumba has led through these storms, facing criticism for his handling of the water crisis, staffing issues and infrastructure delays. But did officials from the city, the county and the state truly collaborate with him or did they stand at a distance, waiting to assign blame?
On the flip side, his runoff opponent, state Sen. John Horhn, who has served for more than three decades, is now seeking to lead the very city he has represented from the Capitol. Voters should examine his legislative record and ask whether he used his influence to help stabilize the administration or only to position himself for this moment.
Blaming politicians is easy. Building cities is hard. And yet that is exactly what’s needed. Jackson’s future will not be secured by a mayor alone. It will take so many of Jackson’s residents — voters, business owners, faith leaders, students, retirees, parents and young people — to move this city forward. That’s the liftoff we need.
It is time to imagine Jackson as a capital city where clean, safe drinking water flows to every home — not just after lawsuits or emergencies, but through proactive maintenance and funding from city, state and federal partnerships. The involvement of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in the effort to improve the water system gives the city leverage.
Public safety must be a guarantee and includes prevention, not just response, with funding for community-based violence interruption programs, trauma services, youth job programs and reentry support. Other cities have done this and it’s working.
Education and workforce development are real priorities, preparing young people not just for diplomas but for meaningful careers. That means investing in public schools and in partnerships with HBCUs, trade programs and businesses rooted right here.
Additionally, city services — from trash collection to pothole repair — must be reliable, transparent and equitable, regardless of zip code or income. Seamless governance is possible when everyone is at the table.
Yes, democracy works because people show up. Not just to vote once, but to attend city council meetings, serve on boards, hold leaders accountable and help shape decisions about where resources go.
This election isn’t just about who gets the title of mayor. It’s about whether Jackson gets another chance at becoming the capital city Mississippi deserves — a place that leads by example and doesn’t lag behind.
The successful Blue Origin mission didn’t happen by chance. It took coordinated effort, diverse expertise and belief in what was possible. The same is true for this city.
We are not launching into space. But we can launch a new era marked by cooperation over conflict, and by sustained civic action over short-term outrage.
On April 22, go vote. Vote not just for a person, but for a path forward because Jackson deserves liftoff. It starts with us.
Pauline Rogers is a longtime advocate for criminal justice reform and the founder of the RECH Foundation, an organization dedicated to supporting formerly incarcerated individuals as they reintegrate into society. She is a Transformative Justice Fellow through The OpEd Project Public Voices Fellowship.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1959, students marched for integrated schools
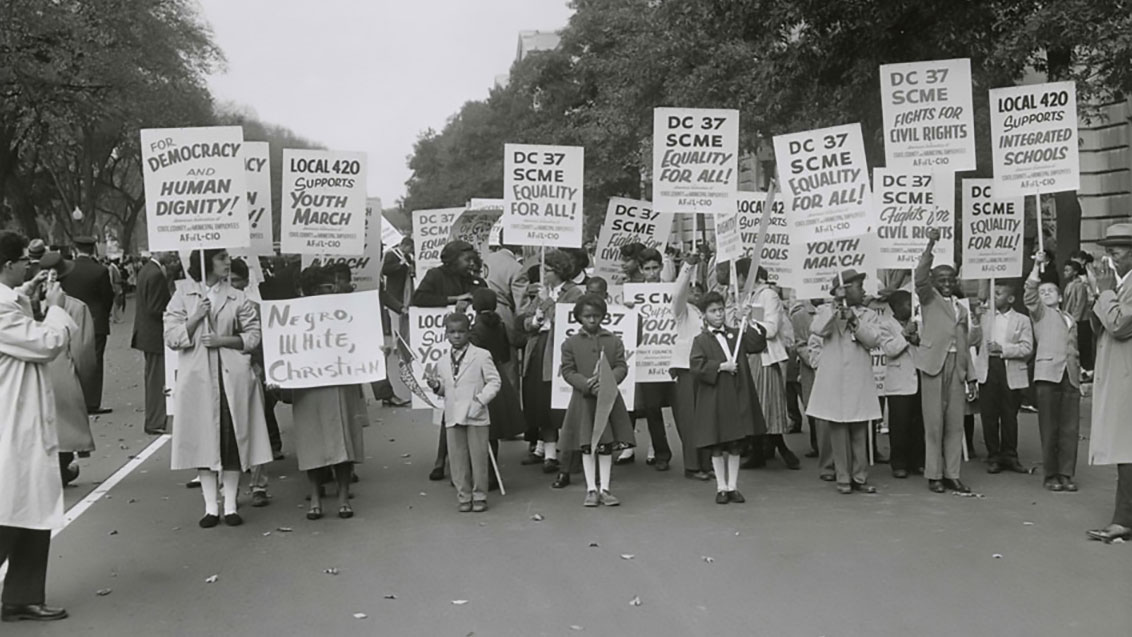

April 18, 1959

About 26,000 students took part in the Youth March for Integrated Schools in Washington, D.C. They heard speeches by Martin Luther King Jr., A. Phillip Randolph and NAACP leader Roy Wilkins.
In advance of the march, false accusations were made that Communists had infiltrated the group. In response, the civil rights leaders put out a statement: “The sponsors of the March have not invited Communists or communist organizations. Nor have they invited members of the Ku Klux Klan or the White Citizens’ Council. We do not want the participation of these groups, nor of individuals or other organizations holding similar views.”
After the march, a delegation of students went to present their demands to President Eisenhower, only to be told by his deputy assistant that “the president is just as anxious as they are to see an America where discrimination does not exist, where equality of opportunity is available to all.”
King praised the students, saying, “In your great movement to organize a march for integrated schools, you have awakened on hundreds of campuses throughout the land a new spirit of social inquiry to the benefit of all Americans.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
-

 Mississippi Today6 days ago
Mississippi Today6 days agoOn this day in 1873, La. courthouse scene of racial carnage
-

 Mississippi Today6 days ago
Mississippi Today6 days agoLawmakers used to fail passing a budget over policy disagreement. This year, they failed over childish bickering.
-

 Local News7 days ago
Local News7 days agoAG Fitch and Children’s Advocacy Centers of Mississippi Announce Statewide Protocol for Child Abuse Response
-

 Local News6 days ago
Local News6 days agoSouthern Miss Professor Inducted into U.S. Hydrographer Hall of Fame
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed4 days agoFoley man wins Race to the Finish as Kyle Larson gets first win of 2025 Xfinity Series at Bristol
-

 Our Mississippi Home7 days ago
Our Mississippi Home7 days agoFood Chain Drama | Our Mississippi Home
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days agoHelene: Renewed focus on health of North Carolina streams | North Carolina
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed4 days agoFederal appeals court upholds ruling against Alabama panhandling laws