William Theisen et al.
Tim Weninger, University of Notre Dame and Ernesto Verdeja, University of Notre Dame
Imagine a country with deep political divisions, where different groups don’t trust each other and violence seems likely. Now, imagine a flood of political images, hateful memes and mocking videos from domestic and foreign sources taking over social media. What is likely to happen next?
The widespread use of social media during times of political trouble and violence has made it harder to prevent conflict and build peace. Social media is changing, with new technologies and strategies available to influence what people think during political crises. These include new ways to promote beliefs and goals, gain support, dehumanize opponents, justify violence and create doubt or dismiss inconvenient facts.
At the same time, the technologies themselves are becoming more sophisticated. More and more, social media campaigns use images such as memes, videos and photos – whether edited or not – that have a bigger impact on people than just text.
It’s harder for AI systems to understand images compared with text. For example, it’s easier to track posts that say “Ukrainians are Nazis” than it is to find and understand fake images showing Ukrainian soldiers with Nazi symbols. But these kinds of images are becoming more common. Just as a picture is worth a thousand words, a meme is worth a thousand tweets.
Our team of computer and social scientists has tackled the challenge of interpreting image content by combining artificial intelligence methods with human subject matter experts to study how visual social media posts change in high-risk situations. Our research shows that these changes in social media posts, especially those with images, serve as strong indicators of coming mass violence.
Surge of memes
Our recent analysis found that in the two weeks leading up to Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine there was a nearly 9,000% increase in the number of posts and a more than 5,000% increase in manipulated images from Russian milbloggers. Milbloggers are bloggers who focus on current military conflicts.
These huge increases show how intense Russia’s online propaganda campaign was and how it used social media to influence people’s opinions and justify the invasion.
This also shows the need to better monitor and analyze visual content on social media. To conduct our analysis, we collected the entire history of posts and images from the accounts of 989 Russian milbloggers on the messaging app Telegram. This includes nearly 6 million posts and over 3 million images. Each post and image was time-stamped and categorized to facilitate detailed analysis.
Media forensics
We had previously developed a suite of AI tools capable of detecting image alterations and manipulations. For instance, one detected image shows a pro-Russian meme mocking anti-Putin journalist and former Russian soldier Arkady Babchenko, whose death was faked by Ukrainian security services to expose an assassination plot against him.
The meme features the language “gamers don’t die, they respawn,” alluding to video game characters who return to life after dying. This makes light of Babchenko’s predicament and illustrates the use of manipulated images to convey political messages and influence public opinion.
This is just one example out of millions of images that were strategically manipulated to promote various narratives. Our statistical analysis revealed a massive increase in both the number of images and the extent of their manipulations prior to the invasion.
Political context is critical
Although these AI systems are very good at finding fakes, they are incapable of understanding the images’ political contexts. It is therefore critical that AI scientists work closely with social scientists in order to properly interpret these findings.
Our AI systems also categorized images by similarity, which then allowed subject experts to further analyze image clusters based on their narrative content and culturally and politically specific meanings. This is impossible to do at a large scale without AI support.
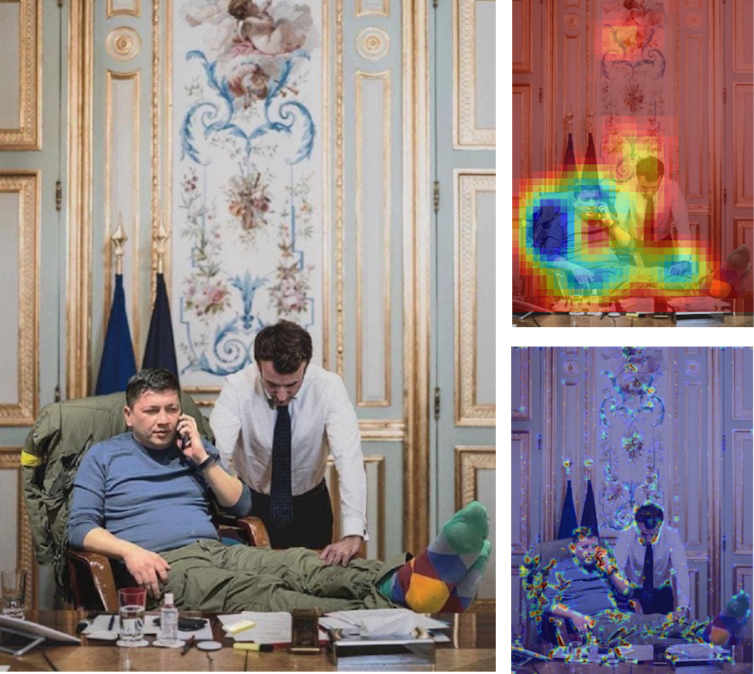
For example, a fake image of French president Emmanuel Macron with Ukrainian governor Vitalii Kim may be meaningless to an AI scientist. But to political scientists the image appears to laud Ukrainians’ outsize courage in contrast to foreign leaders who have appeared to be afraid of Russian nuclear threats. The goal was to reinforce Ukrainian doubts about their European allies.

William Theisen et al.
Meme warfare
The shift to visual media in recent years brings a new type of data that researchers haven’t yet studied much in detail.
Looking at images can help researchers understand how adversaries frame each other and how this can lead to political conflict. By studying visual content, researchers can see how stories and ideas are spread, which helps us understand the psychological and social factors involved.
This is especially important for finding more advanced and subtle ways people are influenced. Projects like this also can contribute to improving early warning efforts and reduce the risks of violence and instability.![]()
Tim Weninger, Collegiate Proessor of Engineering, University of Notre Dame and Ernesto Verdeja, Associate Professor of Peace Studies and Global Politics, University of Notre Dame
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.