Andrii Shelenkov/Stock via Getty Images
Tam Nguyen, University of Dayton
CAPTCHAs are those now ubiquitous challenges you encounter to prove that you’re a human and not a bot when you go to log in to many websites.
Websites and mobile apps have long been attacked by bots on a massive scale. Those malicious bots are programmed to automatically consume a large amount of computing resources, post spam messages, collect data from websites and even register and perform user authentication. This state of affairs led to the introduction of CAPTCHA, which stands for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.
As a computer scientist, I see CAPTCHAs as an effective shield for websites to prevent automated attacks, enhance cybersecurity and improve user experience – at least in the short term. For example, denial-of-service attacks create a bottleneck and cause a web server to become overloaded and unresponsive. CAPTCHAs help stop automated bots from executing such denial-of-service attacks and even fraudulent activities such as sending spam messages and creating fake accounts.
Meanwhile, financial institutions rely on CAPTCHAs to protect against bots trying to steal clients’ data. Additionally, CAPTCHAs improve the integrity of online voting and polls by preventing automated bots from manipulating results.
How CAPTCHAs work
CAPTCHAs are designed to show questions or challenges that are easy for humans but difficult for computer bots to answer. In practice, there are several types of CAPTCHAs: text-based, image-based, audio-based and behavior-based.
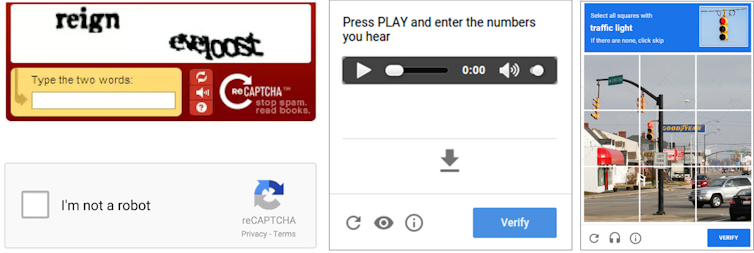
Text-based CAPTCHAs have been very popular since the early days of the internet. This CAPTCHA type requires users to read a distorted and complicated image of text and enter the answer into a text field. A variant of text-based CAPTCHA asks users to solve simple math problems like “18+5” or “23-7.” However, it was recently solved by advanced optical character recognition algorithms, thanks to the proliferation of deep-learning AIs.
Screencaptures by Tam Nguyen
When the text is tuned to be more distorted and more complicated, actual humans ironically fail to provide a correct answer.
Audio CAPTCHA plays a short audio clip containing a series of numbers or letters spoken by a human or synthetic voice, which the user listens to and then types into a provided text field. The input is verified against the correct answer to determine whether the user is human. Like text-based CAPTCHAs, audio CAPTCHA can be difficult for humans to interpret due to factors such as background noise, poor audio quality, heavy distortion and unfamiliar accents.
Image-based CAPTCHAs were introduced to make it more challenging for bots. Users must identify specific objects from images – for example, selecting all image blocks containing traffic lights. This task leverages human visual perception, which is still superior to most computer vision-based bots. However, this type of CAPTCHA also confuses people in many cases.
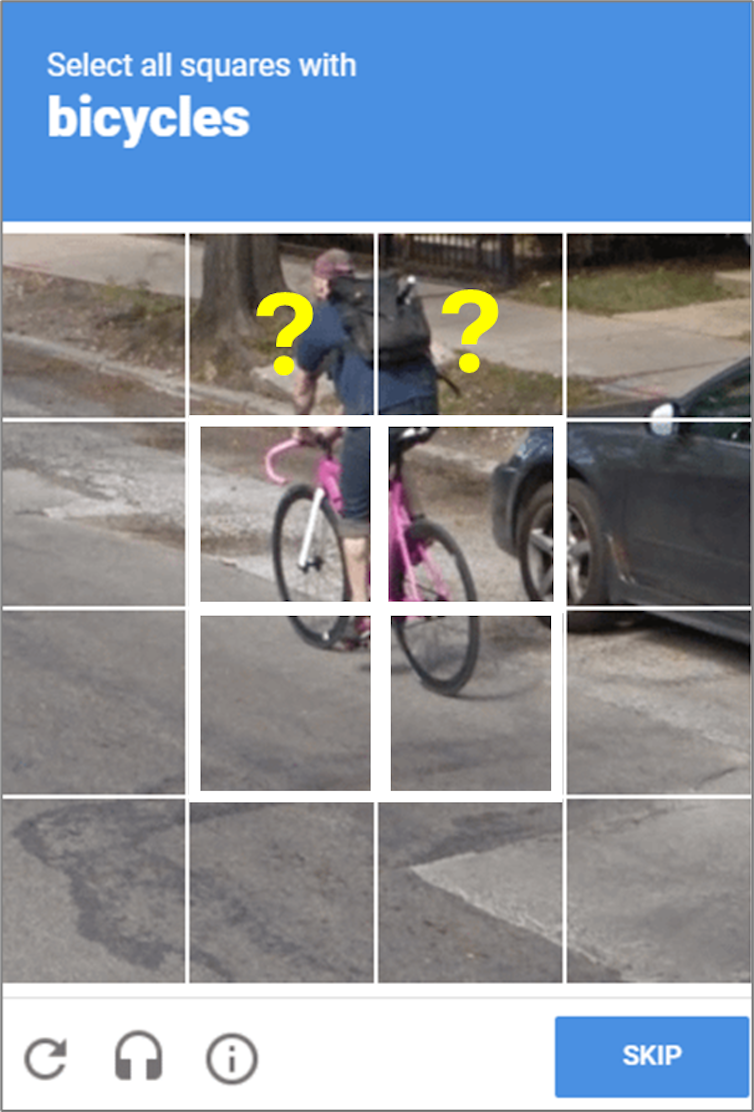

Annotated screencapture by Tam Nguyen
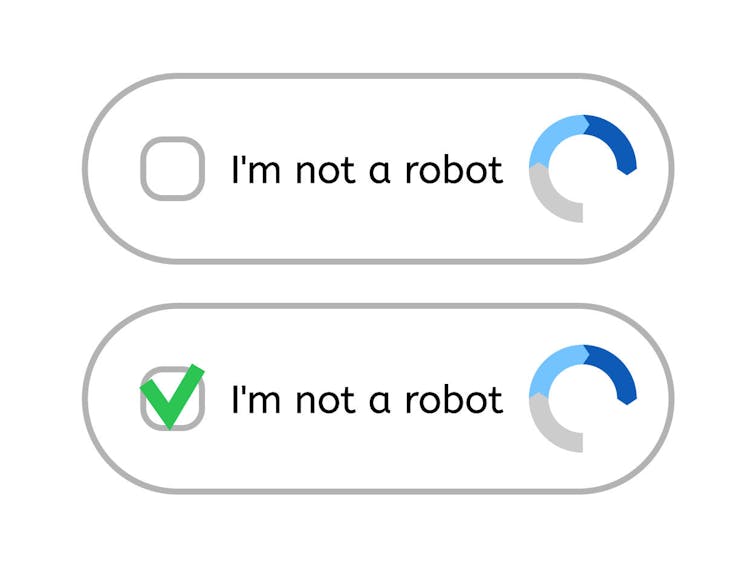
Behavior-based CAPTCHAs analyze user behaviors such as mouse movements and typing patterns. reCAPTCHA, a popular behavior-based CAPTCHA, requires users to check the “I am not a robot” box. During this process, reCAPTCHA analyzes mouse movement and mouse click to differentiate between humans and bots. Humans typically have more varied and less predictable behaviors, while bots often show precise and consistent actions.
AI vs. human
CAPTCHA is one more battleground in the seemingly endless battle between AI and humans. Nowadays, AI has become more advanced, using modern techniques such as deep learning and computer vision to solve CAPTCHA challenges.
For instance, optical character recognition algorithms have improved, making text-based CAPTCHAs less effective. Audio CAPTCHA can be bypassed by advanced speech-to-text technology. Similarly, AI models trained on vast image datasets can solve many image-based CAPTCHAs with high accuracy rates.
On the other side of the battlefield, CAPTCHA researchers have created more complex CAPTCHA technologies. For example, reCAPTCHA assesses user interactions and computes their likelihood of being human.
Ironically, humans are helping AI solve complicated CAPTCHAs. For instance, click farms hire a large pool of low-paid workers to click on ads, such as social media posts, follow accounts, write fake reviews and even solve CAPTCHA questions. Their work is to help AI systems behave like humans in order to defeat CAPTCHAs and other fraud-prevention techniques.

The future of CAPTCHAs
The future of CAPTCHAs will be influenced by the ongoing advancements in AI. The traditional CAPTCHA methods are becoming less effective, thus future CAPTCHA systems are likely to focus more on analyzing user behavior, such as how people interact with websites, making it harder for bots to mimic that behavior.
Websites might turn to the use of biometric CAPTCHAs, such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning, though these raise privacy concerns. CAPTCHA can be replaced by blockchain, which uses verifiable credentials to authenticate users. These credentials, issued by trusted entities and stored in digital wallets, ensure interactions are performed by verified humans rather than bots.
Future CAPTCHAs might work alongside AI systems in real time, constantly adapting and evolving to stay ahead of automated attacks.![]()
Tam Nguyen, Associate Professor of Computer Science, University of Dayton
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.