Mississippi Today
Reddit AMA recap: Medicaid expansion in Mississippi with Senior Political Reporter Geoff Pender
Reddit AMA recap: Medicaid expansion in Mississippi with Senior Political Reporter Geoff Pender
Mississippi's growing health crisis threatens to close at least a dozen hospitals across the state and puts Mississippi in the lead nationally for rates of uninsured people.
Studies have shown and advocates have long touted the benefits of Medicaid expansion, but state leaders remain steadfast in their opposition. As such, Mississippi remains one of only 11 states in the country not to expand the federal-state program.
Mississippi Today launched an ongoing series looking at the impact of the health care crisis on the people and institutions of the state.
As part of that project, Senior Political Reporter Geoff Pender answered readers' questions on Reddit about Medicaid expansion (or the lack thereof) in the state. Here's a recap:
Click to jump to a specific question
Q: Thank you for doing this and continuing to push on this topic.
As I sit here seeing the Greenwood hospital closing while the governor touts tax breaks for companies and the state government refuses this aid… I just do not get it.
Unless I think of all of the non-rational reasons for it.
A: Unfortunately, we are hearing from many corners that Greenwood may be the canary in the coal mine right now. We have heard some dire predictions of late from state hospital and other officials. State Health Officer Dr. Edney recently warned that we're looking at at least half a dozen hospitals on the brink, and others are saying our entire system is troubled. I don't know that Medicaid expansion would be the panacea for all that, but most experts are saying the influx of billions of federal dollars for health care would stave off many of these problems.
Q: As the Q&A article describes, there are political and economic arguments against expansion, but what in your opinion are the underlying motives for the stance? Are the politicians perhaps more driven by financial incentive from opposition groups in addition to maintaining their political platforms for the sake of the party? And as for general people, do you think it’s related to a mentality of being against handouts and of “pulling yourself up by your bootstraps”? What do you think are the underlying feelings and motivations to these stances?
And lastly, how do you think these underlying reasons can be negotiated with to make progress towards achieving expansion?
A: As far as the current drivers of opposition to expansion, I would say they are now more political than economic, and have been so for quite a while. For one thing, we have empirical evidence from other states, including now Louisiana and Arkansas, that show expansion isn’t the budget-buster our leaders once feared.
We also have reams of studies and evidence from other states showing we would see net positive benefits – thousands of jobs created, savings of double-digit percentages in uncompensated care for hospitals, more workforce participation (ours is typically lowest in the country), net GDP growth and even projected growth in population. Also, we’ve seen firsthand over the last two years that Mississippi, with our economy so heavily dependent on federal spending, sees booming state budget growth when there is an influx of billions of federal dollars. We’re sitting on more than $2 billion in basically surplus state money right now, largely the result of the influx of federal pandemic spending.
And again, this expansion is aimed primarily at the “working poor,” people in the gap between being poor enough for other help or being able to afford private insurance or pay medical bills out of pocket. As many have pointed out, a lot of the folks we’re talking about with this are working more than one job. As for pulling one’s self up by bootstraps, too many folks are one ER visit away from not having any bootstraps, and once someone gets a chronic illness because of lack of preventive care, it costs taxpayers anyway (and more).
No, the opposition now would appear to be more purely political (partisan) and philosophical – not wanting expansion of “Obamacare,” and opposition to expansion of a government program, even if in the long run it’s projected to benefit the workforce and private sector.
That opposition to government programs, however, appears to be selective among state leaders. One recent anecdote struck me in particular. Gov. Reeves recently held a press conference to trumpet the state’s work on expanding broadband internet across rural Mississippi. This is being funded with federal tax dollars. Instead of lamenting such government largesse, Reeves vowed to see that “we not only get our fare share, but that we get more than our fair share.” It would appear it’s OK to take hundreds of millions of federal dollars for internet service to areas where the private sector won’t do it, but not OK to take federal money to help keep people alive and well and working.
As for how this opposition might be overcome – I don’t know that anyone has a simple answer to that. One thing I hear all the time, though, even from some who have opposed expansion, is time. I have heard over and again in recent years that it’s probably just a matter of time before Mississippi expands Medicaid. Polling in recent years would indicate the populace may already be a bit ahead of our politicians on this policy … and, of course, look at other states relenting, such as Arkansas, Louisiana.
We attempted to delve into some of this opposition, past and present, here.
READ MORE: Who’s opposed to Mississippi Medicaid expansion and why?
Q: Can Medicaid expansion prevent local hospitals from closing?
A: It's unclear if it definitely would — rural hospitals in particular are facing major headwinds with personnel shortages and costs, supplies, inflation, uncompensated care. But most projections by experts have shown net benefits, and we've seen in other states that expansion helped. Particularly, in Louisiana, rural hospitals saw reductions in uncompensated care costs in the 55% range. This alone could give struggling rural hospitals some breathing room.
This study indicates hospitals in expansion states are less likely to close.
Q: With Medicaid expansion costing far more than initially predicted in other states, it delivering consistently poor health outcomes for those on the program, and it failing to ultimately help save rural providers as seen in Colorado and Indiana…why advocate so intensely for expanding a program that’s heading toward insolvency besides the fact that it will pad the pockets of and expand profits for big hospitals?
A: As for costing more than predicted, as I understand, this has not truly been the case at least on the state level. Some states have seen more people than initially predicted, but that has also been offset by people shifting from their traditional Medicaid to that with the higher match rate from the feds, and other non-direct economic benefits.
As for Colorado, I just recently read a report that rural hospitals there are "about 6 times less likely to close than hospitals in non-expansion states, according to a study by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus." I'm not sure what you are looking at, but would like to see it if you can forward a link.
As for poor health outcomes, I'm not sure Mississippi would have anywhere to go but up. Mississippi Medicaid has had poor health outcomes, but that has been primarily because only the sickest of the sick, so to speak, are on its adult population. Proponents say that the working-poor expansion population would receive more preventive care and improve outcomes — but you are right, that has been one major argument against expansion in Mississippi.
I don't know that expansion would pad the pockets and profits of big hospitals. It would help ameliorate the $600 million or so in uncompensated care that is hammering, in particular, smaller rural hospitals.
READ MORE:
• The Mississippi Health Care Crisis
• Mississippi moms and babies suffer disproportionately. Medicaid expansion could help.
• How Medicaid expansion could have saved Tim’s leg — and changed his life
• Q&A: What is Medicaid expansion, really?
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi prison death under investigation
The Mississippi Bureau of Investigation is investigating the death of an inmate at the Central Mississippi Correctional Facility earlier this year.
Prison officials reportedly told Mississippi authorities that inmate Melvin Cancer had suffered a heart attack, but a recent autopsy has since ruled his death a homicide.
“I’d like for it to be thoroughly investigated to see what did happen,” said Juan Barnett, chairman of the Senate Corrections Committee. “Even though people in prison have committed crimes, I still believe in humane treatment for everybody.”
After fellow inmates at Central Mississippi Correctional Facility repeatedly complained that Cancer would not bathe, prison officials reportedly dragged him into the shower, where he may have suffered fatal injuries.
On Jan. 22, Cancer was declared dead at the University of Mississippi Medical Center. The 53-year-old inmate had been serving eight years in prison after pleading guilty to a 2019 aggravated assault in Hinds County.
Jeremy St. Julian is the third person to serve as superintendent at the Central Mississippi Correctional Facility in less than a year. Some staff members have reportedly been placed on administrative leave.
“Either we’re hiring bad people, or we need to look at the people doing the hiring,” Barnett said. “There has to be some accountability somewhere.”
Public Safety Commissioner Sean Tindell said he could not comment on the matter. The Mississippi Department of Corrections did not respond to a request for comment.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Mississippi Today
A self-proclaimed ‘loose electron’ journeys through Jackson’s political class
The day after Tim Henderson finished third in Jackson’s mayoral primary, garnering 3,499 votes, the retired Air Force lieutenant colonel was planning to pack up his office at the Jackson Medical Mall and be out by the end of the week.
Henderson figured that’s what losing candidates do. Then he said his older brother gave him a different perspective: Henderson had just established a base of people who had rejected the city’s status quo, and he shouldn’t let them down.
“That’s what happens all the time,” Henderson said. “Candidates show up, they don’t win, the stuff they talked about doing, they walk away, and they leave the people hanging, which is partly, probably why people have lost faith in the process.”
As the 54-year-old space industry consultant spoke with friends, family and politicos last week, he began to look at those 3,499 votes differently. Instead of an outright loss, the numbers seemed to represent something remarkable: In a city where name recognition is king, it took less than a year for Henderson to go from a name few knew to finishing just 786 votes shy of the incumbent, Mayor Chokwe Antar Lumumba.
He did it with a handful of volunteers and few connections to the city’s powerbrokers or politically connected church leaders or nonprofits. In fact, Henderson thinks his relatively little clout is precisely why he did so well.
“People insulate themselves inside of certain circles, and the problem a lot of people have with Henderson is I wasn’t connected or associated with any of those cliques,” he said. “People immediately started asking, who knows him?”
Now, Henderson is contemplating what he’s going to do next.
“I can be the mayor of the city hall, or I can be the mayor out here on the streets,” he said.
Beholden mainly to God and the truth, he said, he’s ready to talk – with little filter – about what Jackson needs to anyone who wants to listen. He described himself as “a loose neutron, or a loose electron, free radical.”
“Not radical in the sense of ‘radical’ but somebody that doesn’t have to be guarded in how I do things,” he said, adding, “Now I can say things other people can’t say and I can represent things the right way.”
He’s not sure he’ll endorse anyone. Henderson said that in the past week, he’s met with the Lumumba campaign, as well as state Sen. John Horhn, whose 12,359 votes nearly preempted a runoff. To win the Democratic nomination outright, Horhn would have had to secure around 500 of the votes Henderson or 10 other candidates received.
Both asked what their campaigns needed to do to get Henderson’s support. He says he told them the same thing: Start an Office of Ethics and Accountability, one of his chief campaign goals.
He wouldn’t say which candidate said what. But one told him they weren’t sure the city had the funding for it. He recalled the other asked if Henderson would work with them if they started an Office of Integrity, to which Henderson responded “only by my rules.”
Through a spokesperson, Horhn said he wants to bring more accountability to the city’s procurement process and that his ongoing discussions with Henderson have been “productive.”
Horhn has been a senator representing parts of Jackson since the 1990s, and Lumumba is finishing his second term as mayor. If nothing has changed in the city in the last eight, or 32, years, Henderson reasons that’s because the people with power and connections, including those behind the scenes, don’t want change.
When Henderson moved back to the city two years ago, the Cleveland, Miss. native and Mississippi Valley State University graduate moved in with his brother, who lives in south Jackson.
The retired military man had two goals in mind: Develop the vacant lots he owns near the Westside Community Center — a neighborhood called “the Sub” — and start a gourmet grocery store in downtown Jackson, hopefully on the first floor of the Lamar Life building owned by longtime downtown Jackson developer Andrew Mattiace.
Henderson said he couldn’t find the funding – a common refrain in Jackson – or secure meetings with folks who might provide the funding. Still, his business endeavors bore political fruit as he met people he said encouraged him to run for mayor. That included Robert Gibbs, an attorney and developer who was working to convene a group of community and business leaders to secure a new city leader. The coalition assumed the name Rethink Jackson.
Last year, Gibbs invited Henderson to meet with Rethink Jackson members and others at the Capital Club, a highrise bar owned by Mattiace. The group was looking for a candidate to support, but Henderson recalled that Gibbs told him the meeting was not “an endorsement.”
But when Henderson arrived, he says they kept him waiting in the lobby for 30 minutes before finally calling him up to meet with the dozen or so people in the room – mostly African American leaders – who were sitting at tables around the bar.
Gibbs was there, so were Mattiace and Jeff Good, a local restauranteur.
“Before we move forward, I want to make sure the air is clear: This is not an endorsement,” Henderson recalled telling the room. “And they’re like no, nope, it’s not an endorsement. I say well let me be clear you may not hear what you want to hear this evening. I’m only going to share what I’m comfortable sharing, because what I’m not going to do is have my information travel all across the city. Is that fair? That is fair, right? OK, so let’s talk.”
When the group asked about economic development, Henderson said he brought up the Capitol Police, saying “I don’t care how much police security you put down here, you gotta put something in the parts of the city where people live,” meaning both safety and opportunity in west and south Jackson.
“They can only rob other poor people so much,” Henderson said, to which he recalled the folks in the room “just looked at me.”
Mattiace said he preferred not to comment on the election so he could remain neutral for the sake of his business. Good said he did not have a good memory of the meeting but added he thinks Henderson is a “good guy” and that’s why he did well at the polls.
Gibbs didn’t comment on the meeting but said he’s heavily involved in the Horhn campaign and doesn’t want to hurt it. He did speak to Rethink Jackson as a coalition, adding that the group also met with Horhn, Delano Funches, and Rodney DePriest, an independent, “to identify the person we felt would be the best person to lead the city of Jackson.”
After meeting with him, Henderson said he told one of the folks that he wouldn’t be back – he had a campaign to run. He didn’t hear from the group again.
Rethink Jackson debated and took a vote on which candidates “could come in on day one and start doing the things we felt the city needed in order to turn around,” Gibbs said.
“We had a vote, paper ballot voting, that we took so that people could not necessarily be influenced by someone who was in the room,” he added.
Out of about 50 people, Gibbs said only one person was unsure of Horhn. The endorsement was a campaign score for the senator.
It wasn’t just the business community Henderson says did not ultimately align with his campaign. When he talks about the status quo he wants to undo, he means nonprofits, too.
On the campaign trail, Henderson committed to personally screening all nonprofits that receive city grant funds. He wanted to send out screening criteria, categorize all the buckets of grant funding the city was dispersing, and meet with each nonprofit. But if they didn’t show up, he said he would contact their other funders.
He called this “a dogwhistle” – a tell that he was on to them.
“You’re using my data,” he said. “As the mayor, it’s my data. And if you’re supposed to be working in this city, I want to know outcomes.”
Jackson has an excess of nonprofits, Henderson said, that are all working to tackle similar social ills, from decreasing homelessness and youth violence to improving mental health. Some are doing good work and should be supported to leverage their resources. But for others, those missions are a “smokescreen,” Henderson said, and the problems remain. Coincidentally, this is a similar campaign pillar of conservative talk radio host and independent mayoral candidate Kim Wade.
“Here’s my concern: Things aren’t getting better because people don’t want them to get better,” Henderson said. “If you keep crime high, poverty high, you keep the education system where it is, you keep housing, the lack of affordable housing high, you keep jobs at the minimum wage – the only thing people have as an entry point, there’s no upward mobility. This city will never be what it can be. … Because if you wanted change, you’d work yourself out of a job.”
Within city hall, Henderson said he wanted to “clear the slate” by rehiring every department head, putting out job descriptions, and hiring candidates with a blind application – no names, race or gender attached – to ensure that a person’s “connections” were not taken into account.
“Those connections over time is why we are the way we are,” he said. “Because the most qualified person is not who you’re hiring. You’re hiring someone connected to you.”
Make no mistake: Henderson made connections, too. He said two names include Shirlene Anderson, a former chief of police under Frank Melton, and Hank Anderson, a retired administrator for IBM who worked in former governor Ray Mabus’s administration. Anderson had approached Henderson after the February debate at Duling Hall and later advised him on how to keep his message straight.
After that, Henderson made a point to answer questions as directly as he could during the candidate forums. He said he stressed: “public safety, cleaning it up, public safety, cleaning it up.”

“Everybody else is talking about economic development and all this other stuff,” he said. “I’m like, either you don’t know what you’re talking about, or you’re playing the people, or it’s both. I’m like no, you can’t get any economic development with crime the way it is.”
But perhaps the most important connection Henderson made during his run for office was with Sherri Jones, the first person to join the campaign and the station manager at WMPR.
The pair formed a kinship over their deep skepticism of the city’s elite — Black and white, activists and church leaders, and especially the politicians and the business owners who seem to be looking out for their bottom line and not for the entire community.
“You got two things you gone have to be aware of,” Jones said. “One is racism. The other is classism. Now, when you deal with the classicism, it’s about a certain group of people and a lot of them are African American and then they are connected with white people and they don’t really care if there’s racism involved or not because they got a certain agenda and it’s gonna always come back and be tied to money.”
From the perspective of the leaders at the Capital Club, the business community wants to help Jackson, so finding a mayor who works with them will result in economic advancement across the city.
Jones saw it differently.
“It’s about contracts, it’s about being in charge of the decision, what’s going to stay open, what’s going to close, how things move,” Jones said.
Nothing will change in Jackson if economic development does not include the entire city, Henderson said. South and west, too.
The primary “wasn’t just about low voter turnout,” he said. “It actually speaks to the psychological impact that the environment and the quality of life has had on people, where they totally felt dejected, rejected and disconnected.”
What he wants most of all is to bring back people’s confidence in Jackson and knows it won’t happen overnight.
“It’s about empowering the people in the city to be able to believe in it again,” Henderson said.
How’s he going to do that? He might start a nonprofit.
Editor’s note: Mississippi Today is moving this summer into the Lamar Life Building, operated by Andrew Mattiace, in downtown Jackson.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Crooked Letter Sports Podcast
Podcast: Masters week is back and so is Mississippi’s Mr. Golf Randy Watkins
Former SEC golf champion and PGA touring pro is Crooked Letter’s resident expert on all things golf. He’s back with us to tell us who might win this week’s Masters and why.
Stream all episodes here.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago‘Hands Off!’ Protest Held in Huntsville Saturday | April 5, 2025 | News 19 @ 9 P.M.
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed6 days agoProposal: American military base retailers would exclude 4 hostile nations | North Carolina
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed4 days agoTariffs spark backlash in Virginia over economic impact | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Louisiana News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed4 days agoNew Orleans police investigating hit-and-run crash in Seventh Ward; family says grandmother was hurt
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days agoTrump fires clean energy leader from TVA board without publicly providing a reason
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days agoVersailles asked to conserve water, county steps in to help
-

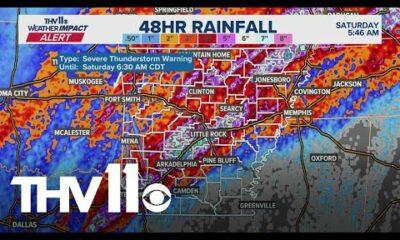
 News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days agoMost of Arkansas dealing with flooding issues | What we know
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days agoMajor flooding around St. Peters after heavy rains