Mississippi Today
On this day in 1870


On this day in 1870

FEBRUARY 25, 1870
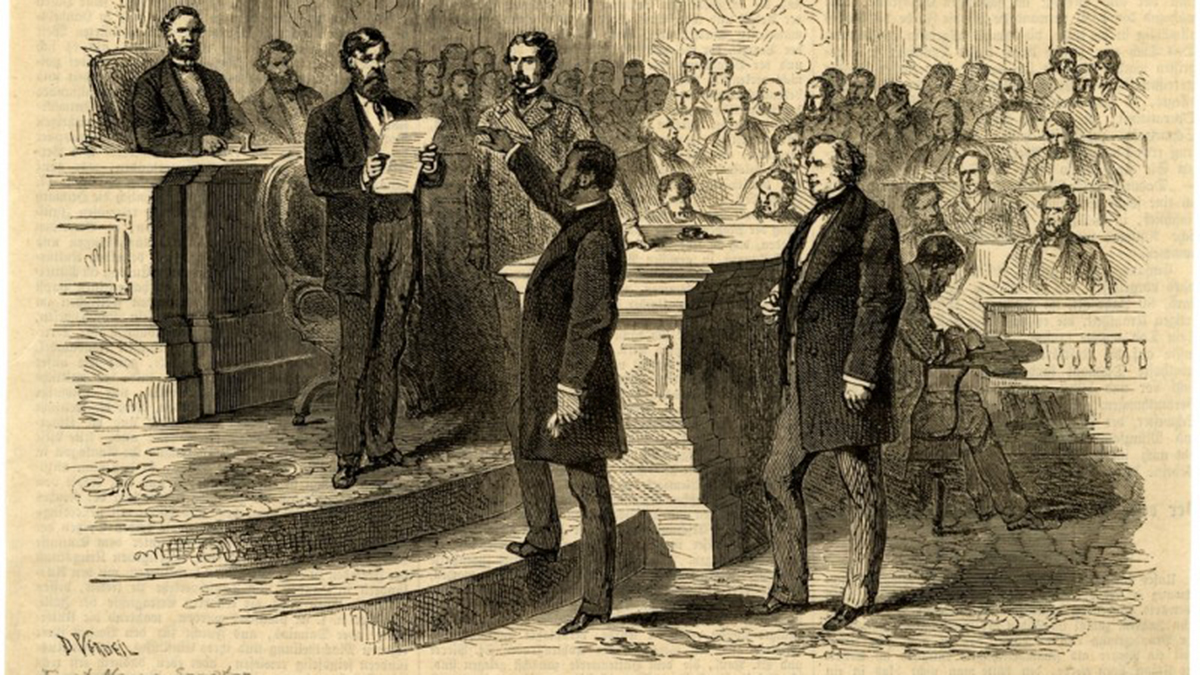

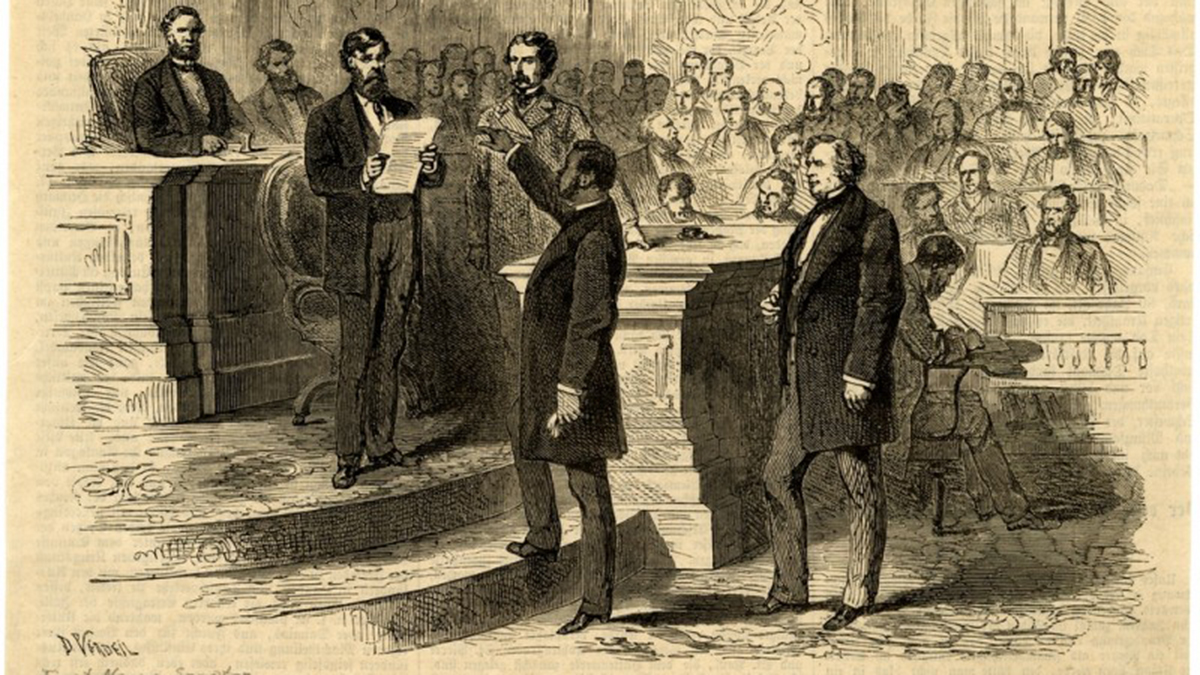
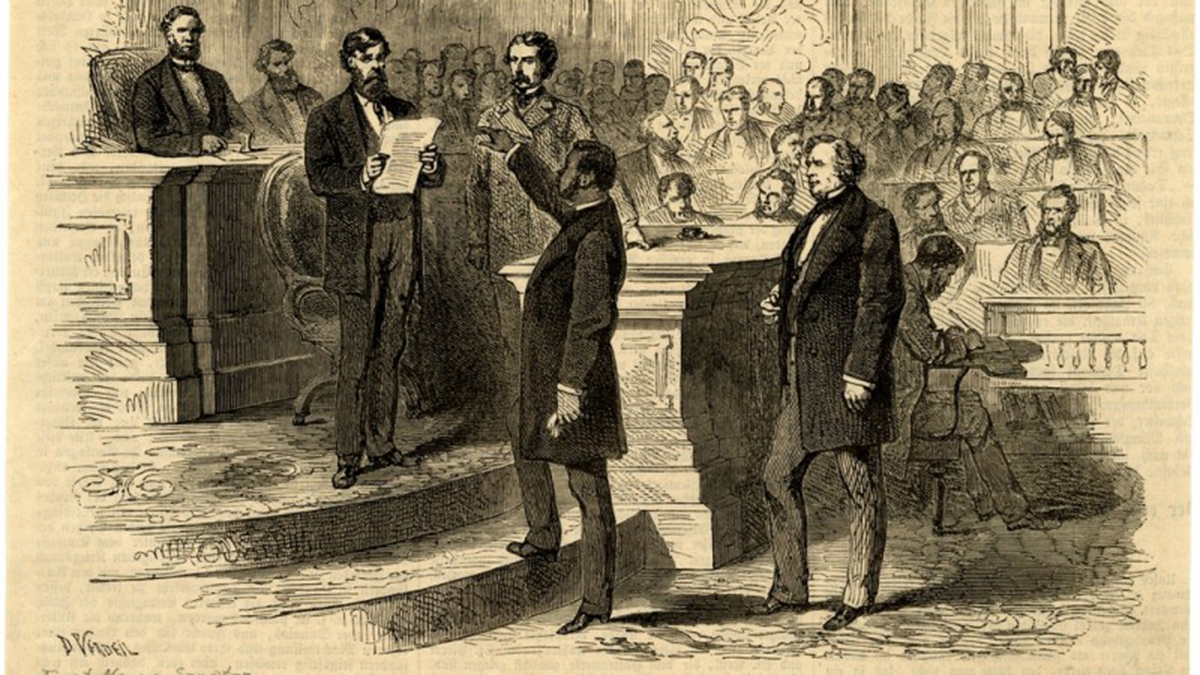
Two days after Mississippi was readmitted to the Union, Hiram Revels became the first Black American elected as U.S. senator. “All men are created equal, says the great Declaration,” Republican Sen, Charles Sumner of Massachusetts said, “and now a great act attests this verity. Today we make the Declaration a reality…. The Declaration was only half established by Independence. The greatest duty remained behind. In assuring the equal rights of all we complete the work.”
Born free in North Carolina, Revels became a national force in an office once held by Jefferson Davis, the former President of the Confederacy. A minister by trade, Revels sought to improve the education of others, working with Black Americans in Indiana, Illinois, Kansas, Kentucky and Tennessee. In 1854, he was imprisoned for preaching to the Black community. After that, he moved to Baltimore, where he served as principal of a Black school.
When the Civil War broke out in 1861, he helped recruit two black regiments from Maryland and later served as chaplain for Black soldiers fighting in Mississippi. After the war ended, he worked for a church in Kansas. On the train, the conductor asked him and his family to move to the smoking car. They refused, and the conductor relented.
Not long after, he and his family settled in Natchez, Mississippi, he wae was elected as an alderman. Winning over both Black and white with his calls for cooperation, he was elected to the Mississippi State Senate, one of more than 30 African Americans to serve in the Legislature during Reconstruction. “We are in the midst of an exciting canvass,” he wrote a friend in a letter. “We are determined that Mississippi shall be settled on a basis of justice and political and legal equality.”
He drew attention as soon as he arrived with his moving words. After Mississippi lawmakers appointed him to the U.S. Senate, a few tried to block him from taking office. Revels remained steadfast and took office. “I find that the prejudice in this country to color is very great, and I sometimes fear that it is on the increase,” he went on to say. “If the nation should take a step for the encouragement of this prejudice against the colored race, can they have any grounds upon which to predicate a hope that heaven will smile upon them and prosper them?”
He supported universal amnesty for former Confederates, requiring only their sworn loyalty to the Union. “I am in favor of removing the disabilities of those upon whom they are imposed in the South,” he said, “just as fast as they give evidence of having become loyal and being loyal.”
After the end of his Senate term in 1871, he became the first president of Alcorn University, the first land-grant school for Black students. He later taught theology at Rust College and died of a stroke in 1901.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1939, Billie Holiday recorded ‘Strange Fruit’

April 20, 1939

Legendary jazz singer Billie Holiday stepped into a Fifth Avenue studio and recorded “Strange Fruit,” a song written by Jewish civil rights activist Abel Meeropol, a high school English teacher upset about the lynchings of Black Americans — more than 6,400 between 1865 and 1950.
Meeropol and his wife had adopted the sons of Julius and Ethel Rosenberg, who were orphaned after their parents’ executions for espionage.
Holiday was drawn to the song, which reminded her of her father, who died when a hospital refused to treat him because he was Black. Weeks earlier, she had sung it for the first time at the Café Society in New York City. When she finished, she didn’t hear a sound.
“Then a lone person began to clap nervously,” she wrote in her memoir. “Then suddenly everybody was clapping.”
The song sold more than a million copies, and jazz writer Leonard Feather called it “the first significant protest in words and music, the first unmuted cry against racism.”
After her 1959 death, both she and the song went into the Grammy Hall of Fame, Time magazine called “Strange Fruit” the song of the century, and the British music publication Q included it among “10 songs that actually changed the world.”
David Margolick traces the tune’s journey through history in his book, “Strange Fruit: Billie Holiday and the Biography of a Song.” Andra Day won a Golden Globe for her portrayal of Holiday in the film, “The United States vs. Billie Holiday.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Mississippians are asked to vote more often than people in most other states

Not long after many Mississippi families celebrate Easter, they will be returning to the polls to vote in municipal party runoff elections.
The party runoff is April 22.
A year does not pass when there is not a significant election in the state. Mississippians have the opportunity to go to the polls more than voters in most — if not all — states.
In Mississippi, do not worry if your candidate loses because odds are it will not be long before you get to pick another candidate and vote in another election.
Mississippians go to the polls so much because it is one of only five states nationwide where the elections for governor and other statewide and local offices are held in odd years. In Mississippi, Kentucky and Louisiana, the election for governor and other statewide posts are held the year after the federal midterm elections. For those who might be confused by all the election lingo, the federal midterms are the elections held two years after the presidential election. All 435 members of the U.S. House and one-third of the membership of the U.S. Senate are up for election during every midterm. In Mississippi, there also are important judicial elections that coincide with the federal midterms.
Then the following year after the midterms, Mississippians are asked to go back to the polls to elect a governor, the seven other statewide offices and various other local and district posts.
Two states — Virginia and New Jersey — are electing governors and other state and local officials this year, the year after the presidential election.
The elections in New Jersey and Virginia are normally viewed as a bellwether of how the incumbent president is doing since they are the first statewide elections after the presidential election that was held the previous year. The elections in Virginia and New Jersey, for example, were viewed as a bad omen in 2021 for then-President Joe Biden and the Democrats since the Republican in the swing state of Virginia won the Governor’s Mansion and the Democrats won a closer-than-expected election for governor in the blue state of New Jersey.
With the exception of Mississippi, Louisiana, Kentucky, Virginia and New Jersey, all other states elect most of their state officials such as governor, legislators and local officials during even years — either to coincide with the federal midterms or the presidential elections.
And in Mississippi, to ensure that the democratic process is never too far out of sight and mind, most of the state’s roughly 300 municipalities hold elections in the other odd year of the four-year election cycle — this year.
The municipal election impacts many though not all Mississippians. Country dwellers will have no reason to go to the polls this year except for a few special elections. But in most Mississippi municipalities, the offices for mayor and city council/board of aldermen are up for election this year.
Jackson, the state’s largest and capital city, has perhaps the most high profile runoff election in which state Sen. John Horhn is challenging incumbent Mayor Chokwe Antar Lumumba in the Democratic primary.
Mississippi has been electing its governors in odd years for a long time. The 1890 Mississippi Constitution set the election for governor for 1895 and “every four years thereafter.”
There is an argument that the constant elections in Mississippi wears out voters, creating apathy resulting in lower voter turnout compared to some other states.
Turnout in presidential elections is normally lower in Mississippi than the nation as a whole. In 2024, despite the strong support for Republican Donald Trump in the state, 57.5% of registered voters went to the polls in Mississippi compared to the national average of 64%, according to the United States Elections Project.
In addition, Mississippi Today political reporter Taylor Vance theorizes that the odd year elections for state and local officials prolonged the political control for Mississippi Democrats. By 1948, Mississippians had started to vote for a candidate other than the Democrat for president. Mississippians began to vote for other candidates — first third party candidates and then Republicans — because of the national Democratic Party’s support of civil rights.
But because state elections were in odd years, it was easier for Mississippi Democrats to distance themselves from the national Democrats who were not on the ballot and win in state and local races.
In the modern Mississippi political environment, though, Republicans win most years — odd or even, state or federal elections. But Democrats will fare better this year in municipal elections than they do in most other contests in Mississippi, where the elections come fast and often.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1977, Alex Haley awarded Pulitzer for ‘Roots’

April 19, 1977

Alex Haley was awarded a special Pulitzer Prize for “Roots,” which was also adapted for television.
Network executives worried that the depiction of the brutality of the slave experience might scare away viewers. Instead, 130 million Americans watched the epic miniseries, which meant that 85% of U.S. households watched the program.
The miniseries received 36 Emmy nominations and won nine. In 2016, the History Channel, Lifetime and A&E remade the miniseries, which won critical acclaim and received eight Emmy nominations.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoFoley man wins Race to the Finish as Kyle Larson gets first win of 2025 Xfinity Series at Bristol
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoFederal appeals court upholds ruling against Alabama panhandling laws
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed3 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed3 days agoDrivers brace for upcoming I-70 construction, slowdowns
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days agoFDA warns about fake Ozempic, how to spot it
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed5 days agoLieutenant governor race heats up with early fundraising surge | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days agoTwo dead, 9 injured after shooting at Conway park | What we know
-

 Mississippi Today3 days ago
Mississippi Today3 days agoSee how much your Mississippi school district stands to lose in Trump’s federal funding freeze
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days agoAbandoned property causing issues in Pine Lawn, neighbor demands action