News from the South - North Carolina News Feed
NC tops 2 millions ballots cast in 2024 General Election
SUMMARY: State election officials report a strong early voter turnout in North Carolina, despite long lines at polling places. So far, over 2.3 million voters have cast their ballots, with early voting continuing until November 2. Election officials anticipate smooth results on Election Night and noted that millions of registered voters have yet to participate. Karen Brinson Bell, the Executive Director of the State Board of Elections, addressed voters in 25 counties affected by Hurricane Helen, urging them to request absentee ballots quickly. This special accommodation allows voters to drop off completed ballots at various locations if mailing is not feasible by the deadline.
The ballots cast represents a turnout of about 26% of North Carolina’s nearly 7.8 million registered voters.
More: abc11.com
Download: https://abc11.com/apps/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ABC11/
Threads: https://www.threads.net/@abc11_wtvd
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ABC11_WTVD
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/abc11_wtvd/
TIKTOK: https://www.tiktok.com/@abc11_eyewitnessnews
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/c/ABC11-WTVD
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed
White House officials hold prayer vigil for Charlie Kirk
SUMMARY: Republican lawmakers, conservative leaders, and Trump administration officials held a prayer vigil and memorial at the Kennedy Center honoring slain activist Charlie Kirk, founder of Turning Point USA. Kirk was killed in Utah, where memorials continue at Utah Valley University and Turning Point USA’s headquarters. Police say 22-year-old Tyler Robinson turned himself in but has not confessed or cooperated. Robinson’s roommate, his boyfriend who is transitioning, is cooperating with authorities. Investigators are examining messages Robinson allegedly sent on Discord joking about the shooting. Robinson faces charges including aggravated murder, obstruction of justice, and felony firearm discharge.
White House officials and Republican lawmakers gathered at the Kennedy Center at 6 p.m. to hold a prayer vigil in remembrance of conservative activist Charlie Kirk.
https://abc11.com/us-world/
Download: https://abc11.com/apps/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ABC11/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/abc11_wtvd/
Threads: https://www.threads.net/@abc11_wtvd
TIKTOK: https://www.tiktok.com/@abc11_eyewitnessnews
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed
Family, friends hold candlelight vigil in honor of Giovanni Pelletier
SUMMARY: Family and friends held a candlelight vigil in Apex to honor Giovanni Pelletier, a Fuquay Varina High School graduate whose body was found last month in a Florida retention pond. Giovanni went missing while visiting family, after reportedly acting erratically and leaving his cousins’ car. Loved ones remembered his infectious smile, laughter, and loyal friendship, expressing how deeply he impacted their lives. His mother shared the family’s ongoing grief and search for answers as authorities continue investigating his death. Despite the sadness, the community’s support has provided comfort. A celebration of life mass is planned in Apex to further commemorate Giovanni’s memory.
“It’s good to know how loved someone is in their community.”
More: https://abc11.com/post/giovanni-pelletier-family-friends-hold-candlelight-vigil-honor-wake-teen-found-dead-florida/17811995/
Download: https://abc11.com/apps/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ABC11/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/abc11_wtvd/
Threads: https://www.threads.net/@abc11_wtvd
TIKTOK: https://www.tiktok.com/@abc11_eyewitnessnews
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed
NC Courage wins 2-1 against Angel City FC
SUMMARY: The North Carolina Courage defeated Angel City FC 2-1 in Cary, ending their unbeaten streak. Monaca scored early at the 6th minute, followed by Bull City native Brianna Pinto’s goal at the 18th minute, securing a 2-0 halftime lead. Angel City intensified in the second half, scoring in the 88th minute, but the Courage held firm defensively to claim victory. Pinto expressed pride in the win, emphasizing the team’s unity and playoff ambitions. Nearly 8,000 fans attended. Coverage continues tonight at 11, alongside college football updates, including the Tar Heels vs. Richmond game live from Chapel Hill.
Saturday’s win was crucial for the Courage as the regular season starts to wind down.
https://abc11.com/post/north-carolina-courage-wins-2-1-angel-city-fc/17810234/
Download: https://abc11.com/apps/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ABC11/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/abc11_wtvd/
Threads: https://www.threads.net/@abc11_wtvd
TIKTOK: https://www.tiktok.com/@abc11_eyewitnessnews
-
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
Lexington man accused of carjacking, firing gun during police chase faces federal firearm charge
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
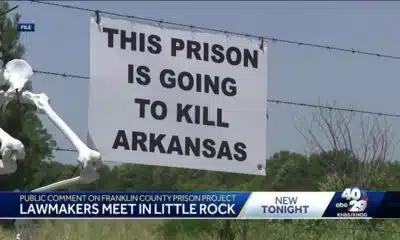
Group in lawsuit say Franklin county prison land was bought before it was inspected
-
The Center Square6 days ago
California mother says daughter killed herself after being transitioned by school | California
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
Local, statewide officials react to Charlie Kirk death after shooting in Utah
-
Local News6 days ago
US stocks inch to more records as inflation slows and Oracle soars
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed6 days ago
Arkansas medical marijuana sales on pace for record year
-
Local News Video6 days ago
William Carey University holds 'tailgates and tourniquets' blood drive
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
Zaxby's Player of the Week: Dylan Jackson, Vigor WR