BG046/Bauer-Griffin/GC Images
Alvin Thomas, University of Wisconsin-Madison and Quinn Kinzer, University of Wisconsin-Madison
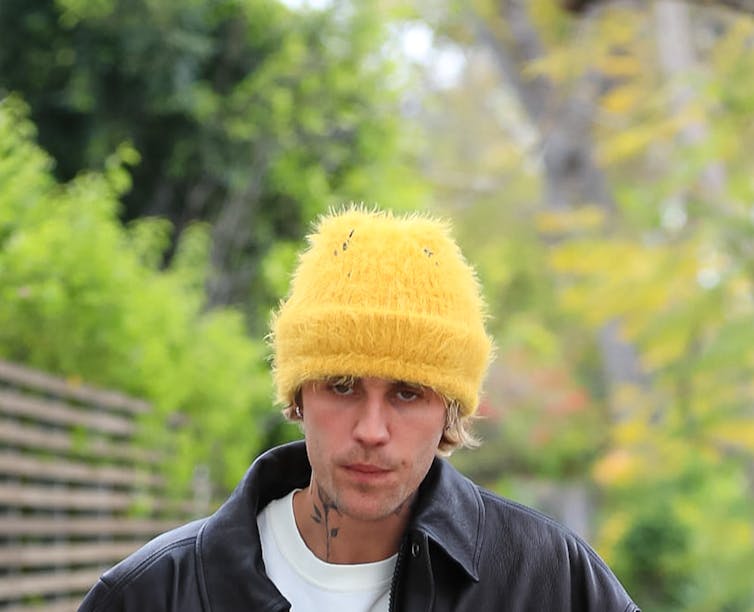
A few weeks before Justin Bieber and his wife, Hailey, announced in May 2024 that they were expecting, the pop icon posted a selfie where he appears tearful and distraught.
While media attention quickly pivoted to the pregnancy, there was little attention paid to the significance of a male celebrity and expectant father publicly sharing his vulnerability.
Yet Bieber’s social media post is notable for making his internal struggle visible.
Emotional pain is linked to serious health issues. But the public’s response to male expressions of emotion and vulnerability is often minimizing, if not dismissive. In response to Bieber’s tearful post, for example, Hailey described him as a “pretty crier.”
A year ago, the Canadian rapper Dax released the song “To Be a Man.” He said at the time: “This is a song I poured my heart into. I’m praying this reaches everyone who needs it.”
Today, the song’s message remains timely. It includes the lyrics:
Yeah, I know this life can really beat you down, uh
You wanna scream but you won’t make a sound, uh
Got so much weight that you’ve been holdin’
But won’t show any emotion, as a man, that goes unspoken
As researchers who study fatherhood and the roles that men play in their families, we recognize the loneliness and pain in these lyrics. We have heard fathers describe the toll of attempting to keep a lid on their feelings.
In a recent study we conducted on 75 new and expectant Black fathers, they spoke of the need to address individual and collective trauma. This, they said, would ultimately help support their families. But they said resources to help men with their mental health are often unavailable or very limited. They said they often feel invisible to health providers.
“Being a father and a man,” one participant said, “you have to keep the peace and be strong on the outside. But on the inside, you know, you’re falling apart.”
Dax’s lyrics and our research reflect an enduring social health challenge – the deafening silence that typically surrounds men’s mental health.
The toll of isolation on men
In May 2023, U.S. Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy released an advisory highlighting what he described as an epidemic of loneliness and isolation in the country. Our research confirms this scourge.
Since men’s social support networks – colleagues, family, close childhood friends – are often less robust than women’s, the epidemic disproportionately impacts men. The resulting solitude has very real health consequences.

Matthias Balk/picture alliance via Getty Images
In Murthy’s report, loneliness is associated with negative health outcomes, including a “29% increased risk of heart disease, a 32% increased risk of stroke, and a 50% increased risk of developing dementia for older adults. Additionally, lacking social connection increases risk of premature death by more than 60%.”
While Murthy’s report focuses on both men and women, research shows that men are less likely than women to seek mental health services. Additionally, men hold more negative attitudes toward seeking help, and they prematurely terminate treatment more often than women.
With these consequences in mind, a caring society may ask: Why are men carrying the brunt of this health risk, and what can be done about it?
Redefining men’s value beyond breadwinning
Many factors can contribute to feelings of isolation and disconnection among men.
In “To Be A Man,” Dax points toward one prominent factor:
As a man, we gotta pave our way
Our only function is to work and slave
There’s no respect for you if you ain’t paid
You’re disregarded as a human and you can’t complain
Traditional definitions of masculinity emphasize the importance of men’s role as breadwinners.
An uncertain economy and increasingly expensive housing and food prices make the ability to financially provide for a family elusive for many men. These factors also undermine men’s sense of self and contribute to loneliness and feelings of isolation.
As partners and fathers, men are still often perceived as deficient if they can’t provide economically. And societal norms stress that they are not valued for their capacity as caregivers, even if they are more involved in raising their children than ever before.
This is out of touch with reality.
Men play an important role as caregivers in their children’s lives, according to our research, and exert a powerful influence on children’s health and well-being. Men also find meaning in their roles as fathers.
As Dax says:
As a man, our son is our horizon
The cost of suppressed vulnerability
Beyond pressures to provide, men also have to overcome enduring stereotypes that suggest they should be stoic and keep their fears and sadness to themselves.
Here, too, gender norms are in need of an update. Boys and men need to feel comfortable presenting their true, authentic selves to the world. When they suppress their vulnerability, it creates a barrier to seeking help. It also perpetuates stigma and the epidemic of loneliness.

Getty Images
There is a complex interplay between society’s assumptions and beliefs about men and fatherhood.
Men, consequently, are less likely than women to seek mental health services. Health providers, as a result, are more likely to underdiagnose and misdiagnose men. Additionally, when health resources are made available, they are often not tailored to men’s needs.
Societal expectations can create unbearable pressure for men. And the most marginalized groups, like low-income Black fathers, bear a disproportionate burden, research shows. This became more evident during the COVID-19 pandemic, when Black fathers working in high-risk and essential jobs prioritized supporting their children and families over their own risk of infection and mental health.
As men continue to redefine their roles within families and communities, it’s important for society to create a space that acknowledges and embraces their vulnerabilities and full humanity in all social roles.
Men need outlets for their pain. They would benefit from relationships – with partners, family and friends – that support and nurture them in times of joy and through the emotional challenges. Their loneliness will continue to be disproportionate without the necessary connection to services.
Men can consider engaging in low-stakes discussion groups in their communities, with online groups and in their churches. They may also seek out therapists in person or online for introductory sessions to test out the therapeutic interaction before establishing a more consistent pattern of therapy services.
In “To Be a Man,” Dax sings:
No wonder most men are so depressed
All the things that they can’t express
It’s the circle of life, as a man, you provide
They don’t know what you’re worth ‘til the day that you die
As the Biebers adjust to life as parents, Justin may find people he can talk to about his experiences and emotions, people who see and value him fully. And we hope the same for every man and father, living their life out of the spotlight and doing the best they can for themselves and for their family.![]()
Alvin Thomas, Associate Professor, Phyllis Northway Faculty Fellow, University of Wisconsin-Madison and Quinn Kinzer, Graduate student and PhD Candidate, Department of Consumer Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.