News from the South - Alabama News Feed
Many more cities ban sleeping outside despite a lack of shelter space • Alabama Reflector
Many more cities ban sleeping outside despite a lack of shelter space
by Robbie Sequeira, Alabama Reflector
January 27, 2025
Since the U.S. Supreme Court’s City of Grants Pass v. Johnson ruling last June allowing localities to ban outdoor camping even if there is no homeless shelter space available, roughly 150 cities in 32 states have passed or strengthened such ordinances.
Another 40 or so local bans are pending, according to data sent to Stateline by the National Homelessness Law Center. The measures vary in detail, but they typically include prohibitions on camping, sleeping or storing property on public land. Many also include buffer zones near schools, parks or businesses.
Bans often allow for steep fines and jail time. In Indio, California, for example, people caught camping illegally could face a penalty of up to $1,000 and up to six months in jail. The ordinance in Fresno, California, bans sitting, lying, sleeping or camping on public property anytime, anywhere, with a penalty of up to a year in jail. Elmira, New York, includes sleeping in vehicles in its camping ban.
GET THE MORNING HEADLINES.
Housing advocates and experts anticipate the surge in camping bans to continue in 2025. Supporters of the bans argue that homeless encampments endanger nearby residents and businesses. Critics say the prohibitions will just criminalize visible street homelessness and move it somewhere else.
“The idea behind anti-camping laws is to make homelessness so uncomfortable that people won’t want to experience it. But homelessness is already incredibly uncomfortable, especially during disasters,” said Samantha Batko, a senior fellow in the Housing and Communities Division at the Urban Institute. “Criminalizing homelessness doesn’t solve the problem — it just punishes people, makes it harder for them to find housing or jobs, and keeps them stuck in a cycle of instability.”
!function(){“use strict”;window.addEventListener(“message”,(function(a){if(void 0!==a.data[“datawrapper-height”]){var e=document.querySelectorAll(“iframe”);for(var t in a.data[“datawrapper-height”])for(var r=0;r California has the highest number of camping bans, with more than 40 ordinances either passed or introduced since July. It also has about 30% of the nation’s homeless individuals, followed by New York, Florida and Washington state, according to a U.S. Housing and Urban Development report to Congress in 2022. California Democratic Gov. Newsom invested heavily in encampment clearance and housing, allocating $131 million to municipalities after the Grants Pass ruling. He also issued an executive order to cities to “urgently address homeless encampments.” Elizabeth Funk, CEO of DignityMoves, a nonprofit that is helping California cities address unsheltered homelessness, anticipates a rise in anti-camping policies in 2025. Still, she said, the Grants Pass ruling could require cities to build more temporary shelters. “It really is a policy decision, and we have chosen that the only valid use of taxpayer money is permanent housing. But the reality is … we can’t build our way out of this at a million dollars per unit,” said Funk. “Grants Pass removes the excuse that cities can’t act. Unsheltered homelessness is solvable — it starts with providing a roof.” Florida’s updated law, passed last year, requires counties and municipalities to ban sleeping or camping in public spaces such as parks, sidewalks and the state’s many beaches. Many local governments scrambled to put local ordinances in place to comply with the law. And as of Jan. 1, residents and business owners have the right to sue municipalities if local efforts to address homelessness are deemed insufficient. The state has around 31,000 homeless residents. The idea that the problem is such a small number of people … and no matter how much we spend on it, we’re not spending enough to actually fix it, is very frustrating. – Gainesville, Florida, Mayor Harvey Ward Gainesville, Florida, Mayor Harvey Ward said the state’s requirements haven’t dramatically changed the city’s response to homelessness. Gainesville city officials noted philosophical disagreements with the state when they passed an anti-camping ordinance in December to avoid any potential legal action for noncompliance. The ordinance carries no jail time but includes a fine. Ward said in an interview that he’s seen a major decrease in visible chronic homelessness in the city’s community plaza from a decade ago, a shift he attributes to the opening of more shelter spaces over the years. “The good news is we don’t have 100 people a night sleeping on the community plaza anymore. I can see progress. I’m just not sure how to make that sort of leap in progress again,” said Ward, who is a registered Democrat, though the mayoral position is nonpartisan. He said the state’s ban mandate also complicates how Gainesville and other cities respond to chronic street homelessness, especially given Florida’s bottom-tier spending on mental health services. “The idea that the problem is such a small number of people — fewer than 1,000 chronic homeless folks in any year — and no matter how much we spend on it, we’re not spending enough to actually fix it, is very frustrating,” Ward said. “We’ve plateaued. There are folks who, for whatever reason, either can’t be admitted to a shelter because of past issues or refuse to go. But they’re not doing anything illegal, so what do we do? How do we help someone who refuses services and isn’t breaking the law?” The rise in anti-camping ordinances after the Grants Pass ruling was a predictable outcome, even in cities that have no other options for people who don’t have homes, said Jesse Rabinowitz, campaign and communications director at the National Homelessness Law Center. “A large misconception is that people choose to experience homelessness. But no one chooses to sleep outside. People are forced into homelessness because elected officials fail to ensure safe and affordable housing,” said Rabinowitz. “The Grants Pass approach — making cities inhospitable to force people to leave — has been tried before. It’s expensive, ineffective, and only prolongs homelessness.” Yet the approach is quickly gaining ground. In November, Arizona voters approved a ballot measure allowing property owners to apply for reimbursements for public nuisance expenses when the government fails to enforce laws related to camping and loitering. A Republican-led bill in Washington state — where six municipalities have passed or strengthened anti-camping ordinances since the Grants Pass ruling — would require most local governments to ban encampments near schools and parks by May 2027. It would offer grants for encampment sweeps, but also would pull funding from localities that don’t enforce the ban. The bill remains in committee. Among the state’s cities with a ban in place is Spokane Valley, which updated its ordinance last fall. The updates include upgrading the violation of being in a city park after dark from a civil infraction to a misdemeanor, and changing the definition of “camping” to include sleeping overnight with or without camping gear. Little has changed with enforcement in the interim months, wrote city spokesperson Jill Smith in an email to Stateline. The city also has several employees dedicated to connecting unhoused residents with services, she said, and it added a second outreach police officer in December. Devon Kurtz, the public safety policy director at the Cicero Institute, a conservative think tank, argues that camping bans are necessary to address unsafe encampments and unsheltered homelessness, and that they can be part of a system that helps reluctant individuals receive help. In a recently published interview with the Philanthropy Roundtable, which advises conservative philanthropists, Kurtz warned that “homeless encampments are toxic environments filled with waste and trash, and are often hotbeds of crime.” Advocates in many states are pushing back. After a successful petitioning effort by local residents, the city of Morgantown, West Virginia, will allow voters to decide in April whether to overturn a new camping ban passed last fall. As of November, the city had 28 shelter beds to serve an estimated homeless population of 150. A 2024 RAND study found that policy changes — such as encampment sweeps and camping bans — in three Los Angeles neighborhoods temporarily reduced visible homelessness, but within months the unsheltered populations rose slightly in two of the communities and doubled in the third. The survey found chronic mental and physical health issues and substance use disorders affecting more than half of respondents, with Skid Row residents being the oldest and least healthy. Experts also argue that these laws are ineffective and costly, with a 2020 federal report finding sweeps in four cities cost $1,672 to $6,208 per unsheltered person annually. Jeremy Ney, a data researcher who publishes the American Inequality newsletter, said that while a lack of affordable housing is a root cause of rising homelessness, responses to homelessness need to accompany policies that address other chronic barriers to stability. “Housing alone is not enough. We also need employment, mental health, addiction and social service support systems that can ensure people stay in those homes,” Ney said. Stateline is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Stateline maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Scott S. Greenberger for questions: info@stateline.org. YOU MAKE OUR WORK POSSIBLE. Alabama Reflector is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Alabama Reflector maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Brian Lyman for questions: info@alabamareflector.com. The post Many more cities ban sleeping outside despite a lack of shelter space • Alabama Reflector appeared first on alabamareflector.com‘What do we do?’
‘No one chooses to sleep outside’
Do they work?
News from the South - Alabama News Feed
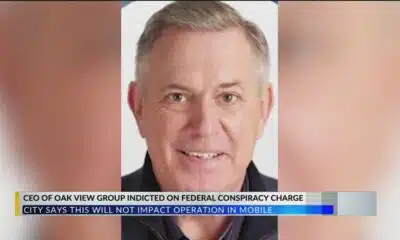
Mobile Arena management CEO indicted on federal charges
SUMMARY: The CEO of Oak View Group (OVG), hired to manage Mobile’s new arena, was indicted on federal conspiracy charges linked to bid-rigging in another city. Despite this, Mobile officials say the arena project remains unaffected and on schedule for early 2027 completion. OVG secured a 22-year contract in February to manage the new Mobile Arena, the Mobile Convention Center, and the Saenger Theatre, receiving $400,000 annually for operations, maintenance, and event booking. The City of Mobile confirmed no bidding was involved in contract selection, and a local OVG team now oversees these venues.
The head of the company hired to manage the new Mobile Arena is facing federal charges.
News from the South - Alabama News Feed
Mobile first responders bring home medals from World Police and Fire Games
SUMMARY: Mobile first responders excelled at the recent World Police and Fire Games in Birmingham, an Olympic-style event featuring over 60 sports with participants from 70+ countries. Mobile Police Officer Defferey Hollis won gold in the challenge ride and bronze in the slow ride, while Officer Josh Hart earned silver in the challenge ride, benefiting from local barricade-handling skills. Mobile Firefighter Collin Bryan placed fourth in the triathlon despite a broken foot sustained just weeks prior. The Games have been held biennially since 1985, uniting over 80,000 first responders worldwide. The team from Mobile aims for more victories at the next event in Perth, Australia.
At the World Police and Fire Games, first responders from all over the world competed in Olympic-style events. Several Mobile first responders represented the United States, bringing home medals.
News from the South - Alabama News Feed
Pediatrician Discusses MMR Vaccine Amid High Measles Case Numbers | July 9, 2025 | News 19 at 6 p.m.
SUMMARY: Measles cases in the U.S. have surged to levels not seen since the 1990s, following increased vaccine skepticism after the COVID-19 pandemic. Pediatrician Dr. William Van Cleave emphasizes the MMR vaccine’s safety and effectiveness, noting two doses provide up to 96% protection. This year, children 19 and younger make up the majority of measles cases, with three reported deaths. Despite no cases in Alabama, neighboring states like Tennessee and Georgia have seen outbreaks. Concerns about vaccine side effects have grown, even influencing federal vaccine board changes. Dr. Van Cleave urges vaccination, especially as school increases exposure to illnesses.
Measles cases in the U.S. have reached a more than 30-year high
News 19 is North Alabama’s News Leader! We are the CBS affiliate in North Alabama and the Tennessee Valley since November 28, 1963.
https://whnt.com/
https://www.facebook.com/whntnews19
https://www.instagram.com/whntnews19/
https://twitter.com/whnt
-
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed6 days ago
Real-life Uncle Sam's descendants live in Arkansas
-
News from the South - Georgia News Feed5 days ago
'Big Beautiful Bill' already felt at Georgia state parks | FOX 5 News
-
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days ago
LOFT report uncovers what led to multi-million dollar budget shortfall
-
News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days ago
Alabama schools to lose $68 million in federal grants under Trump freeze
-
News from the South - Missouri News Feed7 days ago
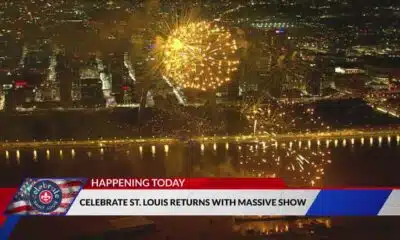
Celebrate St. Louis returns with new Superman-themed drone show
-
News from the South - Tennessee News Feed6 days ago
Officers run for cover after man in car fired shots at them in Downtown Memphis
-
The Center Square6 days ago
Alcohol limits at odds in upcoming dietary guidelines | National
-
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
Tropical Depression Three to bring rain, gusty winds to the CSRA this Fourth of July weekend