Mississippi Today
Justice Department slams ‘unconstitutional conditions’ at Mississippi prisons

The Justice Department is accusing the state of Mississippi of violating the constitutional rights of those held in four prisons: the Mississippi State Penitentiary at Parchman, the Central Mississippi Correctional Facility, the South Mississippi Correctional Institution and Wilkinson County Correctional Facility.
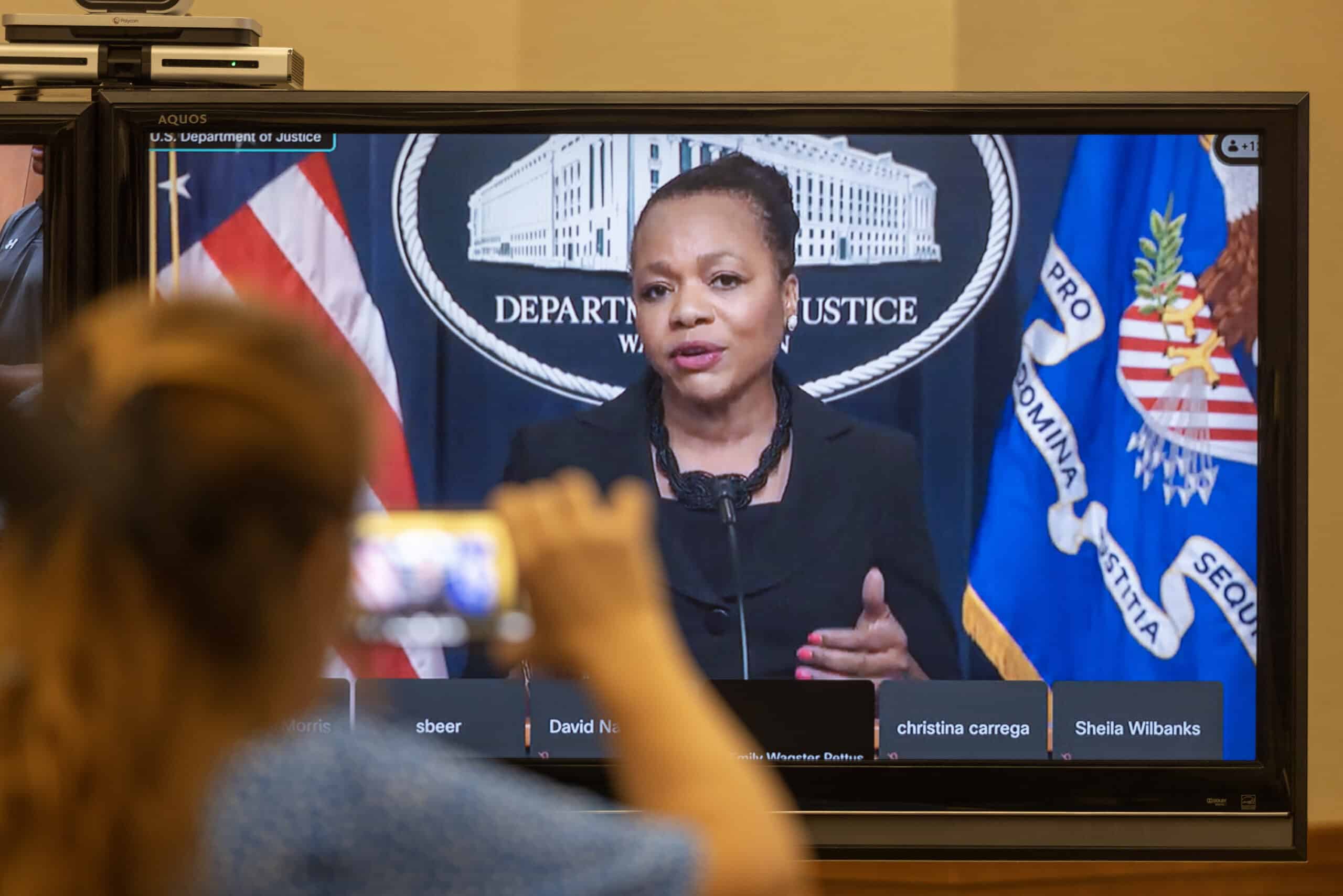
“Our work makes clear that people do not abandon their civil and constitutional rights at the jailhouse door,” Assistant Attorney General Kristen Clarke of the Justice Department’s Civil Rights Division told reporters in a press conference Wednesday. “The unconstitutional conditions in Mississippi’s prisons have existed for far too long, and we hope that this announcement marks a turning point towards implementing sound, evidence-based solutions to these entrenched problems.”
Department officials released a 60-page report Wednesday that centers on the three prisons besides Parchman. The report concluded that the Mississippi Department of Corrections “does not adequately supervise incarcerated people, control contraband, and investigate incidents of harm and misconduct. These basic safety failures and the poor living conditions inside the facilities promote violence, including sexual assault. Gangs operate in the void left by staff and use violence to control people and traffic contraband.”

Clarke said one major reason for this problem is that vacancy rates for correctional officers run between 30% and 50% at these prisons.
“It should be corrections officers running prisons, not gangs,” said U.S. Attorney Todd Gee for the Southern District of Mississippi. “When inmates are forced to join gangs, they bring that violent culture with them when they are released.”
A former gang intelligence officer estimated that more than half of those inside the Central Mississippi prison belong to gangs, according to the report. In recent years, the percentage of validated gang members inside Wilkinson was as high as 90%.
“The strength of prison gangs inside the MDOC facilities that we investigated is so great that even some staff members have gang affiliations and are on the gangs’ payroll,” the report says.
A coordinator attributed the gangs’ strength “to staff corruption and estimated that more than half the staff are on the payroll of gangs,” according to the report.
Corrections Commissioner Burl Cain has repeatedly vowed to put the gangs out of business and replace them with faith-based alternatives. The Justice Department concluded that “these efforts are inadequate. MDOC’s statewide gang coordinator could not share any metrics that assess the effectiveness of their gang control strategy. Nor do MDOC’s measures appear from our review to have broken the gangs’ stranglehold over MDOC facilities.”
The report also alleged that housing practices at some prisons “create a substantial risk of serious harm. MDOC holds hundreds of people at Central Mississippi and Wilkinson [a private prison run by MTC] in restrictive housing for prolonged periods in appalling conditions. Restrictive housing units are unsanitary, hazardous, and chaotic, with little supervision. They are breeding grounds for suicide, self-inflicted injury, fires, and assaults.”
MDOC officials have not responded to a request for comment about the Justice Department report. MTC, which operates Wilkinson, said in an emailed response that the Justice Department’s conclusions about the Wilkinson prison were drawn from visits conducted nearly two years ago and it has made “many improvements since.”
“While some challenges are inherent in operating a correctional facility, especially at facilities that house high-security inmates like Wilkinson, we continue to enhance the services we provide,” MTC said.
“The report serves as a reminder of the broad challenges faced by most, if not all, correctional facilities in all jurisdictions. These include staffing, contraband, and inmate behavior.”
Management & Training Corporation (MTC) was founded on a mission to help people improve their lives through education, training, and rehabilitation. We invest often and heavily in programming.
These constitutional violations are “systemic problems that have been going on for years,” according to the report.
In 2019, the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting and ProPublica published a series of stories on these prisons, exposing grisly violence, gang control and subhuman living conditions, noting that lawmakers had known about these issues for years and had done little to fix Parchman and the other prisons.
After that reporting, U.S. Rep. Bennie Thompson, D-Miss., and others called on the Justice Department to investigate. The department began to do that in February 2020, starting with Parchman, which the department concluded in April 2022 that those imprisoned were being subjected to violence, inadequate medical care and lack of suicide prevention.
Asked what steps those officials have taken on Parchman since the Justice Department’s 2022 report, Clarke replied, “We are aware of preliminary steps they have taken, but as laid out in great detail, the problems are severe, egregious and long-standing.”
In its latest report, Justice Department officials concluded that all four prisons are “riddled with violence. … Gross understaffing, poor supervision, and inadequate investigations create an environment where violent gang activity and dangerous contraband trafficking proliferate.”
Central Mississippi averages an assault every other day between September 2020 and June 2022, 23 of them requiring hospitalization, according to the report. South Mississippi reported nearly 100 assaults, about 4o of them requiring hospitalization. And a fifth of the more than 150 assaults at Wilkinson required hospitalization.
These numbers underestimate the violence, the report says. “In light of the large number of documented assaults …, MDOC officials cannot claim ignorance of the substantial threat of violence at these facilities.”
At Central Mississippi, camera footage showed an inmate choking and kicking a victim in the head at 3:41 a.m. on an unspecified date. Later, another assailant punched him in the face. By 8:43 a.m., the body was rigid.
It wasn’t until 8:45 a.m., five hours after the assault, that an officer ever came to the cell. It was the officer bringing the morning meal.
Medical help arrived 20 minutes later, but it was far too late. The victim, who wasn’t identified, died.
“The Warden’s report makes no mention of an officer being present on the housing unit at any point during the five hours between the assault and the [man] foaming at the mouth,” according to the report.
At South Mississippi, gang members attacked a man over $68 that he supposedly owed, the report says. “The assailants dragged the victim across different zones of the same housing unit, then after he lost consciousness, brought him to the showers and poured cold water from a garbage can on him to wake him up. Once the victim started coughing and spitting up water, the assailants continued the assault, pouring boiling hot water on him and beating him. The attackers reportedly prohibited anyone in the housing area from contacting medical [services] following the assault. After conferring with other gang members, the assailants agreed to request a security check from officers, because of the severity of the victim’s injuries. Responding staff found the victim lying on the floor behind benches. He was unable to stand up and moaned when asked questions. He had burns over 10–20% of his body, a nasal fracture, head injury, lack of cognitive response and encephalopathy (brain injury).”
The report details how often no one is monitoring the prisons’ video surveillance.
Violence at these prisons includes sexual assaults. The Prison Rape Elimination Act Manager for Central Mississippi receives between 20 and 25 complaints a month, and that number doesn’t include the attacks that go unreported.
Justice Department officials determined that staff could easily introduce contraband into these prisons.
“Drugs, cell phones, and weapons are the most common type of contraband found in the facilities,” the report says. “Many of the assaultive incidents at Central Mississippi, South Mississippi, and Wilkinson, involve contraband weapons. During one altercation at Wilkinson, an incarcerated individual sustained a laceration to his chest. Security staff recovered a piece of a kitchen knife from the scene. After an assault at Wilkinson that sent an incarcerated person to the hospital, staff recovered an eight-inch implement.”
In a single month in 2022, Wilkinson officials recovered 28 grams of meth, 8 ounces of marijuana and 10 cellphones. Over a 13-month period, South Mississippi found 1,200 cellphones, which are commonly used to “conduct business, including contraband trafficking,” according to the report.
The volume of these drugs “leads to extreme, drug-induced behaviors that contribute to violence and fatal overdoses,” according to the report. “An individual who died at Wilkinson after cutting himself and assaulting and choking his cellmate was found to have amphetamine and methamphetamine in his system.”
In addition to the lack of staff to monitor towers and videos, the report found officers “fail to do basic security tasks such as making rounds, counting incarcerated persons, and keeping doors secure. MDOC has long known about this gross understaffing and the harm it causes, but has failed to take reasonable, effective measures to fix the problem.”
Since 2020, when Gov. Tate Reeves appointed Cain, MDOC has raised starting pay for correctional officers, lowered eligibility requirements, shortened training and expedited hiring.
Despite that, the prisons are operating at “dangerously low staffing levels,” the report says. Despite significant pay raises, the pay remains lower than “other correctional agencies in the region and in other industries in Mississippi.”
MDOC also struggles to retain those it hires. One human resources officer said South Mississippi lost about half of its new hires from the previous year.
The reasons why? People aren’t prepared for the job, some have gang affiliations, and others help bring in contraband, sometimes “because of threats from incarcerated individuals,” sometimes because of “significant money being paid to officers.”
U.S. Attorney Clay Joyner for the Northern District of Mississippi said that ensuring “constitutional and humane conditions of confinement in our prisons is a key part of public safety. By allowing physical violence, illegal gang activity, and contraband to run rampant, Mississippi not only violates the rights of people incarcerated at these facilities, but also compromises the legitimacy of law enforcement efforts to protect our communities.”
UPDATE 2/28/24: This story has been updated to include MTC’s response to the report.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Mississippi Today
Derrick Simmons: Monday’s Confederate Memorial Day recognition is awful for Mississippians
Editor’s note: This essay is part of Mississippi Today Ideas, a platform for thoughtful Mississippians to share fact-based ideas about our state’s past, present and future. You can read more about the section here.
Each year, in a handful of states, public offices close, flags are lowered and official ceremonies commemorate “Confederate Memorial Day.”
Mississippi is among those handful of states that on Monday will celebrate the holiday intended to honor the soldiers who fought for the Confederacy during the Civil War.
But let me be clear: celebrating Confederate Memorial Day is not only racist but is bad policy, bad governance and a deep stain on the values we claim to uphold today.
First, there is no separating the Confederacy from the defense of slavery and white supremacy. The Confederacy was not about “states’ rights” in the abstract; it was about the right to own human beings. Confederate leaders themselves made that clear.
Confederate Vice President Alexander Stephens declared in his infamous “Cornerstone Speech” that the Confederacy was founded upon “the great truth that the negro is not equal to the white man.” No amount of revisionist history can erase the fact that the Confederacy’s cause was fundamentally rooted in preserving racial subjugation.
To honor that cause with a state holiday is to glorify a rebellion against the United States fought to defend the indefensible. It is an insult to every citizen who believes in equality and freedom, and it is a cruel slap in the face to Black Americans, whose ancestors endured the horrors of slavery and generations of systemic discrimination that followed.
Beyond its moral bankruptcy, Confederate Memorial Day is simply bad public policy. Holidays are public statements of our values. They are moments when a state, through official sanction, tells its citizens: “This is what we believe is worthy of honor.” Keeping Confederate Memorial Day on the calendar sends a message that a government once committed to denying basic human rights should be celebrated.
That message is not just outdated — it is dangerous. It nurtures the roots of racism, fuels division and legitimizes extremist ideologies that threaten our democracy today.
Moreover, there are real economic and administrative costs to shutting down government offices for this purpose. In a time when states face budget constraints, workforce shortages and urgent civic challenges, it is absurd to prioritize paid time off to commemorate a failed and racist insurrection. Our taxpayer dollars should be used to advance justice, education, infrastructure and economic development — not to prop up a lost cause of hate.
If we truly believe in moving forward together as one people, we must stop clinging to symbols that represent treason, brutality and white supremacy. There is a legislative record that supports this move in a veto-proof majority changing the state Confederate flag in 2020. Taking Confederate Memorial Day off our official state holiday calendar is another necessary step toward a more inclusive and just society.
Mississippi had the largest population of enslaved individuals in 1865 and today has the highest percentage of Black residents in the United States. We should not honor the Confederacy or Confederate Memorial Day. We should replace it.
Replacing a racist holiday with one that celebrates emancipation underscores the state’s rich African American history and promotes a more inclusive understanding of its past. It would also align the state’s observances with national efforts to commemorate the end of slavery and the ongoing pursuit of equality.
I will continue my legislative efforts to replace Confederate Memorial Day as a state holiday with Juneteenth, which commemorates the freedom for America’s enslaved people.
It’s time to end Confederate Memorial Day once and for all.
Derrick T. Simmons, D-Greensville, serves as the minority leader in the state Senate. He represents Bolivar, Coahoma and Washington counties in the Mississippi Senate.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The post Derrick Simmons: Monday's Confederate Memorial Day recognition is awful for Mississippians appeared first on mississippitoday.org
Note: The following A.I. based commentary is not part of the original article, reproduced above, but is offered in the hopes that it will promote greater media literacy and critical thinking, by making any potential bias more visible to the reader –Staff Editor.
Political Bias Rating: Left-Leaning
This article argues against the celebration of Confederate Memorial Day, stating it glorifies a racist and failed rebellion that is harmful to societal values. It critiques the holiday as a symbol of white supremacy and advocates for replacing it with Juneteenth to honor emancipation. The language used, such as referring to the Confederate cause as “moral bankruptcy,” and the call to replace the holiday reflects a progressive stance on social justice and racial equality, common in left-leaning perspectives. Additionally, the writer urges action for inclusivity and justice, positioning the argument within modern liberal values.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1903, W.E.B. Du Bois urged active resistance to racist policies
April 27, 1903

W.E.B. Du Bois, in his book, “The Souls of Black Folk,” called for active resistance to racist policies: “We have no right to sit silently by while the inevitable seeds are sown for a harvest of disaster to our children, black and white.”
He described the tension between being Black and being an American: “One ever feels his twoness, — an American, a Negro; two souls, two thoughts, two unreconciled strivings; two warring ideals in one dark body, whose strength alone keeps it from being torn asunder.”
He criticized Washington’s “Atlanta Compromise” speech. Six years later, Du Bois helped found the NAACP and became the editor of its monthly magazine, The Crisis. He waged protests against the racist silent film “The Birth of a Nation” and against lynchings of Black Americans, detailing the 2,732 lynchings between 1884 and 1914.
In 1921, he decried Harvard University’s decisions to ban Black students from the dormitories as an attempt to renew “the Anglo-Saxon cult, the worship of the Nordic totem, the disenfranchisement of Negro, Jew, Irishman, Italian, Hungarian, Asiatic and South Sea Islander — the world rule of Nordic white through brute force.”
In 1929, he debated Lothrop Stoddard, a proponent of scientific racism, who also happened to belong to the Ku Klux Klan. The Chicago Defender’s front page headline read, “5,000 Cheer W.E.B. DuBois, Laugh at Lothrup Stoddard.”
In 1949, the FBI began to investigate Du Bois as a “suspected Communist,” and he was indicted on trumped-up charges that he had acted as an agent of a foreign state and had failed to register. The government dropped the case after Albert Einstein volunteered to testify as a character witness.
Despite the lack of conviction, the government confiscated his passport for eight years. In 1960, he recovered his passport and traveled to the newly created Republic of Ghana. Three years later, the U.S. government refused to renew his passport, so Du Bois became a citizen of Ghana. He died on Aug. 27, 1963, the eve of the March on Washington.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Jim Hood’s opinion provides a roadmap if lawmakers do the unthinkable and can’t pass a budget
On June 30, 2009, Sam Cameron, the then-executive director of the Mississippi Hospital Association, held a news conference in the Capitol rotunda to publicly take his whipping and accept his defeat.
Cameron urged House Democrats, who had sided with the Hospital Association, to accept the demands of Republican Gov. Haley Barbour to place an additional $90 million tax on the state’s hospitals to help fund Medicaid and prevent the very real possibility of the program and indeed much of state government being shut down when the new budget year began in a few hours. The impasse over Medicaid and the hospital tax had stopped all budget negotiations.
Barbour watched from a floor above as Cameron publicly admitted defeat. Cameron’s decision to swallow his pride was based on a simple equation. He told news reporters, scores of lobbyists and health care advocates who had set up camp in the Capitol as midnight on July 1 approached that, while he believed the tax would hurt Mississippi hospitals, not having a Medicaid budget would be much more harmful.
Just as in 2009, the Legislature ended the 2025 regular session earlier this month without a budget agreement and will have to come back in special session to adopt a budget before the new fiscal year begins on July 1. It is unlikely that the current budget rift between the House and Senate will be as dramatic as the 2009 standoff when it appeared only hours before the July 1 deadline that there would be no budget. But who knows what will result from the current standoff? After all, the current standoff in many ways seems to be more about political egos than policy differences on the budget.
The fight centers around multiple factors, including:
- Whether legislation will be passed to allow sports betting outside of casinos.
- Whether the Senate will agree to a massive projects bill to fund local projects throughout the state.
- Whether leaders will overcome hard feelings between the two chambers caused by the House’s hasty final passage of a Senate tax cut bill filled with typos that altered the intent of the bill without giving the Senate an opportunity to fix the mistakes.
- Whether members would work on a weekend at the end of the session. The Senate wanted to, the House did not.
It is difficult to think any of those issues will rise to the ultimate level of preventing the final passage of a budget when push comes to shove.
But who knows? What we do know is that the impasse in 2009 created a guideline of what could happen if a budget is not passed.
It is likely that parts, though not all, of state government will shut down if the Legislature does the unthinkable and does not pass a budget for the new fiscal year beginning July 1.
An official opinion of the office of Attorney General Jim Hood issued in 2009 said if there is no budget passed by the Legislature, those services mandated in the Mississippi Constitution, such as a public education system, will continue.
According to the Hood opinion, other entities, such as the state’s debt, and court and federal mandates, also would be funded. But it is likely that there will not be funds for Medicaid and many other programs, such as transportation and aspects of public safety that are not specifically listed in the Mississippi Constitution.
The Hood opinion reasoned that the Mississippi Constitution is the ultimate law of the state and must be adhered to even in the absence of legislative action. Other states have reached similar conclusions when their legislatures have failed to act, the AG’s opinion said.
As is often pointed out, the opinion of the attorney general does not carry the weight of law. It serves only as a guideline, though Gov. Tate Reeves has relied on the 2009 opinion even though it was written by the staff of Hood, who was Reeves’ opponent in the contentious 2019 gubernatorial campaign.
But if the unthinkable ever occurs and the Legislature goes too far into a new fiscal year without adopting a budget, it most likely will be the courts — moreso than an AG’s opinion — that ultimately determine if and how state government operates.
In 2009 Sam Cameron did not want to see what would happen if a budget was not adopted. It also is likely that current political leaders do not want to see the results of not having a budget passed before July 1 of this year.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed2 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed2 days agoMissouri lawmakers on the cusp of legalizing housing discrimination
-

 SuperTalk FM5 days ago
SuperTalk FM5 days agoNew Amazon dock operations facility to bring 1,000 jobs to Marshall County
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoPrayer Vigil Held for Ronald Dumas Jr., Family Continues to Pray for His Return | April 21, 2025 | N
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoTrump touts manufacturing while undercutting state efforts to help factories
-

 Mississippi Today7 days ago
Mississippi Today7 days ago‘Trainwreck on the horizon’: The costly pains of Mississippi’s small water and sewer systems
-

 News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days agoMeteorologist Chita Craft is tracking a Severe Thunderstorm Warning that's in effect now
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed7 days agoTaking video of military bases using drones could be outlawed | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoFederal report due on Lumbee Tribe of North Carolina’s path to recognition as a tribal nation