Archives and Special Collections, Colorado State University
Tobi Jacobi, Colorado State University and Caitlin Clark, Colorado State University
Many bakers working at high altitudes have carefully followed a standard recipe only to reach into the oven to find a sunken cake, flat cookies or dry muffins.
Experienced mountain bakers know they need a few tricks to achieve the same results as their fellow artisans working at sea level.
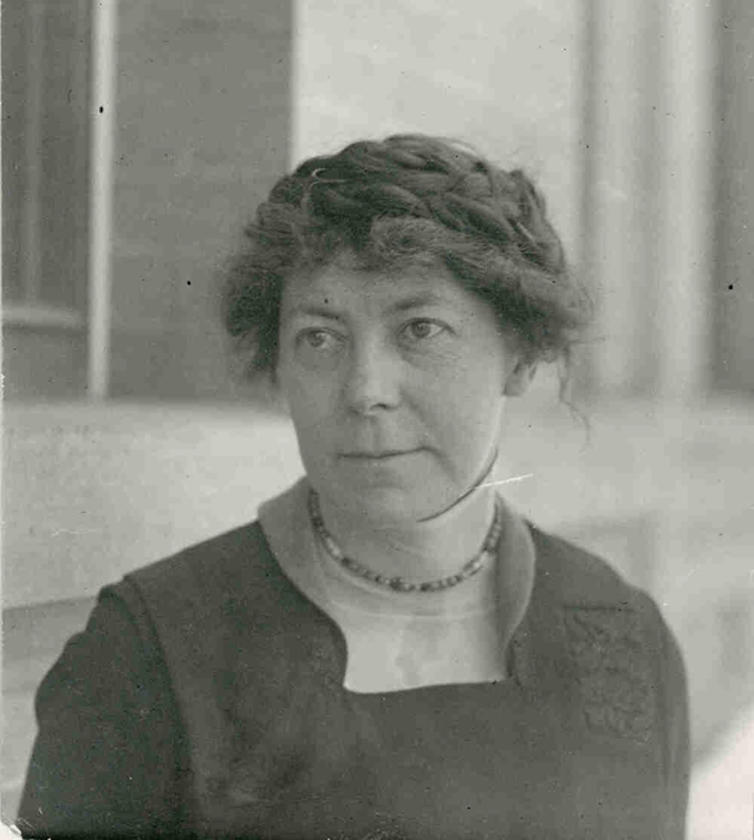
These tricks are more than family lore, however. They originated in the early 20th century thanks to research on high-altitude baking done by Inga Allison, then a professor at Colorado State University. It was Allison’s scientific prowess and experimentation that brought us the possibility of perfect high-altitude brownies and other baked goods.

Archives and Special Collections, Colorado State University
We are two current academics at CSU whose work has been touched by Allison’s legacy.
One of us – Caitlin Clark – still relies on Allison’s lessons a century later in her work as a food scientist in Colorado. The other – Tobi Jacobi – is a scholar of women’s rhetoric and community writing, and an enthusiastic home baker in the Rocky Mountains, who learned about Allison while conducting archival research on women’s work and leadership at CSU.
That research developed into “Knowing Her,” an exhibition Jacobi developed with Suzanne Faris, a CSU sculpture professor. The exhibit highlights dozens of women across 100 years of women’s work and leadership at CSU and will be on display through mid-August 2025 in the CSU Fort Collins campus Morgan Library.
A pioneer in home economics
Inga Allison is one of the fascinating and accomplished women who is part of the exhibit.
Allison was born in 1876 in Illinois and attended the University of Chicago, where she completed the prestigious “science course” work that heavily influenced her career trajectory. Her studies and research also set the stage for her belief that women’s education was more than preparation for domestic life.
In 1908, Allison was hired as a faculty member in home economics at Colorado Agricultural College, which is now CSU. She joined a group of faculty who were beginning to study the effects of altitude on baking and crop growth. The department was located inside Guggenheim Hall, a building that was constructed for home economics education but lacked lab equipment or serious research materials.

Archives and Special Collections, Colorado State University
Allison took both the land grant mission of the university with its focus on teaching, research and extension and her particular charge to prepare women for the future seriously. She urged her students to move beyond simple conceptions of home economics as mere preparation for domestic life. She wanted them to engage with the physical, biological and social sciences to understand the larger context for home economics work.
Such thinking, according to CSU historian James E. Hansen, pushed women college students in the early 20th century to expand the reach of home economics to include “extension and welfare work, dietetics, institutional management, laboratory research work, child development and teaching.”
News articles from the early 1900s track Allison giving lectures like “The Economic Side of Natural Living” to the Colorado Health Club and talks on domestic science to ladies clubs and at schools across Colorado. One of her talks in 1910 focused on the art of dishwashing.
Allison became the home economics department chair in 1910 and eventually dean. In this leadership role, she urged then-CSU President Charles Lory to fund lab materials for the home economics department. It took 19 years for this dream to come to fruition.
In the meantime, Allison collaborated with Lory, who gave her access to lab equipment in the physics department. She pieced together equipment to conduct research on the relationship between cooking foods in water and atmospheric pressure, but systematic control of heat, temperature and pressure was difficult to achieve.
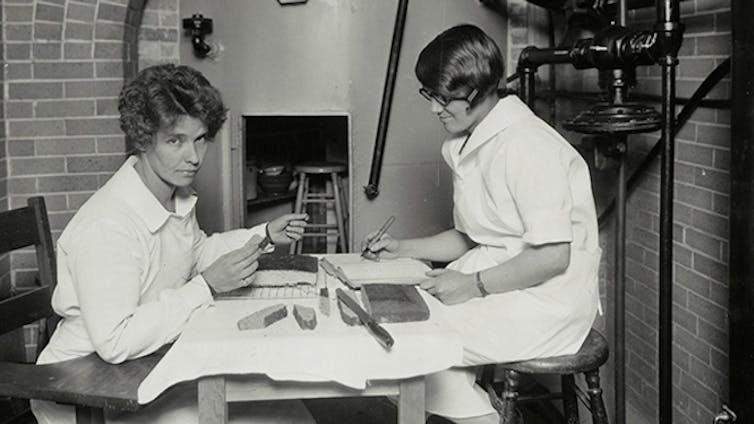
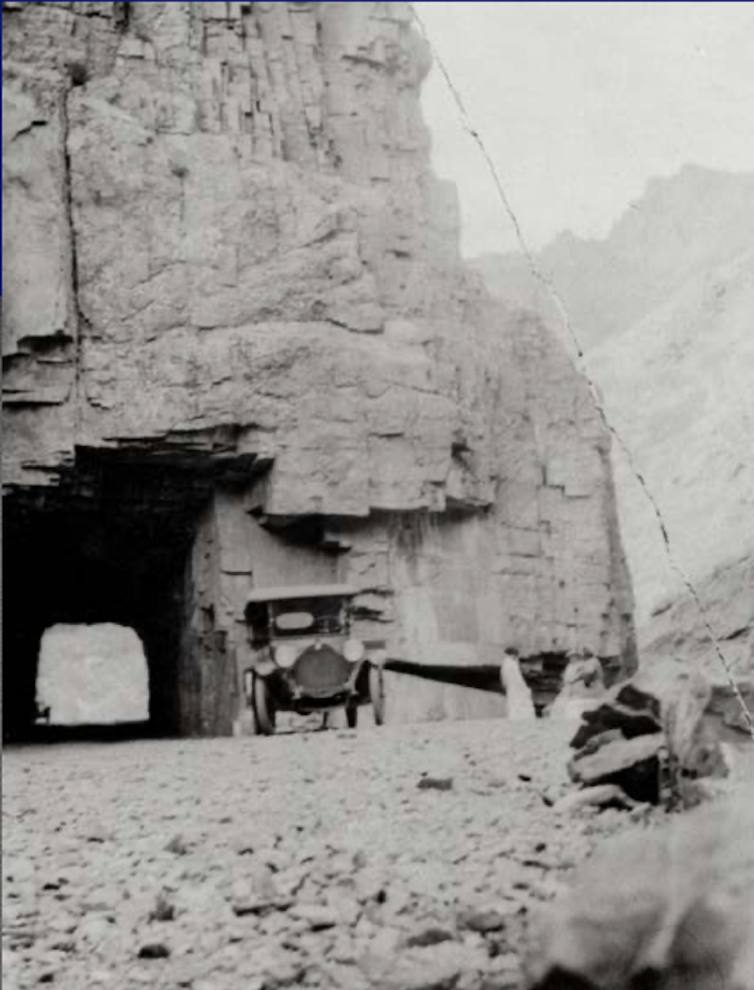
She sought other ways to conduct high-altitude experiments and traveled across Colorado where she worked with students to test baking recipes in varied conditions, including at 11,797 feet in a shelter house on Fall River Road near Estes Park.

Archives and Special Collections, Colorado State University
But Allison realized that recipes baked at 5,000 feet in Fort Collins and Denver simply didn’t work in higher altitudes. Little advancement in baking methods occurred until 1927, when the first altitude baking lab in the nation was constructed at CSU thanks to Allison’s research. The results were tangible — and tasty — as public dissemination of altitude-specific baking practices began.
A 1932 bulletin on baking at altitude offers hundreds of formulas for success at heights ranging from 4,000 feet to over 11,000 feet. Its author, Marjorie Peterson, a home economics staff person at the Colorado Experiment Station, credits Allison for her constructive suggestions and support in the development of the booklet.
Science of high-altitude baking
As a senior food scientist in a mountain state, one of us – Caitlin Clark – advises bakers on how to adjust their recipes to compensate for altitude. Thanks to Allison’s research, bakers at high altitude today can anticipate how the lower air pressure will affect their recipes and compensate by making small adjustments.
The first thing you have to understand before heading into the kitchen is that the higher the altitude, the lower the air pressure. This lower pressure has chemical and physical effects on baking.
Air pressure is a force that pushes back on all of the molecules in a system and prevents them from venturing off into the environment. Heat plays the opposite role – it adds energy and pushes molecules to escape.
When water is boiled, molecules escape by turning into steam. The less air pressure is pushing back, the less energy is required to make this happen. That’s why water boils at lower temperatures at higher altitudes – around 200 degrees Fahrenheit in Denver compared with 212 F at sea level.
So, when baking is done at high altitude, steam is produced at a lower temperature and earlier in the baking time. Carbon dioxide produced by leavening agents also expands more rapidly in the thinner air. This causes high-altitude baked goods to rise too early, before their structure has fully set, leading to collapsed cakes and flat muffins. Finally, the rapid evaporation of water leads to over-concentration of sugars and fats in the recipe, which can cause pastries to have a gummy, undesirable texture.
Allison learned that high-altitude bakers could adjust to their environment by reducing the amount of sugar or increasing liquids to prevent over-concentration, and using less of leavening agents like baking soda or baking powder to prevent dough from rising too quickly.
Allison was one of many groundbreaking women in the early 20th century who actively supported higher education for women and advanced research in science, politics, humanities and education in Colorado.
Others included Grace Espy-Patton, a professor of English and sociology at CSU from 1885 to 1896 who founded an early feminist journal and was the first woman to register to vote in Fort Collins. Miriam Palmer was an aphid specialist and master illustrator whose work crafting hyper-realistic wax apples in the early 1900s allowed farmers to confirm rediscovery of the lost Colorado Orange apple, a fruit that has been successfully propagated in recent years.
In 1945, Allison retired as both an emerita professor and emerita dean at CSU. She immediately stepped into the role of student and took classes in Russian and biochemistry.
In the fall of 1958, CSU opened a new dormitory for women that was named Allison Hall in her honor.
“I had supposed that such a thing happened only to the very rich or the very dead,” Allison told reporters at the dedication ceremony.
Read more of our stories about Colorado.![]()
Tobi Jacobi, Professor of English, Colorado State University and Caitlin Clark, Senior Food Scientist at the CSU Spur Food Innovation Center, Colorado State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.