Antonio Masiello/Getty Images
Mathew Schmalz, College of the Holy Cross
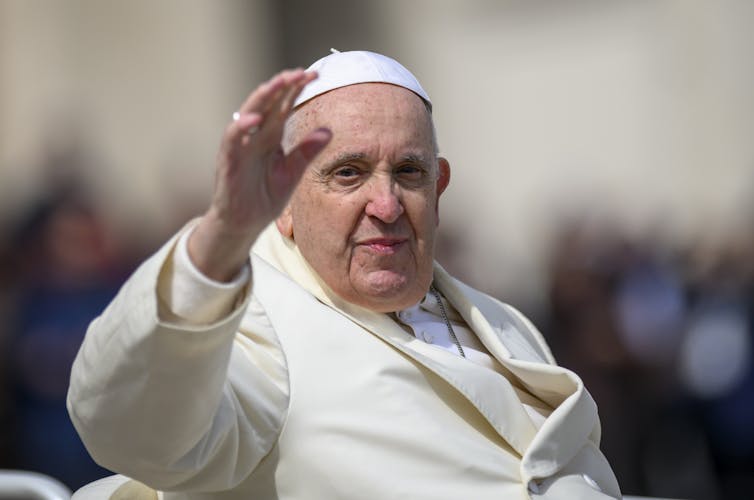
Pope Francis, who remains in critical condition and hospitalized as he battles pneumonia in both lungs, was elected pope on March 13, 2013, after the surprise resignation of Benedict XVI.
Prior to becoming pope, he was Jorge Mario Bergoglio, archbishop of Buenos Aires, and was the first person from the Americas to be elected to the papacy. He was also the first pope to choose Francis as his name, thus honoring St. Francis of Assisi, a 13th-century mystic whose love for nature and the poor have inspired Catholics and non-Catholics alike.
Pope Francis chose not to wear the elaborate clothing, like red shoes or silk vestments, associated with other popes. As a scholar of global Catholicism, however, I would argue that the changes Francis brought to the papacy were more than skin deep. He opened the church to the outside world in ways none of his predecessors had done before.
Care for the marginalized
Pope Francis reached out personally to the poor. For example, he turned a Vatican plaza into a refuge for the homeless, whom he called “nobles of the street.”

Jesuit General Curia via Getty Images
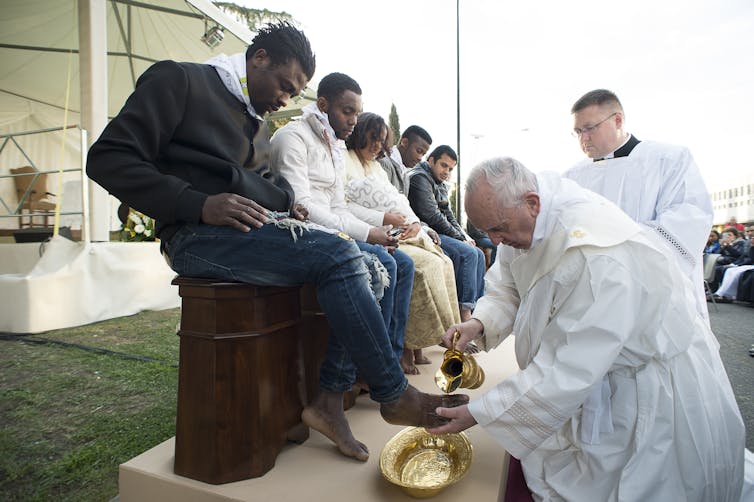
He washed the feet of migrants and prisoners during the traditional foot-washing ceremony on the Thursday before Easter. In an unprecedented act for a pope, he also washed the feet of non-Christians.
He encouraged a more welcoming attitude toward gay and lesbian Catholics and invited transgender people to meet with him at the Vatican.
On other contentious issues, Francis reaffirmed official Catholic positions. He labeled homosexual behavior a “sin,” although he also stated that it should not be considered a crime. Francis criticized gender theory for “blurring” differences between men and women.
While he maintained the church’s position that all priests should be male, he made far-reaching changes that opened various leadership roles to women. Francis was the first pope to appoint a woman to head an administrative office at the Vatican. Also for the first time, women were included in the 70-member body that selects bishops and the 15-member council that oversees Vatican finances. Shortly before his death, he appointed an Italian nun, Sister Raffaella Petrini, as President of the Vatican City.

Stefano Spaziani/Mondadori Portfolio via Getty Images
Not shy of controversy
Some of Francis’ positions led to opposition in some Catholic circles.
One such issue was related to Francis’ embrace of religious diversity. Delivering an address at the Seventh Congress of Leaders of World and Traditional Religions in Kazakhstan in 2022, he said that members of the world’s different religions were “children of the same heaven.”
While in Morocco, he spoke out against conversion as a mission, saying to the Catholic community that they should live “in brotherhood with other faiths.” To some of his critics, however, such statements undermined the unique truth of Christianity.
During his tenure, the pope called for “synodality,” a more democratic approach to decision making. For example, synod meetings in November 2023 included laypeople and women as voting members. But the synod was resisted by some bishops who feared it would lessen the importance of priests as teachers and leaders.
In a significant move that will influence the choosing of his successor, Pope Francis appointed more cardinals from the Global South. But not all Catholic leaders in the Global South followed his lead on doctrine. For example, African bishops publicly criticized Pope Francis’ December 2023 ruling that allowed blessings of individuals in same sex couples.
His most controversial move was limiting the celebration of the Mass in the older form that uses Latin. This reversed a decision made by Benedict XVI that allowed the Latin Mass to be more widely practiced.
Traditionalists argued that the Latin Mass was an important – and beautiful – part of the Catholic tradition. But Francis believed that it had divided Catholics into separate groups who worshiped differently.
This concern for Catholic unity also led him to discipline two American critics of his reforms, Bishop Joseph Strickland of Tyler, Texas, and Cardinal Raymond Burke. Most significantly, Carlo Maria Viganò, the former Vatican ambassador, or nuncio, to the United States was excommunicated during Francis’ tenure for promoting “schism.”
Recently, Pope Francis also criticized the Trump administration’s efforts to deport migrants. In a letter to US Bishops, he recalled that Jesus, Mary and Joseph had been emigrants and refugees in Egypt. Pope Francis also argued that migrants who enter a country illegally should not be treated as criminals because they are in need and have dignity as human beings.
Writings on ‘the common good’
In his official papal letters, called encyclicals, Francis echoed his public actions by emphasizing the “common good,” or the rights and responsibilities necessary for human flourishing.

L’Osservatore Romano/Pool Photo via AP
His first encyclical in 2013, Lumen Fidei, or “The Light of Faith,” sets out to show how faith can unite people everywhere.
In his next encyclical, Laudato Si’, or “Praise Be to You,” Francis addressed the environmental crisis, including pollution and climate change. He also called attention to unequal distribution of wealth and called for an “integral ecology” that respects both human beings and the environment.
His third encyclical in 2020, Fratelli Tutti, or “Brothers All,” criticized a “throwaway culture” that discards human beings, especially the poor, the unborn and the elderly. In a significant act for the head of the Catholic Church, Francis concluded by speaking of non-Catholics who have inspired him: Martin Luther King Jr., Desmond Tutu and Mahatma Gandhi.
In his last encyclical, Dilexit Nos, or “He Loved Us,” he reflected on God’s Love through meditating on the symbol of the Sacred Heart that depicts flames of love coming from Jesus’ wounded heart that was pierced during the crucifixion.
Francis also proclaimed a special “year of mercy” in 2015-16. The pope consistently argued for a culture of mercy that reflects the love of Jesus Christ, calling him “the face of God’s mercy.”
A historic papacy
Francis’ papacy has been historic. He embraced the marginalized in ways that no pope had done before. He not only deepened the Catholic Church’s commitment to the poor in its religious life but also expanded who is included in its decision making.
The pope did have his critics who thought he went too far, too fast. And whether his reforms take root depends on his successor. Among many things, Francis will be remembered for how his pontificate represented a shift in power in the Catholic Church away from Western Europe to the Global South, where the majority of Catholics now live.![]()
Mathew Schmalz, Professor of Religious Studies, College of the Holy Cross
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.