Horses supported travel, communication, agriculture and warfare across much of the ancient world.
William Taylor, University of Colorado Boulder
Across human history, no single animal has had a deeper impact on human societies than the horse. But when and how people domesticated horses has been an ongoing scientific mystery.
Half a million years ago or more, early human ancestors hunted horses with wooden spears, the very first weapons, and used their bones for early tools. During the late Paleolithic era, as far back as 30,000 years ago or more, ancient artists chose wild horses as their muse: Horses are the most commonly depicted animal in Eurasian cave art.
Following their first domestication, horses became the foundation of herding life in the grasslands of Inner Asia, and key leaps forward in technology such as the chariot, saddle and stirrup helped make horses the primary means of locomotion for travel, communication, agriculture and warfare across much of the ancient world. With the aid of ocean voyages, these animals eventually reached the shores of every major landmass – even Antarctica, briefly.
As they spread, horses reshaped ecology, social structures and economies at a never-before-seen scale. Ultimately, only industrial mechanization supplanted their near-universal role in society.
Because of their tremendous impact in shaping our collective human story, figuring out when, why and how horses became domesticated is a key step toward understanding the world we live in now.
Doing so has proven to be surprisingly challenging. In my new book, “Hoof Beats: How Horses Shaped Human History,” I draw together new archaeological evidence that is revising what scientists like me thought we knew about this story.
Horses have long been revered in the steppes of Inner Asia, as seen by the horse skulls and prayer flags at this monument to racehorses in central Mongolia. William Taylor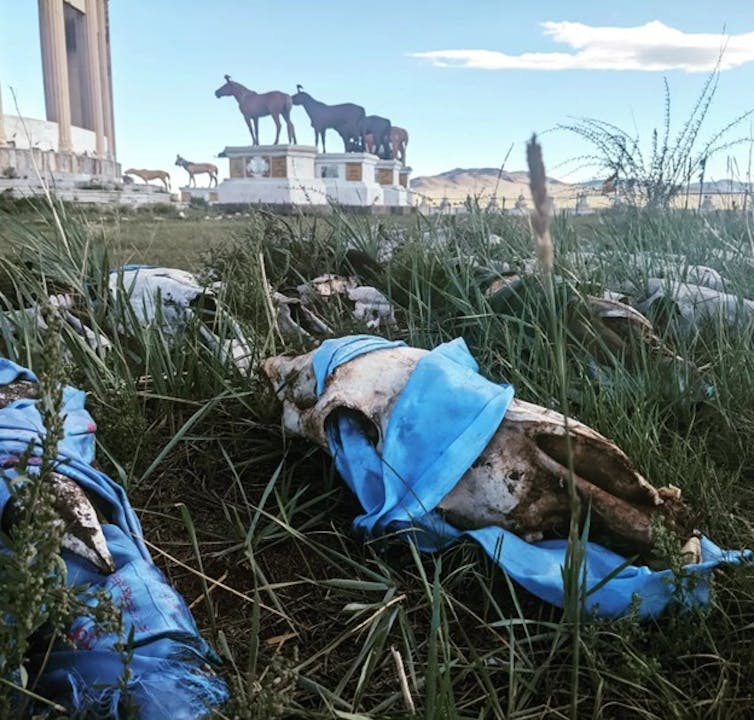
A horse domestication hypothesis
Over the years, almost every time and place on Earth has been suggested as a possible origin point for horse domestication, from Europe tens of thousands of years ago to places such as Saudi Arabia, Anatolia, China or even the Americas.
By far the most dominant model for horse domestication, though, has been the Indo-European hypothesis, also known as the “Kurgan hypothesis.” It argues that, sometime in the fourth millennium BCE or before, residents of the steppes of western Asia and the Black Sea known as the Yamnaya, who built large burial mounds called kurgans, hopped astride horses. The newfound mobility of these early riders, the story goes, helped catalyze huge migrations across the continent, distributing ancestral Indo-European languages and cultures across Eurasia.
But what’s the actual evidence supporting the Kurgan hypothesis for the first horse domestication? Many of the most important clues come from the bones and teeth of ancient animals, via a discipline known as archaeozoology. Over the past 20 years, archaeozoological data seemed to converge on the idea that horses were first domesticated in sites of the Botai culture in Kazakhstan, where scientists found large quantities of horse bones at sites dating to the fourth millennium BCE.
Other kinds of compelling circumstantial evidence started to pile up. Archaeologists discovered evidence of what looked like fence post holes that could have been part of ancient corrals. They also found ceramic fragments with fatty horse residues that, based on isotope measurements, seem to have been deposited in the summer months, a time when milk could be collected from domestic horses.
The scientific smoking gun for early horse domestication, though, was a set of changes found on some Botai horse teeth and jawbones. Like the teeth of many modern and ancient ridden horses, the Botai horse teeth appeared to have been worn down by a bridle mouthpiece, or bit.
Together, the data pointed strongly to the idea of horse domestication in northern Kazakhstan around 3500 BCE – not quite the Yamnaya homeland, but close enough geographically to keep the basic Kurgan hypothesis intact.
There were some aspects of the Botai story, though, that never quite lined up. From the outset, several studies showed that the mix of horse remains found at Botai were unlike those found in most later pastoral cultures: Botai is evenly split between male and female horses, mostly of a healthy reproductive age. Killing off healthy, breeding-age animals like this on a regular basis would devastate a breeding herd. But this demographic blend is common among animals that have been hunted. Some Botai horses even have projectile points embedded in their ribs, showing that they died through hunting rather than a controlled slaughter.
These unresolved loose ends loomed over a basic consensus linking the Botai culture to horse domestication.
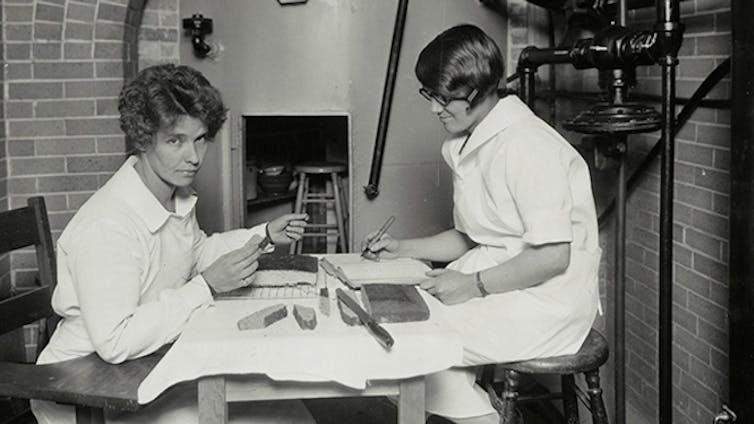
Horse bones from archaeological sites hold clues about humanity’s earliest relationship with horses. Peter Bittner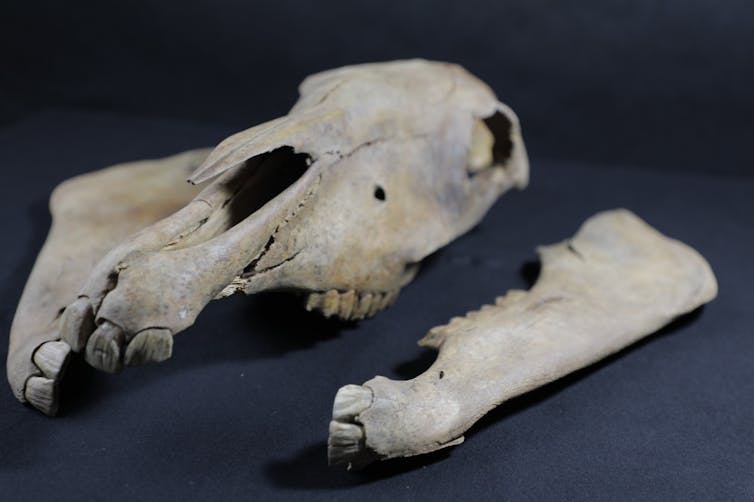
New scientific tools raise more questions
In recent years, as archaeological and scientific tools have rapidly improved, key assumptions about the cultures of Botai, Yamnaya and the early chapters of the human-horse story have been overturned.
First, improved biomolecular tools show that whatever happened at Botai, it had little to do with the domestication of the horses that live today. In 2018, nuclear genomic sequencing revealed that Botai horses were not the ancestors of domestic horses but of Przewalski’s horse, a wild relative and denizen of the steppe that has never been domesticated, at least in recorded history.
Next, when my colleagues and I reconsidered skeletal features linked to horse riding at Botai, we saw that similar issues are also visible in ice age wild horses from North America, which had certainly never been ridden. Even though horse riding can cause recognizable changes to the teeth and bones of the jaw, we argued that the small issues seen on Botai horses can reasonably be linked to natural variation or life history.
This finding reopened the question: Was there horse transport at Botai at all?
Researcher Chance Ward examines a horse jawbone in an archaeology laboratory in Wyoming. Peter Bittner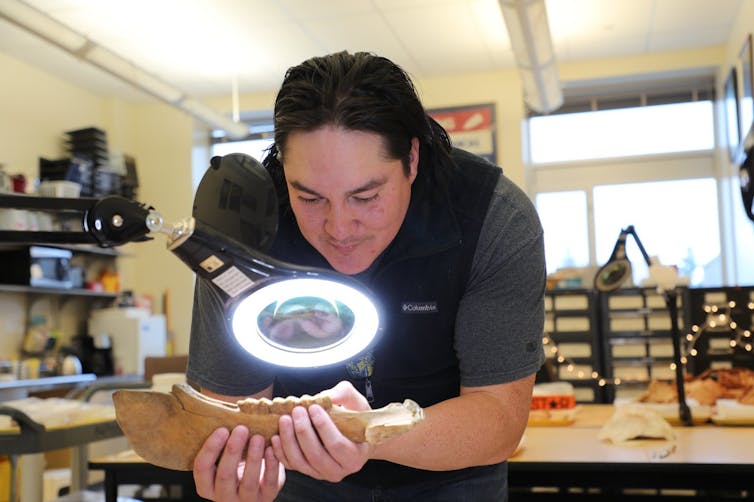
Leaving the Kurgan hypothesis in the past
Over the past few years, trying to make sense of the archaeological record around horse domestication has become an ever more contradictory affair.
For example, in 2023, archaeologists noted that human hip and leg skeletal problems found in Yamnaya and early eastern European burials looked a lot like problems found in mounted riders, consistent with the Kurgan hypothesis. But problems like these can be caused by other kinds of animal transport, including the cattle carts found in Yamnaya-era sites.
So how should archaeologists make sense of these conflicting signals?
A clearer picture may be closer than we think. A detailed genomic study of early Eurasian horses, published in June 2024 in the journal Nature, shows that Yamnaya horses were not ancestors of the first domestic horses, known as the DOM2 lineage. And Yamnaya horses showed no genetic evidence of close control over reproduction, such as changes linked with inbreeding.
Instead, the first DOM2 horses appear just before 2000 BCE, long after the Yamnaya migrations and just before the first burials of horses and chariots also show up in the archaeological record.
Archaeologists investigate an ancient horse jawbone melting from mountain ice in western Mongolia. Yancen Diemberger, CC BY-ND
For now, all lines of evidence seem to converge on the idea that horse domestication probably did take place in the Black Sea steppes, but much later than the Kurgan hypothesis requires. Instead, human control of horses took off just prior to the explosive spread of horses and chariots across Eurasia during the early second millennium BCE.
There’s still more to be settled, of course. In the latest study, the authors point to some funny patterns in the Botai data, especially fluctuations in genetic estimates for generation time – essentially, how long it takes on average for a population of animals to produce offspring. Might these suggest that Botai people still raised those wild Przewalski’s horses in captivity, but only for meat, without a role in transportation? Perhaps. Future research will let us know for sure.
Either way, out of these conflicting signals, one consideration has become clear: The earliest chapters of the human-horse story are ready for a retelling.![]()
William Taylor, Assistant Professor and Curator of Archaeology, University of Colorado Boulder
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.