News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
Coastal Truck Driving School prepares truck drivers for career in demand

SUMMARY: Trucker Appreciation Week highlights the vital role of truck drivers in the U.S. economy. Joel Massie reports on Coastal Truck Driving School, where director Chrissy Powell emphasizes the freedom of driving while acknowledging the profession’s challenges, such as ensuring safety. Student trucker Jaden Francois expresses his passion for driving, while fellow student Philip Henry transitions from the oil field to trucking, seeking a career change. Powell notes that the school not only addresses workforce needs but also transforms lives by offering new opportunities. Coastal operates eight campuses across the South, contributing significantly to the nation’s freight transport.

Coastal Truck Driving School prepares truck drivers for career in demand
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
Judge to weigh Louisiana AG’s challenge to New Orleans jail’s ‘sanctuary’ policy

by Bobbi-Jean Misick, Verite, Louisiana Illuminator
April 20, 2025
NEW ORLEANS – Louisiana Attorney General Liz Murrill is pushing forward with her efforts to force Orleans Parish Sheriff Susan Hutson to drop a longtime policy that generally prohibits deputies from directly engaging in federal immigration enforcement within the city’s jail.
In legal filings, Murrill claims the policy — which the state characterizes as a so-called “sanctuary city” policy — is in direct conflict with a newly passed state law that requires state and local law enforcement agencies to cooperate with federal immigration agencies.
“The consent decree now sits fundamentally at odds with state law as applicable to immigration detainers,” Murrill said in court documents filed Friday (April 11).
A federal court will now determine whether to allow the state of Louisiana to join a 2011 federal suit that resulted in the policy and whether to throw out the policy altogether. A hearing has been set for April 30.
GET THE MORNING HEADLINES.
The state’s campaign against “sanctuary” policies comes as President Donald Trump is pushing local law enforcement agencies to join the federal government in his promised immigration crackdown. Since his inauguration, Trump has ordered the U.S. Department of Homeland Security to push for more partnerships between local law enforcement units and federal immigration agencies. A few have already signed up. Louisiana Gov. Jeff Landry, a longtime immigration hardliner and Trump ally, has worked with Republican lawmakers in the state to enact laws that encourage those collaborations.
As attorney general, Landry criticized a policy adopted by the New Orleans Police Department, under a long-running federal consent decree that blocks officers from enforcing immigration laws.
Neither Murrill’s office nor representatives for U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement responded to requests for comment.
In court filings, Murrill said Hutson “does not oppose the [state’s] intervention” in the case.” But a spokesperson for Hutson said that’s not exactly true.
“It’s more accurate that we take no position regarding the state intervention,” a Sheriff’s Office spokesperson said in an emailed statement on Wednesday.
While she has not taken a position for or against increased collaboration with ICE, in an interview with Fox 8 in December, Hutson noted that the jail’s resources were far too stretched to take on immigration enforcement.
“I’m a lawyer. I believe in following the law and court orders and we do that and so that’s what we’re gonna do, continue to follow the law, but I cannot do ICE’s work,” she said. “It’s too big of a load.”
Potential conflict
The sheriff’s policy stems from a 2013 federal court settlement in a civil rights case involving two New Orleans construction workers picked up on minor charges in 2009 and 2010.
Mario Cacho and Antonio Ocampo sued after they were allegedly illegally held in the city’s jail past the completion of their sentences. The two were held at the request of U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement. The agency issues such “detainer” requests to local law enforcement agencies, asking them to hold onto arrestees who are suspected of immigration violations.
Local agencies are only supposed to honor the hold requests for 48 hours, after which they should let detainees free. But in 2009 and 2010, then-Sheriff Marlin Gusman detained Cacho and Ocampo for months, according to legal filings in their case against the office.
Ocampo and Cacho settled the case with the Sheriff’s Office in 2013, and Gusman agreed to adopt a new policy on immigration investigations. The resulting policy blocks the agency from investigating immigration violations and from detaining immigrants for ICE without a court order, except in certain cases where they are facing charges for a small number of serious violent crimes.
Attorneys for Cacho and Ocampo declined to speak with Verite News on the record. However, filings they submitted to the court last week opposing the state’s intervention in the case argue that Murrill has “blatantly misrepresented the OPSO policy” by falsely claiming it forces the Sheriff’s Office to disregard all ICE detainers.
The sheriff’s office, like the NOPD, has been under a sweeping federal consent decree for more than a decade. But unlike the NOPD, the jail’s consent decree does not demand that deputies stay away from federal immigration enforcement, only that it release anyone subject to an immigration hold after two days. The Justice Department’s Civil Rights Division, which is a party to both consent decrees, has not entered any filings since Murrill moved to bring the state into the Cacho and Ocampo case.
The Department of Justice did not respond to a request for comment.
The OPSO policy remained in place for more than a decade without any controversy until last spring, when the Louisiana Legislature passed a bill — Act 314 — that blocks so-called “sanctuary” policies prohibiting state and local law enforcement officers from cooperating with federal immigration agencies like ICE.
A sheriff’s office spokesperson spokesperson said the agency’s policy on ICE detainers is “governed” by the consent judgement in the case. She declined to comment further, as the state is currently challenging the policy, but affirmed that OPSO is “in full compliance with all applicable state laws and valid court orders related to ICE detainers.”
YOU MAKE OUR WORK POSSIBLE.
This article first appeared on Verite News New Orleans and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. PARSELY = { autotrack: false, onload: function() { PARSELY.beacon.trackPageView({ url: “https://veritenews.org/2025/04/16/judge-to-weigh-new-orleans-jail-sanctuary-murrill/”, urlref: window.location.href }); } }
Louisiana Illuminator is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Louisiana Illuminator maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Greg LaRose for questions: info@lailluminator.com.
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
Professor Carl Nivale’s Easter Parade Report

SUMMARY: Professor Carl Nivale provided a preview of the Easter parades in the French Quarter on April 20th. The historic French Quarter Easter Parade, founded in 1956, starts at 9:45 AM and features ladies in Easter bonnets riding in horse-drawn carriages. The 40th Annual French Quarter Easter Parade follows at 1:00 PM, honoring the late Eric Pollson, with notable riders like Malik Mingo and Meg Ferris. The official Gay Easter Parade begins at 4:30 PM, celebrating its 24th year with colorful costumes and miniature floats. For real-time updates, Professor Nivale encourages using the WWL Parade Tracker app.

The French Quarter Easter Parade and Gay Easter Parade both roll on Sunday, bringing festive fashion, floats, and music to the heart of New Orleans.
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
One state framed wetlands as a flooding solution. Could it work elsewhere?

by Madeline Heim and Caitlin Looby, Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, Louisiana Illuminator
April 19, 2025
ASHLAND, Wis. — In less than 10 years, three catastrophic floods ravaged northwestern Wisconsin and changed the way people think about water.
The most severe, in July 2016, slammed Ashland with up to 10 inches of rain in less than a day — a month’s worth of rain fell in just two hours. As rivers swelled to record highs, major highways broke into pieces and culverts washed away. It took months for roads to reopen, with more than $41 million in damage across seven counties.
The Marengo River, which winds through forests and farmland before meeting the Bad River that flows into Lake Superior, was hit hard during these historic deluges. Centuries earlier, the upper watershed would have held onto that water, but logging and agriculture left the river disconnected from its floodplain, giving the water nowhere safe to go.
Today, the Marengo River stands as an example of a new kind of solution. Following the record floods, state leaders invested in opening up floodplains and restoring wetlands to relieve flooding. As the need to adapt to disasters grows more urgent, the Marengo River serves as an example that there’s a cheaper way to do so: using wetlands.
“We can’t change the weather or the patterns… but we can better prepare ourselves,” said MaryJo Gingras, Ashland County’s conservationist.
Wetlands once provided more natural flood storage across Wisconsin and the Mississippi River Basin, soaking up water like sponges so it couldn’t rush further downstream. But about half of the country’s wetlands have been drained and filled for agriculture and development, and they continue to be destroyed, even as climate change intensifies floods.
As the federal government disposes of rules to protect wetlands, environmental advocates want to rewrite the ecosystem’s narrative to convince more people that restoration is worth it.
Wetlands aren’t just pretty places, advocates argue, but also powerhouses that can save communities money by blunting the impact of flood disasters. A 2024 Wisconsin law geared at preventing such disasters before they happen, inspired by the wetland work in the Marengo River watershed, is going to test that theory.
“Traditionally, the outreach has been, ‘We want to have wetlands out here because they’re good for ducks, frogs and pretty flowers,’” said Tracy Hames, executive director of the Wisconsin Wetlands Association. “What do people care about here? They care about their roads, their bridges, their culverts … how can wetlands help that?”
Bipartisan bill posed wetlands as flood solution
Northern Wisconsin isn’t the only place paying the price for floods. Between 1980 and 2025, the U.S. was struck by 45 billion-dollar flood disasters, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, with a cumulative price tag of nearly $206 billion. Many parts of the vast Mississippi River Basin receive up to eight inches more rain annually than they did 50 years ago, according to a 2022 analysis from Climate Central, a nonprofit organization that analyzes climate science.
Damaging floods are now so common in the states that border the Mississippi River, including Wisconsin, that the issue can’t be ignored, said Haley Gentry, assistant director of the Tulane Institute on Water Resources Law and Policy in New Orleans.
“Even if you don’t agree with certain (regulations) … we absolutely have to find ways to reduce damage,” Gentry said.
Former Wisconsin state Rep. Loren Oldenburg, a Republican who served a flood-prone district in southwest Wisconsin until he lost the seat last year, was interested in how wetlands could help.
Oldenburg joined forces with Republican state Sen. Romaine Quinn, who represents northern Wisconsin and knew of the work in the Marengo River watershed. The lawmakers proposed a grant program for flood-stricken communities to better understand why and where they flood and restore wetlands in areas that need the help most.
Jennifer Western Hauser, policy liaison at the Wisconsin Wetlands Association, met with Democratic and Republican lawmakers to advocate for the bill. She emphasized problems that might get their attention — related to transportation, emergency services, insurance, or conservation — that wetland restoration could solve. She said she got a lot of head-nods as she explained that the cost of continually fixing a washed-out culvert could vanish from storing and slowing floodwaters upstream.
“These are issues that hit all over,” she said. “It’s a relatable problem.”
(MaryJo Gingras/Ashland County Land & Water Conservation Dept.)
The bill passed unanimously and was signed into law by Democratic Gov. Tony Evers in April 2024. Evers and the Republican-controlled Legislature approved $2 million for the program in the state’s most recent budget.
Twenty-three communities applied for the first round of grant funding, which offered two types of grants — one to help assess flood risk, and another grant to help build new wetlands to reduce that risk. Eleven communities were funded, touching most corners of the state, according to Wisconsin Emergency Management, which administered the grants.
Brian Vigue, freshwater policy director for Audubon Great Lakes, said the program shows Wisconsinites have come a long way in how they think about wetlands since 2018, when the state government made it easier for developers to build in them.
There’s an assumption that wetland restoration comes only at the expense of historically lucrative land uses like agriculture or industry, making it hard to gain ground, Vigue said. But when skeptics understand the possible economic benefits, it can change things.
“When you actually find something with the return on investment and can prove that it’s providing these benefits … we were surprised at how readily people that you’d assume wouldn’t embrace a really good, proactive wetland conservation policy, did,” he said.
Private landowners need to see results
About three-quarters of the remaining wetlands in the lower 48 states are on privately owned land, including areas that were targeted for restoration in the Marengo River watershed. That means before any restoration work begins, the landowner must be convinced that the work will help, not hurt them.
For projects like this to work, landowner goals are a priority, said Kyle Magyera, local government outreach specialist at the Wisconsin Wetlands Association, because “they know their property better than anyone else.”
Farmers, for example, can be leery that beefing up wetlands will take land out of production and hurt their bottom line, Magyera said.
In the Marengo watershed, Gingras worked with one landowner who had farmland that wasn’t being used. They created five new wetlands across 10 acres that have already decreased sediment and phosphorus runoff from entering the river. And while there hasn’t been a flood event yet, Gingras expects the water flows to be slowed substantially.
This work goes beyond restoring wetland habitat, Magyera said, it’s about reconnecting waterways. In another project, Magyera worked on a private property where floods carved a new channel in a ravine that funneled the water faster downstream. The property now has log structures that mimic beaver dams to help slow water down and reconnect these systems.
(Mark Hoffman/Milwaukee Journal Sentinel)
Now that the first round of funding has been disbursed in Wisconsin’s grant program, grantees across the state are starting work on their own versions of natural flood control, like that used in Marengo.
In Emilie Park, along the flood-prone East River in Green Bay, a project funded by the program will create 11 acres of new wetlands. That habitat will help store water and serve as an eco-park where community members can stroll through the wetland on boardwalks.
In rural Dane County, about 20 miles from the state capital, a stretch of Black Earth Creek will be reconnected to its floodplain, restoring five and a half acres of wetlands and giving the creek more room to spread out and reduce flood risk. The creek jumped its banks during a near record-breaking 2018 rainstorm, washing out two bridges and causing millions of dollars in damage.
Voluntary program could be of interest elsewhere
Nature-based solutions to flooding have been gaining popularity along the Mississippi River. Wisconsin’s program could serve as a “national model” for how to use wetlands to promote natural flood resilience, Quinn wrote in a 2023 newspaper editorial supporting the bill.
Kyle Rorah, regional director of public policy for the Great Lakes/Atlantic region of Ducks Unlimited, said he’s talking about the Wisconsin grant program to lawmakers in other states in the upper Midwest, and that he sees more appetite for this model than relying on the federal government to protect wetlands.
And Vigue has found that stakeholders in industries like fishing, shipping and recreation are receptive to using wetlands as infrastructure.
But Gentry cautioned that voluntary restoration can only go so far, because it “still allows status-quo development and other related patterns to continue.”
Still, as the federal government backs off of regulation, Gentry said she expects more emphasis on the economic value of wetlands to drive protection.
Some of that is already happening. A 2024 analysis from the Union of Concerned Scientists found that wetlands save Wisconsin and the upper Midwest nearly $23 billion a year that otherwise would be spent combating flooding.
“Every level of government is looking at ways to reduce costs so it doesn’t increase taxes for their constituents,” Gingras said.
John Sabo, director of the ByWater Institute at Tulane University, said as wetlands prove their economic value in reducing flood damage costs, taxpayers will see their value.
“You have to think about (wetlands) as providing services for people,” Sabo said, “if you want to get people on the other side of the aisle behind the idea (of restoring them).”
And although the Wisconsin grant program is small-scale for now, he said if other states bordering the Mississippi River follow its lead, it could reduce flooding across the region.
“If all upstream states start to build upstream wetlands,” he said, “that has downstream impacts.”
YOU MAKE OUR WORK POSSIBLE.
Louisiana Illuminator is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Louisiana Illuminator maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Greg LaRose for questions: info@lailluminator.com.
The post One state framed wetlands as a flooding solution. Could it work elsewhere? appeared first on lailluminator.com
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoFoley man wins Race to the Finish as Kyle Larson gets first win of 2025 Xfinity Series at Bristol
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoFederal appeals court upholds ruling against Alabama panhandling laws
-

 News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days agoTwo dead, 9 injured after shooting at Conway park | What we know
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed3 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed3 days agoDrivers brace for upcoming I-70 construction, slowdowns
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days agoFDA warns about fake Ozempic, how to spot it
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed4 days agoLieutenant governor race heats up with early fundraising surge | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed4 days ago
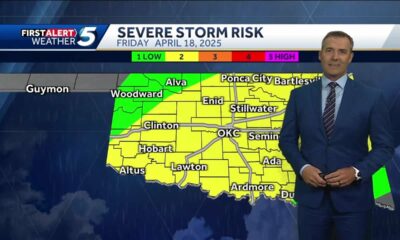
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed4 days agoThursday April 17, 2025 TIMELINE: Severe storms Friday
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days agoAbandoned property causing issues in Pine Lawn, neighbor demands action