Wenhao Wang, Guillaume Ducournau, and Ranjan Singh
Ranjan Singh, University of Notre Dame
Imagine a future where internet connections are not only lightning-fast but also remarkably reliable, even in crowded spaces. This vision is rapidly approaching reality, thanks to new research on terahertz communications technologies. These innovations are set to transform wireless communication, particularly as communications technology advances toward the next generation of networks, 6G.
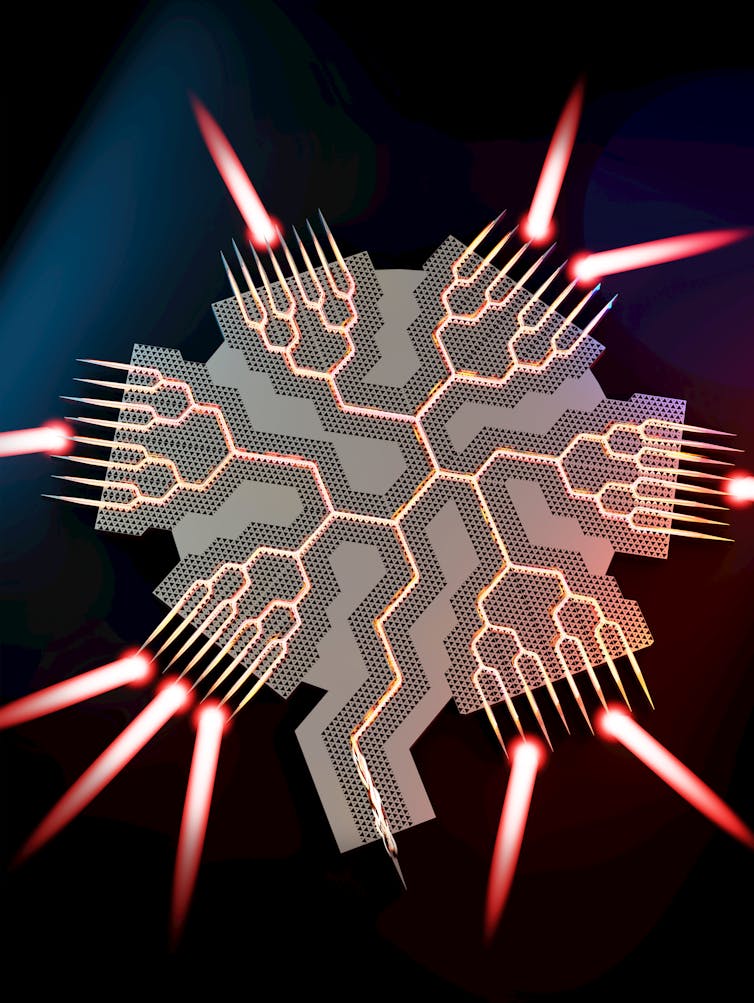
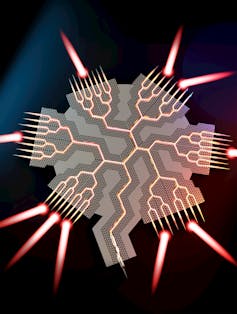
I’m an engineer who focuses on photonics, the study of how light and other electromagnetic waves are generated and detected. In this research, my colleagues and I have developed a silicon topological beamformer chip. Topological refers to physical features in the silicon that help steer terahertz waves, and beamformer refers to the purpose of the chip: forming terahertz waves into directed beams.
Terahertz frequencies are crucial for 6G, which telecommunications companies plan to roll out around 2030. The radio frequency spectrum used by current wireless networks is becoming increasingly congested. Terahertz waves offer a solution by using the relatively unoccupied portion of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and infrared. These higher frequencies can carry massive amounts of data, making them ideal for the data-intensive applications of the future.
Wenhao Wang, Guillaume Ducournau, and Ranjan Singh
Our chip takes a terahertz signal from a single source and splits it into 54 smaller signals, which are then guided through 184 tiny channels with 134 sharp turns. Each beam can transmit and receive data at speeds of 40 to 72 gigabits per second, many times faster than today’s 5G networks.
With the help of artificial intelligence, we designed the chip to have a specific microscopic honeycomb pattern to form lanes for the terahertz waves. The array of channels sends out powerful, focused beams that cover the entire 360 degrees around the chip. This allows a phone or other wireless device anywhere around a Wi-Fi router or other communications device using the chip to receive the high-speed signal. We demonstrated the chip by splitting an input signal of a streaming HD video into four output beams.
Beamformers in wireless networks
Terahertz waves have a shorter range compared with lower-frequency signals used in 4G and 5G networks. Terahertz beamformers address this challenge by precisely directing high-frequency signals to ensure they reach their destination without loss or degradation.
Beamformers are essential for the next generation of wireless communication. Unlike traditional antennas that broadcast signals indiscriminately, beamformers focus signals in specific directions, boosting both efficiency and reliability. Our chip ensures that those beams provide coverage in all directions.
This focused approach not only extends the signal’s range but also improves its quality, even over long distances. Beamformers are likely to be crucial in managing stable connections by reducing interference as the world adds billions of connected devices.
A future with terahertz beamforming
The potential impact of terahertz beamforming chips on everyday life is profound. For example, these chips could make it possible to download a 4K ultrahigh-definition movie in mere seconds compared with 11 minutes over today’s W-Fi, or support immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences without any lag.
Beyond entertainment, they could make real-time holographic communication a reality, where people appear as lifelike holograms. Smart cities could use this technology to seamlessly coordinate traffic systems and emergency responses, while health care could benefit from remote surgeries where doctors control robotic instruments from afar.
The terahertz beamforming chip represents a significant step forward on the path to faster, more reliable wireless communication by overcoming the challenges of high-frequency signal transmission.
Ranjan Singh, Professor of Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.