News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
Cade Cole becomes Louisiana’s newest Supreme Court justice without opposition • Louisiana Illuminator

Cade Cole becomes Louisiana’s newest Supreme Court justice without opposition
by Julie O’Donoghue, Louisiana Illuminator
February 3, 2025
State tax Judge Cade Cole will automatically become the newest member of the Louisiana Supreme Court after being the only candidate to sign up last week for an election to fill the court’s open seat. He will represent District 3, which stretches from Calcasieu Parish to Caddo Parish.
At 42 years old, Cole will be the youngest of the seven justices on the bench. The court’s elected terms last 10 years, but judges are not allowed to run for the office again once they reach the age of 70.
In an interview Sunday, the incoming justice said his swearing-in date hadn’t been scheduled yet.
The Calcasieu Parish resident is a Republican and member of the Federalist Society, a conservative legal organization that is a powerhouse in national GOP politics.
At home in Louisiana, Cole has been a behind-the-scenes operator in state judicial elections, federal judicial appointments, political redistricting and tax policy.
YOU MAKE OUR WORK POSSIBLE.
“We need to defend the constitution,” Cole said of the state Supreme Court’s role in government. “It’s not our job to be a super legislature. … We need to stay in our lane.”
Since 2013, Cole has been Louisiana’s part-time state and local tax judge, where he rules on tax disputes and is one of three members of the Board of State Tax Appeals. Cole was initially appointed to the job by former Gov. Bobby Jindal and then reappointed by former Gov. John Bel Edwards.
The incoming justice also works as an attorney for local municipalities. He is the city attorney for Sulphur and Vinton and was the city magistrate of DeQuincy, where Cole grew up. He also helps cities, parishes and school boards draw their political districts as a contract lawyer.
“He’s one of the brightest individuals I’ve ever known,” said Sulphur Mayor Mike Danahay. “We’re very pleased that he’s been elected.”
A graduate of Tulane University Law School, Cole worked as an assistant district attorney in Calcasieu Parish, where he said he focused on appellate cases.
He received widespread support and endorsements for his supreme court candidacy from several elected officials in the district he will represent on the court.
“I’ve tried to work hard and be fair to everybody, Republicans and Democrats,” he said.
Attorney General Liz Murrill formally endorsed Cole and Gov. Jeff Landry’s political action committee, CAJUN PAC II, donated $5,000 to his campaign.
Calcasieu Parish District Attorney Stephen Dwight also said he happily supported Cole in the race.
“He’s well respected by both sides [of the political spectrum],” said Dwight, a Republican. “I think he will hit the ground running.”
Cole is the second justice to join the Louisiana Supreme Court since its political boundaries were redrawn last spring for the first time in over 30 years. The new district lines moved the base of power of his seat from Shreveport to Lake Charles, where Cole lives and works.
When asked if he helped draw the new Supreme Court map that helped get him elected, Cole replied “not really” and said the map was the product of the justices’ own proposal and changes state lawmakers made.
“The court drew it, and the legislature changed it in a lot of material respects,” he said. “It’s fair to say that I watched it like many other people.”
The latest map created a new majority-Black district and led to the election of the second Black justice to the seven-person court. John Michael Guidry, a longtime state appellate judge and former Democratic state lawmaker, was sworn into that seat last month.
More than 30% of Louisiana’s population identifies as Black, and Cole said he was pleased the Supreme Court political districts were more “reflective of the state population as a whole.”
Cole replaces Justice James Genovese, who stepped down in July after he was picked as the new president of Northwestern State University with the backing of the governor. At the time, Genovese’s job swap raised questions about whether Landry was trying to stack the court with political allies.
Cole said he does not have a personal relationship with the governor, though the two are both active in Republican circles.
Cole also served as a member of the Northwestern State presidential search committee that eventually recommended Genovese for the higher education job.
GET THE MORNING HEADLINES.
Cole said he was picked for the presidential search committee not because of his interest in the Supreme Court seat but because he is considered a state expert in financing college athletics. He helped set up a collective for McNeese State University that leverages name image and likeness deals for college athlete recruitment.
“I’ve been involved in other presidential searches for the UL System,” he said.
Since Genovese stepped down, retired Justice Jeannette Theriot Knoll has been filling in on the Supreme Court in his absence. Cole worked as a law clerk for Knoll at the Supreme Court early in his legal career and said he expects the transition between the two judges to be smooth.
Louisiana Illuminator is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Louisiana Illuminator maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Greg LaRose for questions: info@lailluminator.com.
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
One state framed wetlands as a flooding solution. Could it work elsewhere?

by Madeline Heim and Caitlin Looby, Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, Louisiana Illuminator
April 19, 2025
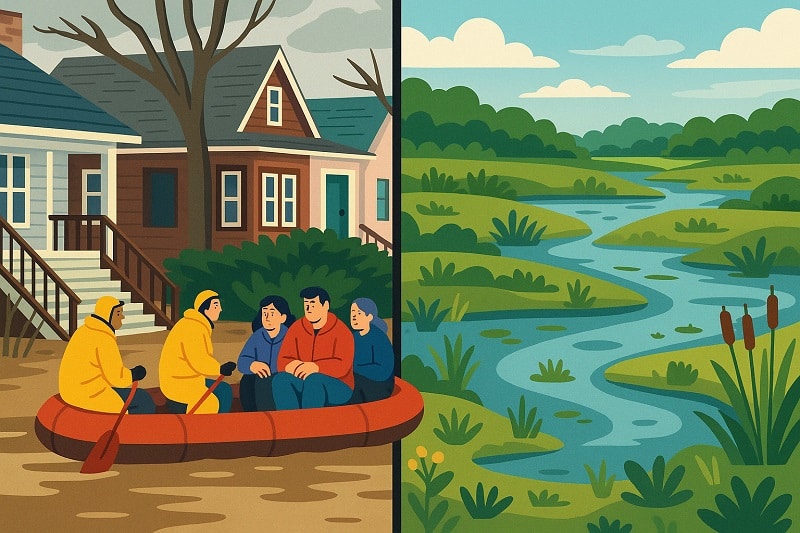
ASHLAND, Wis. — In less than 10 years, three catastrophic floods ravaged northwestern Wisconsin and changed the way people think about water.
The most severe, in July 2016, slammed Ashland with up to 10 inches of rain in less than a day — a month’s worth of rain fell in just two hours. As rivers swelled to record highs, major highways broke into pieces and culverts washed away. It took months for roads to reopen, with more than $41 million in damage across seven counties.
The Marengo River, which winds through forests and farmland before meeting the Bad River that flows into Lake Superior, was hit hard during these historic deluges. Centuries earlier, the upper watershed would have held onto that water, but logging and agriculture left the river disconnected from its floodplain, giving the water nowhere safe to go.
Today, the Marengo River stands as an example of a new kind of solution. Following the record floods, state leaders invested in opening up floodplains and restoring wetlands to relieve flooding. As the need to adapt to disasters grows more urgent, the Marengo River serves as an example that there’s a cheaper way to do so: using wetlands.
“We can’t change the weather or the patterns… but we can better prepare ourselves,” said MaryJo Gingras, Ashland County’s conservationist.
Wetlands once provided more natural flood storage across Wisconsin and the Mississippi River Basin, soaking up water like sponges so it couldn’t rush further downstream. But about half of the country’s wetlands have been drained and filled for agriculture and development, and they continue to be destroyed, even as climate change intensifies floods.
As the federal government disposes of rules to protect wetlands, environmental advocates want to rewrite the ecosystem’s narrative to convince more people that restoration is worth it.
Wetlands aren’t just pretty places, advocates argue, but also powerhouses that can save communities money by blunting the impact of flood disasters. A 2024 Wisconsin law geared at preventing such disasters before they happen, inspired by the wetland work in the Marengo River watershed, is going to test that theory.
“Traditionally, the outreach has been, ‘We want to have wetlands out here because they’re good for ducks, frogs and pretty flowers,’” said Tracy Hames, executive director of the Wisconsin Wetlands Association. “What do people care about here? They care about their roads, their bridges, their culverts … how can wetlands help that?”
Bipartisan bill posed wetlands as flood solution
Northern Wisconsin isn’t the only place paying the price for floods. Between 1980 and 2025, the U.S. was struck by 45 billion-dollar flood disasters, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, with a cumulative price tag of nearly $206 billion. Many parts of the vast Mississippi River Basin receive up to eight inches more rain annually than they did 50 years ago, according to a 2022 analysis from Climate Central, a nonprofit organization that analyzes climate science.
Damaging floods are now so common in the states that border the Mississippi River, including Wisconsin, that the issue can’t be ignored, said Haley Gentry, assistant director of the Tulane Institute on Water Resources Law and Policy in New Orleans.
“Even if you don’t agree with certain (regulations) … we absolutely have to find ways to reduce damage,” Gentry said.
Former Wisconsin state Rep. Loren Oldenburg, a Republican who served a flood-prone district in southwest Wisconsin until he lost the seat last year, was interested in how wetlands could help.
Oldenburg joined forces with Republican state Sen. Romaine Quinn, who represents northern Wisconsin and knew of the work in the Marengo River watershed. The lawmakers proposed a grant program for flood-stricken communities to better understand why and where they flood and restore wetlands in areas that need the help most.
Jennifer Western Hauser, policy liaison at the Wisconsin Wetlands Association, met with Democratic and Republican lawmakers to advocate for the bill. She emphasized problems that might get their attention — related to transportation, emergency services, insurance, or conservation — that wetland restoration could solve. She said she got a lot of head-nods as she explained that the cost of continually fixing a washed-out culvert could vanish from storing and slowing floodwaters upstream.
“These are issues that hit all over,” she said. “It’s a relatable problem.”
(MaryJo Gingras/Ashland County Land & Water Conservation Dept.)
The bill passed unanimously and was signed into law by Democratic Gov. Tony Evers in April 2024. Evers and the Republican-controlled Legislature approved $2 million for the program in the state’s most recent budget.
Twenty-three communities applied for the first round of grant funding, which offered two types of grants — one to help assess flood risk, and another grant to help build new wetlands to reduce that risk. Eleven communities were funded, touching most corners of the state, according to Wisconsin Emergency Management, which administered the grants.
Brian Vigue, freshwater policy director for Audubon Great Lakes, said the program shows Wisconsinites have come a long way in how they think about wetlands since 2018, when the state government made it easier for developers to build in them.
There’s an assumption that wetland restoration comes only at the expense of historically lucrative land uses like agriculture or industry, making it hard to gain ground, Vigue said. But when skeptics understand the possible economic benefits, it can change things.
“When you actually find something with the return on investment and can prove that it’s providing these benefits … we were surprised at how readily people that you’d assume wouldn’t embrace a really good, proactive wetland conservation policy, did,” he said.
Private landowners need to see results
About three-quarters of the remaining wetlands in the lower 48 states are on privately owned land, including areas that were targeted for restoration in the Marengo River watershed. That means before any restoration work begins, the landowner must be convinced that the work will help, not hurt them.
For projects like this to work, landowner goals are a priority, said Kyle Magyera, local government outreach specialist at the Wisconsin Wetlands Association, because “they know their property better than anyone else.”
Farmers, for example, can be leery that beefing up wetlands will take land out of production and hurt their bottom line, Magyera said.
In the Marengo watershed, Gingras worked with one landowner who had farmland that wasn’t being used. They created five new wetlands across 10 acres that have already decreased sediment and phosphorus runoff from entering the river. And while there hasn’t been a flood event yet, Gingras expects the water flows to be slowed substantially.
This work goes beyond restoring wetland habitat, Magyera said, it’s about reconnecting waterways. In another project, Magyera worked on a private property where floods carved a new channel in a ravine that funneled the water faster downstream. The property now has log structures that mimic beaver dams to help slow water down and reconnect these systems.
(Mark Hoffman/Milwaukee Journal Sentinel)
Now that the first round of funding has been disbursed in Wisconsin’s grant program, grantees across the state are starting work on their own versions of natural flood control, like that used in Marengo.
In Emilie Park, along the flood-prone East River in Green Bay, a project funded by the program will create 11 acres of new wetlands. That habitat will help store water and serve as an eco-park where community members can stroll through the wetland on boardwalks.
In rural Dane County, about 20 miles from the state capital, a stretch of Black Earth Creek will be reconnected to its floodplain, restoring five and a half acres of wetlands and giving the creek more room to spread out and reduce flood risk. The creek jumped its banks during a near record-breaking 2018 rainstorm, washing out two bridges and causing millions of dollars in damage.
Voluntary program could be of interest elsewhere
Nature-based solutions to flooding have been gaining popularity along the Mississippi River. Wisconsin’s program could serve as a “national model” for how to use wetlands to promote natural flood resilience, Quinn wrote in a 2023 newspaper editorial supporting the bill.
Kyle Rorah, regional director of public policy for the Great Lakes/Atlantic region of Ducks Unlimited, said he’s talking about the Wisconsin grant program to lawmakers in other states in the upper Midwest, and that he sees more appetite for this model than relying on the federal government to protect wetlands.
And Vigue has found that stakeholders in industries like fishing, shipping and recreation are receptive to using wetlands as infrastructure.
But Gentry cautioned that voluntary restoration can only go so far, because it “still allows status-quo development and other related patterns to continue.”
Still, as the federal government backs off of regulation, Gentry said she expects more emphasis on the economic value of wetlands to drive protection.
Some of that is already happening. A 2024 analysis from the Union of Concerned Scientists found that wetlands save Wisconsin and the upper Midwest nearly $23 billion a year that otherwise would be spent combating flooding.
“Every level of government is looking at ways to reduce costs so it doesn’t increase taxes for their constituents,” Gingras said.
John Sabo, director of the ByWater Institute at Tulane University, said as wetlands prove their economic value in reducing flood damage costs, taxpayers will see their value.
“You have to think about (wetlands) as providing services for people,” Sabo said, “if you want to get people on the other side of the aisle behind the idea (of restoring them).”
And although the Wisconsin grant program is small-scale for now, he said if other states bordering the Mississippi River follow its lead, it could reduce flooding across the region.
“If all upstream states start to build upstream wetlands,” he said, “that has downstream impacts.”
YOU MAKE OUR WORK POSSIBLE.
Louisiana Illuminator is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Louisiana Illuminator maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Greg LaRose for questions: info@lailluminator.com.
The post One state framed wetlands as a flooding solution. Could it work elsewhere? appeared first on lailluminator.com
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
Easter Weekend: Muggy, warm, and windy

SUMMARY: Easter Weekend will be warm, muggy, and breezy, with mostly cloudy skies and temperatures in the low 80s. Current conditions are in the low 70s, making it a sticky day for events like the Crescent City Classic. While there’s a slight chance of rain on Sunday, most of the day will remain dry. Winds from the southeast could gust near 30 mph. Next week, a front will bring increased rain chances and storms starting Monday, with unsettled conditions continuing into Tuesday and Wednesday. Despite this, warm temperatures in the 80s will persist throughout the week.

Easter Weekend looks very nice! It will be hot, humid, and windy with high temperatures in the lower 80s both afternoons. More clouds will be around with some breaks
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed
Vicente Fernandez and Freddy Fender join National Recording Registry

SUMMARY: This year, Vicente Fernandez’s “El Rey” and Freddy Fender’s “Before the Next Teardrop Falls” were inducted into the National Recording Registry, alongside Lin-Manuel Miranda’s *Hamilton* album. Congressman Joaquin Castro has championed the inclusion of more Latino artists in the registry, noting that Latino representation is only 5%. Over the last three years, with input from constituents, Castro has successfully nominated 30 songs and albums, including iconic Latino tracks. He advocates for more Latino contributions to be recognized, including Selena’s work. Castro will continue gathering nominations for 2026, aiming to better reflect Latino cultural influence in the registry.

Each year since 2000, the Library of Congress has selected influential songs and albums to be preserved in the National Recording Registry. This year, three Latino artists were inducted — two of them with deep roots in Latino culture and South Texas.
-

 Mississippi Today7 days ago
Mississippi Today7 days agoLawmakers used to fail passing a budget over policy disagreement. This year, they failed over childish bickering.
-

 Mississippi Today7 days ago
Mississippi Today7 days agoOn this day in 1873, La. courthouse scene of racial carnage
-

 Local News7 days ago
Local News7 days agoSouthern Miss Professor Inducted into U.S. Hydrographer Hall of Fame
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days agoFoley man wins Race to the Finish as Kyle Larson gets first win of 2025 Xfinity Series at Bristol
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days agoFederal appeals court upholds ruling against Alabama panhandling laws
-

 News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days ago1 dead after 7 people shot during large gathering at Crosby gas station, HCSO says
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days agoJacksonville University only school with 2 finalist teams in NASA’s 2025 Human Lander Challenge
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed7 days agoInsects as food? ‘We are largely ignoring the largest group of organisms on earth’