Raul Arboleda/AFP via Getty Images
Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com.
Why do dogs love to play with trash? – Sarah G٫ age 11٫ Seguin٫ Texas
When I think about why dogs do something, I try to imagine what motivates them. What does a dog get out of playing with trash? As a veterinarian and a professor who teaches college students about companion animals, I believe there’s an easy answer: Garbage smells delicious and tastes good to dogs.
Dogs have an amazing sense of smell. They have 300 million receptors for smell in their noses, while humans have only 6 million. People can make use of this sniffing ability to train dogs to detect illegal drugs, explosives and endangered species, and to help locate people lost in the woods.
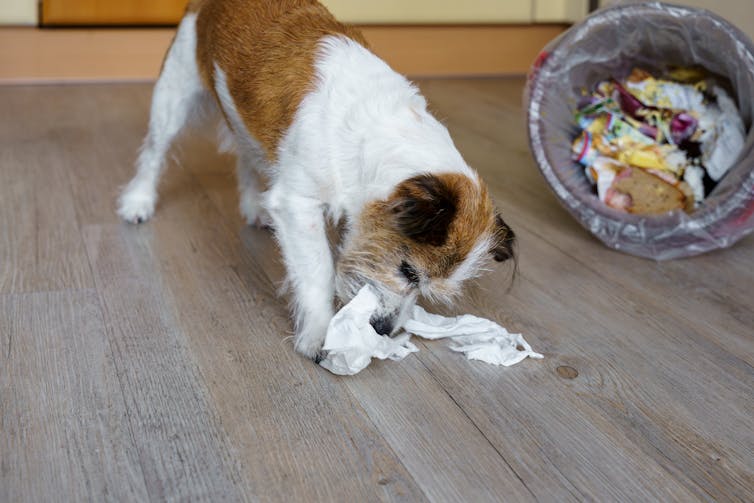
While you might not like how your trash smells, to your dog it is an appealing buffet brimming with apple cores, banana peels, meat scraps and stale bread. Even used napkins and paper towels are tempting to dogs, when they are smeared with and carry the smell of yesterday’s lunch.
Because dogs can find trace amounts of explosives or a person buried under 6 feet (1.8 meters) of snow after an avalanche, they are certainly capable of locating last night’s pizza crust and chicken bones in the kitchen garbage can.
Sometimes it’s hard to see what the attraction is. My Australian cattle dog mix, Sparky, loves to eat used tissues – gross, right?
Even empty cans smell inviting to dogs. Trash cans in kitchens and bathrooms are often at their nose level, too, making for easy access. Add to that the fact that if the dog got into the garbage once and found something tasty, they will likely keep searching with the hope of being rewarded again.

Raul Arboleda/AFP via Getty Images
Thrill of the hunt
Searching and digging around for food is natural for dogs because it provides some of the thrill of the hunt, even if they just ate and aren’t hungry.
The most successful prehistoric dogs ate the bones and scraps that humans left behind more than 10,000 years ago. Hanging around humans and their garbage was a way they could get plenty to eat. Even your pup today has some of those same old searching instincts.
While our trash has changed from the days of hunting and gathering, the discarded paper napkins, plastic wrappers and food scraps we throw away all still smell like food to dogs. And this scavenging behavior is still hardwired in our pampered pets. Although it may look to us like they’re playing, our dogs’ sniffing out and tearing things up from the trash and tossing them around mimics what their ancestors did when they tugged on and tore up an animal carcass they had found.
Many people take advantage of this instinct and use “snuffle mats” – cloth or paper where food is hidden – or puzzle feeding toys to keep their pups’ minds active. Having to hunt for and find their food helps them use their noses and sharpens their skills.
Annoying or even dangerous
While spreading trash all over the home may be natural for dogs, cleaning it up is no fun for the people they live with. And if your dog pokes its nose in a garbage can, it could be in danger. Eating plastic bags, string, chicken bones, chemicals or rotten food can cause blockages, diarrhea and poisoning. Commonly referred to as “garbage gut,” garbage poisoning can be life-threatening.
I’ve treated dogs that cut their tongues and mouths on cans or broken glass. I once performed surgery to remove a corncob from the intestines of a dog that had eaten it a month earlier. He was certainly relieved when he woke up.
How can you keep your dogs away from the trash?
It can be hard to train a dog to leave garbage alone, especially if they have found a tasty morsel or two by raiding the trash can in the past. I recommend that you invest in a garbage can with a lid closed by a latch that they can’t open. If that fails, you can put garbage – especially food scraps – out of reach in a closet, cupboard or behind a closed door.
My trash cans are all behind closed doors, and the bathroom doors are always shut, which also keeps my cat, Penny, from unrolling the toilet tissue. But that’s another story. Our kitchen trash is in a latched cupboard.
No one knows exactly what goes through dogs’ minds. And yet looking at what motivates your canine companion and how dog behaviors have evolved may help explain why these animals do the things they do.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.![]()
Nancy Dreschel, Associate Teaching Professor of Small Animal Science, Penn State
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.