What you expect can influence what you think you see.
Todd M. Freeberg, University of Tennessee
Animal behavior research relies on careful observation of animals. Researchers might spend months in a jungle habitat watching tropical birds mate and raise their young. They might track the rates of physical contact in cattle herds of different densities. Or they could record the sounds whales make as they migrate through the ocean.
Animal behavior research can provide fundamental insights into the natural processes that affect ecosystems around the globe, as well as into our own human minds and behavior.
I study animal behavior – and also the research reported by scientists in my field. One of the challenges of this kind of science is making sure our own assumptions don’t influence what we think we see in animal subjects. Like all people, how scientists see the world is shaped by biases and expectations, which can affect how data is recorded and reported. For instance, scientists who live in a society with strict gender roles for women and men might interpret things they see animals doing as reflecting those same divisions.
The scientific process corrects for such mistakes over time, but scientists have quicker methods at their disposal to minimize potential observer bias. Animal behavior scientists haven’t always used these methods – but that’s changing. A new study confirms that, over the past decade, studies increasingly adhere to the rigorous best practices that can minimize potential biases in animal behavior research.
Biases and self-fulfilling prophecies
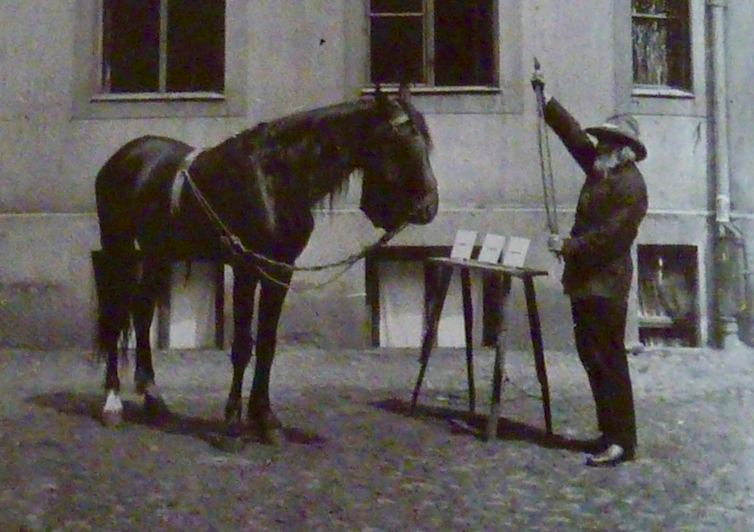
A German horse named Clever Hans is widely known in the history of animal behavior as a classic example of unconscious bias leading to a false result.
Around the turn of the 20th century, Clever Hans was purported to be able to do math. For example, in response to his owner’s prompt “3 + 5,” Clever Hans would tap his hoof eight times. His owner would then reward him with his favorite vegetables. Initial observers reported that the horse’s abilities were legitimate and that his owner was not being deceptive.
However, careful analysis by a young scientist named Oskar Pfungst revealed that if the horse could not see his owner, he couldn’t answer correctly. So while Clever Hans was not good at math, he was incredibly good at observing his owner’s subtle and unconscious cues that gave the math answers away.
In the 1960s, researchers asked human study participants to code the learning ability of rats. Participants were told their rats had been artificially selected over many generations to be either “bright” or “dull” learners. Over several weeks, the participants ran their rats through eight different learning experiments.
In seven out of the eight experiments, the human participants ranked the “bright” rats as being better learners than the “dull” rats when, in reality, the researchers had randomly picked rats from their breeding colony. Bias led the human participants to see what they thought they should see.
Eliminating bias
Given the clear potential for human biases to skew scientific results, textbooks on animal behavior research methods from the 1980s onward have implored researchers to verify their work using at least one of two commonsense methods.
One is making sure the researcher observing the behavior does not know if the subject comes from one study group or the other. For example, a researcher would measure a cricket’s behavior without knowing if it came from the experimental or control group.
The other best practice is utilizing a second researcher, who has fresh eyes and no knowledge of the data, to observe the behavior and code the data. For example, while analyzing a video file, I count chickadees taking seeds from a feeder 15 times. Later, a second independent observer counts the same number.
Yet these methods to minimize possible biases are often not employed by researchers in animal behavior, perhaps because these best practices take more time and effort.
In 2012, my colleagues and I reviewed nearly 1,000 articles published in five leading animal behavior journals between 1970 and 2010 to see how many reported these methods to minimize potential bias. Less than 10% did so. By contrast, the journal Infancy, which focuses on human infant behavior, was far more rigorous: Over 80% of its articles reported using methods to avoid bias.
It’s a problem not just confined to my field. A 2015 review of published articles in the life sciences found that blind protocols are uncommon. It also found that studies using blind methods detected smaller differences between the key groups being observed compared to studies that didn’t use blind methods, suggesting potential biases led to more notable results.
In the years after we published our article, it was cited regularly and we wondered if there had been any improvement in the field. So, we recently reviewed 40 articles from each of the same five journals for the year 2020.
We found the rate of papers that reported controlling for bias improved in all five journals, from under 10% in our 2012 article to just over 50% in our new review. These rates of reporting still lag behind the journal Infancy, however, which was 95% in 2020.
All in all, things are looking up, but the animal behavior field can still do better. Practically, with increasingly more portable and affordable audio and video recording technology, it’s getting easier to carry out methods that minimize potential biases. The more the field of animal behavior sticks with these best practices, the stronger the foundation of knowledge and public trust in this science will become.![]()
Todd M. Freeberg, Professor and Associate Head of Psychology, University of Tennessee
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.