A rose by any other name would not smell as sweet to a robot.
Ambuj Tewari, University of Michigan
Over 100 years ago, Alexander Graham Bell asked the readers of National Geographic to do something bold and fresh – “to found a new science.” He pointed out that sciences based on the measurements of sound and light already existed. But there was no science of odor. Bell asked his readers to “measure a smell.”
Today, smartphones in most people’s pockets provide impressive built-in capabilities based on the sciences of sound and light: voice assistants, facial recognition and photo enhancement. The science of odor does not offer anything comparable. But that situation is changing, as advances in machine olfaction, also called “digitized smell,” are finally answering Bell’s call to action.
Research on machine olfaction faces a formidable challenge due to the complexity of the human sense of smell. Whereas human vision mainly relies on receptor cells in the retina – rods and three types of cones – smell is experienced through about 400 types of receptor cells in the nose.
Machine olfaction starts with sensors that detect and identify molecules in the air. These sensors serve the same purpose as the receptors in your nose.
But to be useful to people, machine olfaction needs to go a step further. The system needs to know what a certain molecule or a set of molecules smells like to a human. For that, machine olfaction needs machine learning.
Applying machine learning to smells
Machine learning, and particularly a kind of machine learning called deep learning, is at the core of remarkable advances such as voice assistants and facial recognition apps.
Machine learning is also key to digitizing smells because it can learn to map the molecular structure of an odor-causing compound to textual odor descriptors. The machine learning model learns the words humans tend to use – for example, “sweet” and “dessert” – to describe what they experience when they encounter specific odor-causing compounds, such as vanillin.
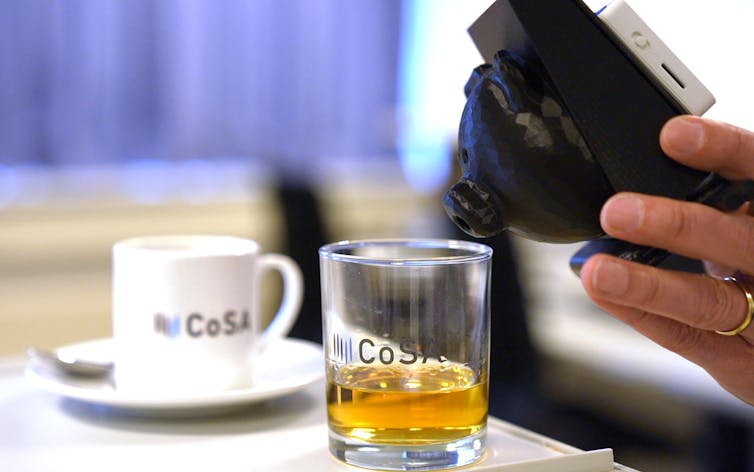
A university research prototype artificial nose can distinguish between coffee and whiskey.
However, machine learning needs large datasets. The web has an unimaginably huge amount of audio, image and video content that can be used to train artificial intelligence systems that recognize sounds and pictures. But machine olfaction has long faced a data shortage problem, partly because most people cannot verbally describe smells as effortlessly and recognizably as they can describe sights and sounds. Without access to web-scale datasets, researchers weren’t able to train really powerful machine learning models.
However, things started to change in 2015 when researchers launched the DREAM Olfaction Prediction Challenge. The competition released data collected by Andreas Keller and Leslie Vosshall, biologists who study olfaction, and invited teams from around the world to submit their machine learning models. The models had to predict odor labels like “sweet,” “flower” or “fruit” for odor-causing compounds based on their molecular structure.
The top performing models were published in a paper in the journal Science in 2017. A classic machine learning technique called random forest, which combines the output of multiple decision tree flow charts, turned out to be the winner.
I am a machine learning researcher with a longstanding interest in applying machine learning to chemistry and psychiatry. The DREAM challenge piqued my interest. I also felt a personal connection to olfaction. My family traces its roots to the small town of Kannauj in northern India, which is India’s perfume capital. Moreover, my father is a chemist who spent most of his career analyzing geological samples. Machine olfaction thus offered an irresistible opportunity at the intersection of perfumery, culture, chemistry and machine learning.
Progress in machine olfaction started picking up steam after the DREAM challenge concluded. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many cases of smell blindness, or anosmia, were reported. The sense of smell, which usually takes a back seat, rose in public consciousness. Additionally, a research project, the Pyrfume Project, made more and larger datasets publicly available.
Smelling deeply
By 2019, the largest datasets had grown from less than 500 molecules in the DREAM challenge to about 5,000 molecules. A Google Research team led by Alexander Wiltschko was finally able to bring the deep learning revolution to machine olfaction. Their model, based on a type of deep learning called graph neural networks, established state-of-the-art results in machine olfaction. Wiltschko is now the founder and CEO of Osmo, whose mission is “giving computers a sense of smell.”
Recently, Wiltschko and his team used a graph neural network to create a “principal odor map,” where perceptually similar odors are placed closer to each other than dissimilar ones. This was not easy: Small changes in molecular structure can lead to large changes in olfactory perception. Conversely, two molecules with very different molecular structures can nonetheless smell almost the same.
Such progress in cracking the code of smell is not only intellectually exciting but also has highly promising applications, including personalized perfumes and fragrances, better insect repellents, novel chemical sensors, early detection of disease, and more realistic augmented reality experiences. The future of machine olfaction looks bright. It also promises to smell good.![]()
Ambuj Tewari, Professor of Statistics, University of Michigan
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
























































