Erick Bravo/IODP
Molly Colleen McCanta, University of Tennessee
“Core on deck!”
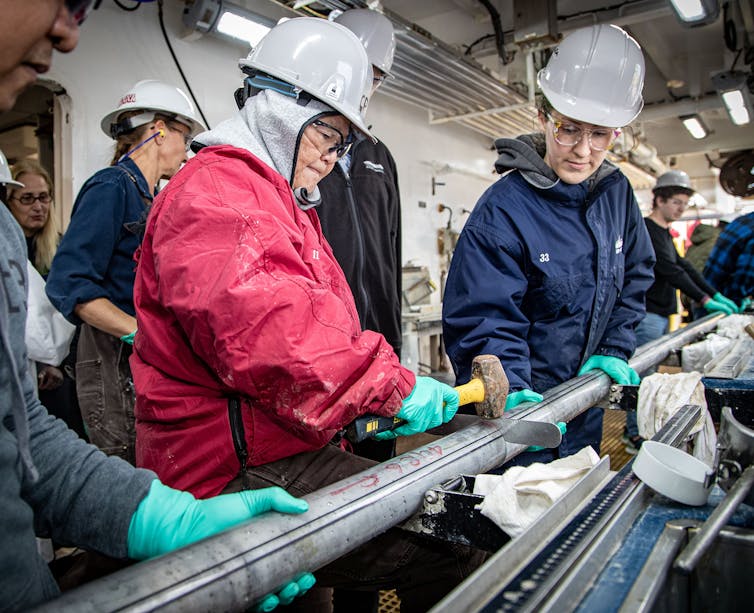
For two months, whenever I heard that cry, I would run up to the deck of the JOIDES Resolution to watch the crew pull up a 30-foot (10-meter) cylindrical tube filled with layered, multicolored rock and sediment drilled from the seafloor beneath our ship.

Erick Bravo/IODP
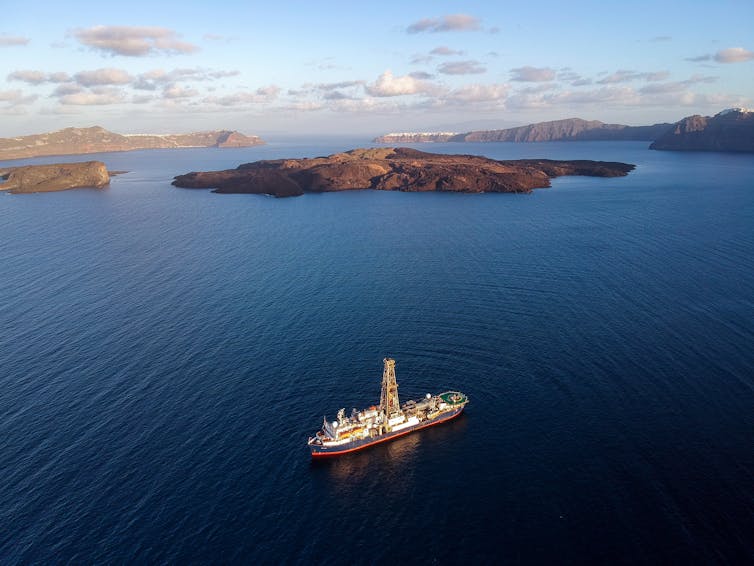
In the winter of 2022, I spent two months cruising the south Aegean Sea on board the International Ocean Discovery Program’s JOIDES Resolution as part of IODP Expedition 398. My geologist colleagues and I used this former oil exploration ship to drill deep into the seafloor and reveal the volcanic history of the area off the coast of Santorini, Greece.
As a scientist who studies the chemistry of volcanic rocks, I use my expertise to correlate volcanic sediments to the eruption that caused them and to understand the conditions that magma experienced both at depth underneath a volcano and during an eruption.
Our expedition’s drilling of the seafloor revealed a massive but previously unknown volcanic eruption that took place more than 500,000 years ago. This discovery expands our understanding of the volcanic activity in the chain of volcanoes comprising the South Aegean Volcanic Arc, which will allow for a more accurate hazard analysis of this region.
Building a more complete volcanic history
Archaeologists have long been fascinated with the late Bronze Age eruption of Santorini around 1600 BCE. This eruption is associated with the decline of the Minoan civilization on the nearby island of Crete. Geologists also have significant interest in the region, due to the volatility of the volcanic and seismic activity in this area that is home to about 15,000 residents and attracts around 2 million tourists per year.
Although there’s significant on-land documentation of the Santorini volcano, scientists know that this record is incomplete. On land, erosion, vegetation and additional eruptive events often cover or obscure older volcanic deposits, resulting in a fragmentary history. The deep-sea drilling enabled by the IODP’s JOIDES Resolution gives researchers access to a geologic record rarely preserved on land.
Following a volcanic eruption, pyroclastic materials – pieces of rock and ash formed during the eruption – settle through the water column to collect on the seafloor. There, clays and biological material, such as the shells of tiny marine organisms, rain down continuously, capping the volcanic rock deposits. This process preserves a record of an individual eruption as a single layer. Layers build with time, with each successive volcanic event creating a near-continuous chronologic record of the volcanic history of the region.
Expedition 398’s mission was to access this deep-sea record in order to document the extensive history of eruptions in each area of concentrated volcanic activity.
IODP Expedition 398
IODP Expedition 398 collected drill cores to better understand the volcanic history and recurrence interval of the Santorini, Christiana and Kolumbo volcanoes in this region. The JOIDES Resolution crew drilled 12 sites to a maximum depth of 2,950 feet (900 meters) below the seafloor. We recovered more than 11,000 feet (3,356 meters) of total core over 780 cores.
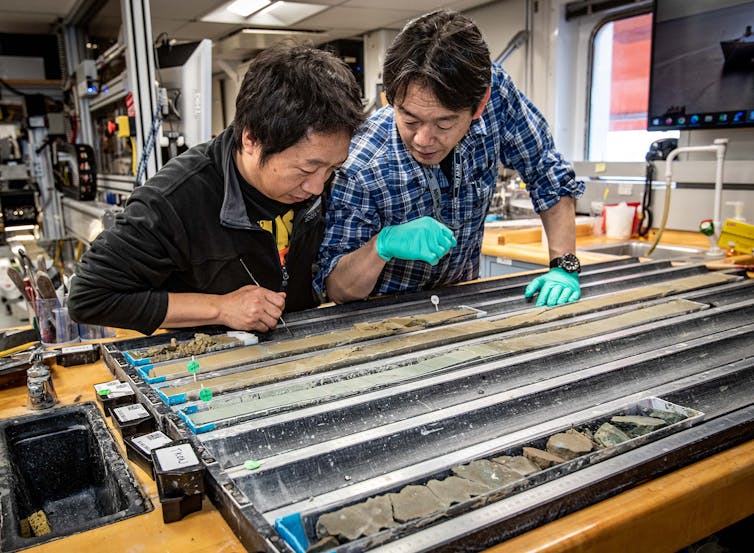
As technicians cut the core into 4½-foot (1½-meter) sections, scientists would gather to see what material had been recovered. After bringing the cores to surface pressure, the team would split them lengthwise, photograph them, analyze them for physical properties such as magnetic susceptibility, and describe the material. Core describers measure and record the geologic composition of each rocky unit contained within.

Erick Bravo/IODP
As the geochemistry lab lead, I took small samples of multiple layers of volcanic rock and ash to dissolve into solution and analyze for their trace element composition. During an eruption, magma crystallizes and mixes with elements in the water and rock it comes into contact with. The resulting chemical changes in the magma are unique to the conditions of that particular eruption. So once I figure out the chemical composition of the deposit samples, I can fingerprint their volcanic origin.
Our discovery: The Archaeos Tuff
During the expedition, our group of researchers discovered a thick, white pumice layer at multiple sites, in several different basins. Shipboard biostratigraphy dated each occurrence of the layer to the same age: between 510,000 and 530,000 years ago. Geochemical correlations suggested the composition was the same across drill holes as well.
Finding the same layer across these basins allows our research team to model how big the eruption that caused it might have been. We used seismic data collected during the expedition to determine that the bulk volume of the volcanic sediment is about 21 cubic miles (90 cubic kilometers), with thicknesses up to 490 feet (150 meters) in some places. In addition, we determined that this layer of volcanic rock was spread over 1,100 square miles (3,000 square kilometers) of this region in the southern Aegean Sea.

Thomas Ronge/IODP
Our team named this deposit the Archaeos Tuff, from the Greek word archea for ancient. The name reflects the rock’s Greek origin, as well as the fact that it was significantly older than much of the volcanic activity we know about on land.
Based on the Archaeos Tuff’s characteristics, we can understand the nature of the volcanic eruption that formed it. Its thickness and distribution over a wide area suggest that the Archaeos Tuff is the result of a single, high-intensity eruption. The numerous vesicles, or tiny holes, in the rock indicate that a large amount of gas was released at the same time as the liquid magma. These little gas bubbles paint a picture of a powerful eruption in which a great deal of volatile gas was released quite quickly.
Yet despite its evident size and ferocity, this eruption did not correlate with any previously known on-land deposits or large eruptions. The relative lack of on-land material suggests a mainly submarine eruption. Once we knew what we were looking for, our team was able to match our newly discovered deep-sea layer of volcanic sediment to a few small, previously uncorrelated on-land deposits on Santorini, Christiana and Anafi islands. The presence of these deposits indicates some breach of the sea surface during the eruption, which again fits with our picture of an energetic eruption.
Further study of the Archaeos Tuff’s composition and age confirmed the unique nature of the rock deposit left by this eruption. Based on the data we collected, our team believes the Archaeos Tuff is the result of an eruption six times bigger than the Bronze Age Minoan eruption, leaving behind rock deposits 30 times thicker. The presence of such a large volcanic deposit tells us that the South Aegean Volcanic Arc is more capable of producing large submarine volcanic eruptions than scientists previously recognized.
Identifying the Archaeos Tuff expands what we know about volcanic processes in the south Aegean Sea. It suggests a greater propensity for hazardous submarine volcanism than previously realized – and that officials need to reevaluate volcanic hazards to the surrounding population.![]()
Molly Colleen McCanta, Associate Professor of Petrology and Planetary Geoscience, University of Tennessee
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.