Hormonal contraceptives have functions that go beyond just birth control.
Natalie C. Tronson, University of Michigan
More than 85% of women – and more than 300 million people worldwide at any given time – use hormonal contraceptives for at least five years of their life. Although primarily taken for birth control, many people also use hormonal contraceptives to manage a variety of symptoms related to menstruation, from cramps and acne to mood swings.
For up to 10% of women, however, hormone contraceptives can increase their risk of depression. Hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, are crucial for brain health. So, how does modifying hormone levels with hormone contraceptives affect mental health?
I am a researcher studying the neuroscience of stress and emotion-related processes. I also study sex differences in vulnerability and resilience to mental health disorders. Understanding how hormone contraceptives affect mood can help researchers predict who will experience positive or negative effects.
How do hormone contraceptives work?
In the U.S. and other western countries, the most common form of hormonal contraceptive is “the pill” – a combination of a synthetic estrogen and a synthetic progesterone, two hormones involved in regulation of the menstrual cycle, ovulation and pregnancy. Estrogen coordinates the timed release of other hormones, and progesterone maintains a pregnancy.
This may seem counterintuitive – why do naturally occurring hormones required for pregnancy also prevent pregnancy? And why does taking a hormone reduce the levels of that same hormone?
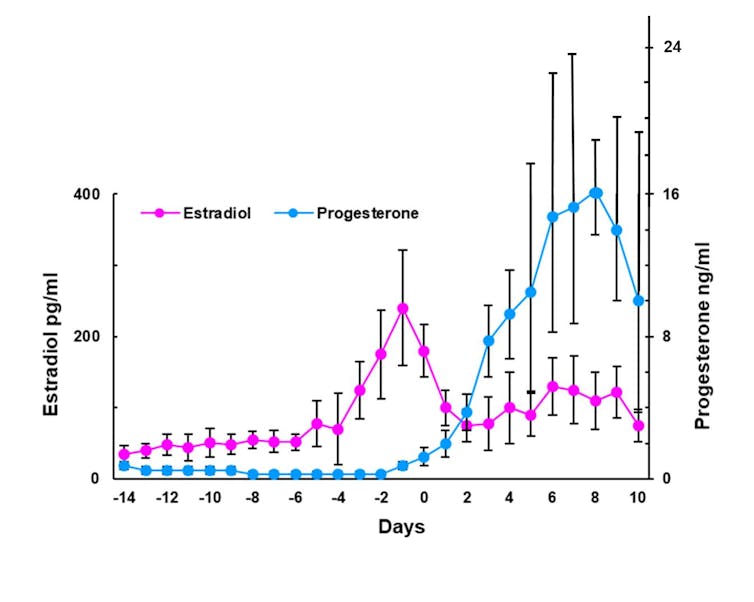
When estrogen and progesterone reach a certain threshold level, the body decreases their production.
Dharani Kalidasan/R.I. McLachlan et al. 1987 via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Hormone cycles are tightly controlled by the hormones themselves. When progesterone levels increase, it activates processes in cells that shut off production of more progesterone. This is called a negative feedback loop.
Estrogen and progesterone from the daily pill, or other common forms of contraceptives such as implants or vaginal rings, cause the body to decrease production of those hormones, reducing them to levels observed outside the fertile window of the cycle. This disrupts the tightly orchestrated hormonal cycle required for ovulation, menstruation and pregnancy.
Brain effects of hormonal contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives affect more than just the ovaries and uterus.
The brain, specifically an area called the hypothalamus, controls the synchronization of ovarian hormone levels. Although they're called “ovarian hormones,” estrogen and progesterone receptors are also present throughout the brain.
Estrogen and progesterone have broad effects on neurons and cellular processes that have nothing to do with reproduction. For example, estrogen plays a role in processes that control memory formation and protect the brain against damage. Progesterone helps regulate emotion.
By changing the levels of these hormones in the brain and the body, hormonal contraceptives may modulate mood – for better or for worse.
Hormonal contraceptives interact with stress
Estrogen and progesterone also regulate the stress response – the body's “fight-or-flight” reaction to physical or psychological challenges.
The main hormone involved in the stress response – cortisol in humans and corticosterone in rodents, both abbreviated to CORT – is primarily a metabolic hormone, meaning that increasing blood levels of these hormones during stressful conditions results in more energy mobilized from fat stores. The interplay between stress systems and reproductive hormones is a crucial link between mood and hormone contraceptives, as energy regulation is extremely important during pregnancy.
So what happens to someone's stress response when they're on hormonal contraceptives?
When exposed to a mild stressor – sticking an arm in cold water, for example, or standing to give a public speech – women using hormone contraceptives show a smaller increase in CORT than people not on hormone contraceptives.
Researchers saw the same effect in rats and mice – when treated daily with a combination of hormones that mimic the pill, female rats and mice also show a suppression of the stress response.
Hormonal contraceptives and depression
Do hormonal contraceptives increase depression risk? The short answer is it varies from person to person. But for most people, probably not.
It's important to note that neither increased nor decreased stress responses are directly related to risk for or resilience against depression. But stress is closely related to mood, and chronic stress substantially increases risk for depression. By modifying stress responses, hormone contraceptives change the risk for depression after stress, leading to “protection” against depression for many people and “increased risk” for a minority of people. More than 9 out of 10 people who use hormonal contraceptives will not experience decreased mood or depression symptoms, and many will experience improved mood.
But researchers don't yet know who will experience increased risk. Genetic factors and previous stress exposures increase risk for depression, and it seems that similar factors contribute to mood changes related to hormone contraception.
Currently, hormone contraceptives are usually prescribed by trial and error – if one type causes side effects in a patient, another with a different dose, delivery method or formulation might be better. But the process of “try-and-see” is inefficient and frustrating, and many people give up instead of switching to a different option. Identifying the specific factors that increase depression risk and better communicating the benefits of hormone contraception beyond birth control can help patients make more informed health care decisions.
Natalie C. Tronson, Associate Professor of Psychology, University of Michigan
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.