Mississippi Today
Federal panel prescribes new mental health strategy to curb maternal deaths

For help, call or text the National Maternal Mental Health Hotline at 1-833-TLC-MAMA (1-833-852-6262) or contact the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline by dialing or texting “988.” Spanish-language services are also available.
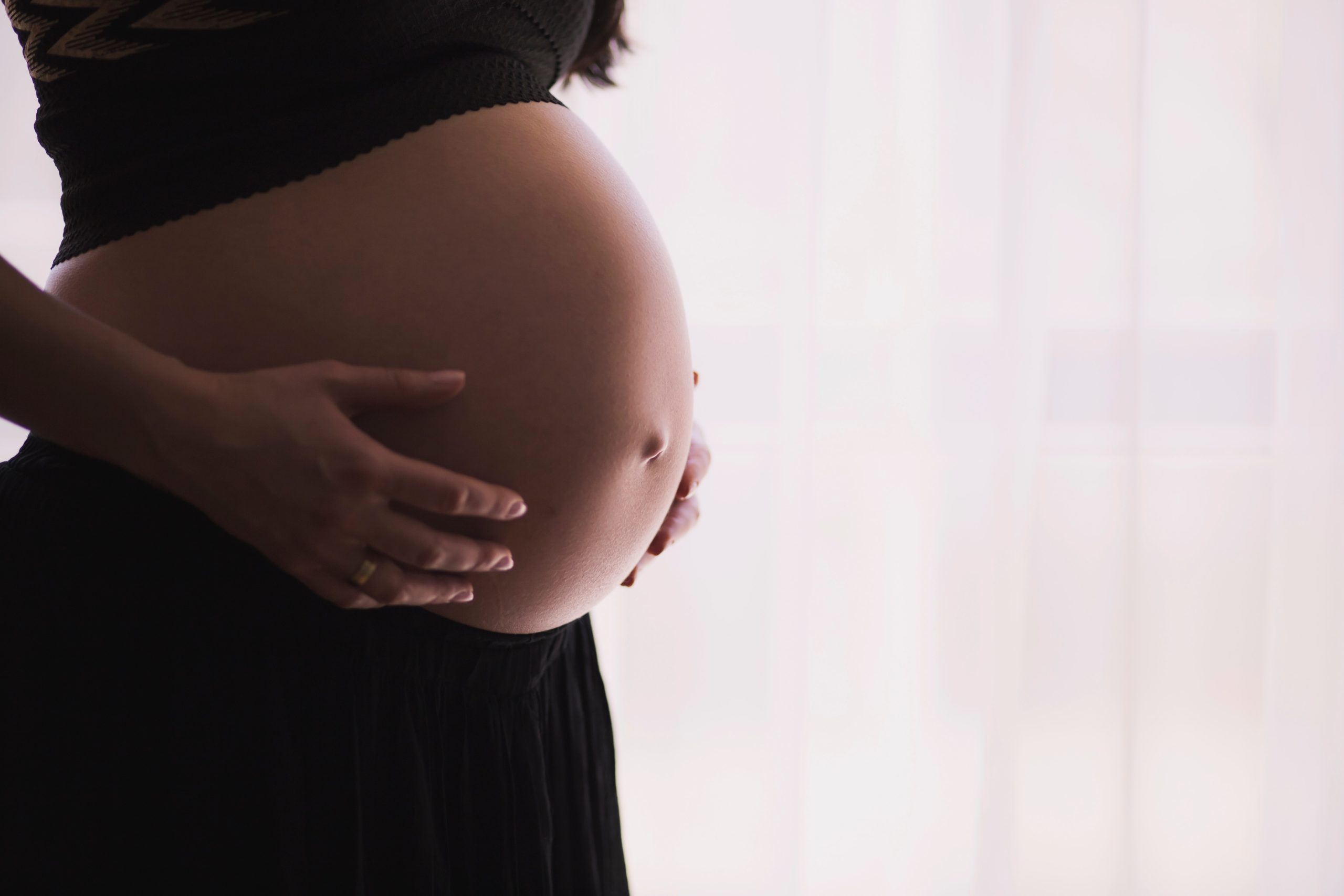
BRIDGEPORT, Conn. — Milagros Aquino was trying to find a new place to live and had been struggling to get used to new foods after she moved to Bridgeport from Peru with her husband and young son in 2023.
When Aquino, now 31, got pregnant in May 2023, “instantly everything got so much worse than before,” she said. “I was so sad and lying in bed all day. I was really lost and just surviving.”
Aquino has lots of company.
Perinatal depression affects as many as 20% of women in the United States during pregnancy, the postpartum period, or both, according to studies. In some states, anxiety or depression afflicts nearly a quarter of new mothers or pregnant women.
Many women in the U.S. go untreated because there is no widely deployed system to screen for mental illness in mothers, despite widespread recommendations to do so. Experts say the lack of screening has driven higher rates of mental illness, suicide, and drug overdoses that are now the leading causes of death in the first year after a woman gives birth.
“This is a systemic issue, a medical issue, and a human rights issue,” said Lindsay R. Standeven, a perinatal psychiatrist and the clinical and education director of the Johns Hopkins Reproductive Mental Health Center.
Standeven said the root causes of the problem include racial and socioeconomic disparities in maternal care and a lack of support systems for new mothers. She also pointed a finger at a shortage of mental health professionals, insufficient maternal mental health training for providers, and insufficient reimbursement for mental health services. Finally, Standeven said, the problem is exacerbated by the absence of national maternity leave policies, and the access to weapons.
Those factors helped drive a 105% increase in postpartum depression from 2010 to 2021, according to the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
For Aquino, it wasn’t until the last weeks of her pregnancy, when she signed up for acupuncture to relieve her stress, that a social worker helped her get care through the Emme Coalition, which connects girls and women with financial help, mental health counseling services, and other resources.
Mothers diagnosed with perinatal depression or anxiety during or after pregnancy are at about three times the risk of suicidal behavior and six times the risk of suicide compared with mothers without a mood disorder, according to recent U.S. and international studies in JAMA Network Open and The BMJ.
The toll of the maternal mental health crisis is particularly acute in rural communities that have become maternity care deserts, as small hospitals close their labor and delivery units because of plummeting birth rates, or because of financial or staffing issues.
This week, the Maternal Mental Health Task Force — co-led by the Office on Women’s Health and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and formed in September to respond to the problem — recommended creating maternity care centers that could serve as hubs of integrated care and birthing facilities by building upon the services and personnel already in communities.
The task force will soon determine what portions of the plan will require congressional action and funding to implement and what will be “low-hanging fruit,” said Joy Burkhard, a member of the task force and the executive director of the nonprofit Policy Center for Maternal Mental Health.
Burkhard said equitable access to care is essential. The task force recommended that federal officials identify areas where maternity centers should be placed based on data identifying the underserved. “Rural America,” she said, “is first and foremost.”
There are shortages of care in “unlikely areas,” including Los Angeles County, where some maternity wards have recently closed, said Burkhard. Urban areas that are underserved would also be eligible to get the new centers.
“All that mothers are asking for is maternity care that makes sense. Right now, none of that exists,” she said.
Several pilot programs are designed to help struggling mothers by training and equipping midwives and doulas, people who provide guidance and support to the mothers of newborns.
In Montana, rates of maternal depression before, during, and after pregnancy are higher than the national average. From 2017 to 2020, approximately 15% of mothers experienced postpartum depression and 27% experienced perinatal depression, according to the Montana Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System. The state had the sixth-highest maternal mortality rate in the country in 2019, when it received a federal grant to begin training doulas.
To date, the program has trained 108 doulas, many of whom are Native American. Native Americans make up 6.6% of Montana’s population. Indigenous people, particularly those in rural areas, have twice the national rate of severe maternal morbidity and mortality compared with white women, according to a study in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Stephanie Fitch, grant manager at Montana Obstetrics & Maternal Support at Billings Clinic, said training doulas “has the potential to counter systemic barriers that disproportionately impact our tribal communities and improve overall community health.”
Twelve states and Washington, D.C., have Medicaid coverage for doula care, according to the National Health Law Program. They are California, Florida, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Jersey, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, and Virginia. Medicaid pays for about 41% of births in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Jacqueline Carrizo, a doula assigned to Aquino through the Emme Coalition, played an important role in Aquino’s recovery. Aquino said she couldn’t have imagined going through such a “dark time alone.” With Carrizo’s support, “I could make it,” she said.
Genetic and environmental factors, or a past mental health disorder, can increase the risk of depression or anxiety during pregnancy. But mood disorders can happen to anyone.
Teresa Martinez, 30, of Price, Utah, had struggled with anxiety and infertility for years before she conceived her first child. The joy and relief of giving birth to her son in 2012 were short-lived.
Without warning, “a dark cloud came over me,” she said.
Martinez was afraid to tell her husband. “As a woman, you feel so much pressure and you don’t want that stigma of not being a good mom,” she said.
In recent years, programs around the country have started to help doctors recognize mothers’ mood disorders and learn how to help them before any harm is done.
One of the most successful is the Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Program for Moms, which began a decade ago and has since spread to 29 states. The program, supported by federal and state funding, provides tools and training for physicians and other providers to screen and identify disorders, triage patients, and offer treatment options.
But the expansion of maternal mental health programs is taking place amid sparse resources in much of rural America. Many programs across the country have run out of money.
The federal task force proposed that Congress fund and create consultation programs similar to the one in Massachusetts, but not to replace the ones already in place, said Burkhard.
In April, Missouri became the latest state to adopt the Massachusetts model. Women on Medicaid in Missouri are 10 times as likely to die within one year of pregnancy as those with private insurance. From 2018 through 2020, an average of 70 Missouri women died each year while pregnant or within one year of giving birth, according to state government statistics.
Wendy Ell, executive director of the Maternal Health Access Project in Missouri, called her service a “lifesaving resource” that is free and easy to access for any health care provider in the state who sees patients in the perinatal period.
About 50 health care providers have signed up for Ell’s program since it began. Within 30 minutes of a request, the providers can consult over the phone with one of three perinatal psychiatrists. But while the doctors can get help from the psychiatrists, mental health resources for patients are not as readily available.
The task force called for federal funding to train more mental health providers and place them in high-need areas like Missouri. The task force also recommended training and certifying a more diverse workforce of community mental health workers, patient navigators, doulas, and peer support specialists in areas where they are most needed.
A new voluntary curriculum in reproductive psychiatry is designed to help psychiatry residents, fellows, and mental health practitioners who may have little or no training or education about the management of psychiatric illness in the perinatal period. A small study found that the curriculum significantly improved psychiatrists’ ability to treat perinatal women with mental illness, said Standeven, who contributed to the training program and is one of the study’s authors.
Nancy Byatt, a perinatal psychiatrist at the University of Massachusetts Chan School of Medicine who led the launch of the Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Program for Moms in 2014, said there is still a lot of work to do.
“I think that the most important thing is that we have made a lot of progress and, in that sense, I am kind of hopeful,” Byatt said.
Cheryl Platzman Weinstock’s reporting is supported by a grant from the National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation. KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Did you miss our previous article…
https://www.biloxinewsevents.com/?p=359245
Mississippi Today
Early voting proposal killed on last day of Mississippi legislative session
Mississippi will remain one of only three states without no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting.
Senate leaders, on the last day of their regular 2025 session, decided not to send a bill to Gov. Tate Reeves that would have expanded pre-Election Day voting options. The governor has been vocally opposed to early voting in Mississippi, and would likely have vetoed the measure.
The House and Senate this week overwhelmingly voted for legislation that established a watered-down version of early voting. The proposal would have required voters to go to a circuit clerk’s office and verify their identity with a photo ID.
The proposal also listed broad excuses that would have allowed many voters an opportunity to cast early ballots.
The measure passed the House unanimously and the Senate approved it 42-7. However, Sen. Jeff Tate, a Republican from Meridian who strongly opposes early voting, held the bill on a procedural motion.
Senate Elections Chairman Jeremy England chose not to dispose of Tate’s motion on Thursday morning, the last day the Senate was in session. This killed the bill and prevented it from going to the governor.
England, a Republican from Vancleave, told reporters he decided to kill the legislation because he believed some of its language needed tweaking.
The other reality is that Republican Gov. Tate Reeves strongly opposes early voting proposals and even attacked England on social media for advancing the proposal out of the Senate chamber.
England said he received word “through some sources” that Reeves would veto the measure.
“I’m not done working on it, though,” England said.
Although Mississippi does not have no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting, it does have absentee voting.
To vote by absentee, a voter must meet one of around a dozen legal excuses, such as temporarily living outside of their county or being over 65. Mississippi law doesn’t allow people to vote by absentee purely out of convenience or choice.
Several conservative states, such as Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas and Florida, have an in-person early voting system. The Republican National Committee in 2023 urged Republican voters to cast an early ballot in states that have early voting procedures.
Yet some Republican leaders in Mississippi have ardently opposed early voting legislation over concerns that it undermines election security.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi Legislature approves DEI ban after heated debate
Mississippi lawmakers have reached an agreement to ban diversity, equity and inclusion programs and a list of “divisive concepts” from public schools across the state education system, following the lead of numerous other Republican-controlled states and President Donald Trump’s administration.
House and Senate lawmakers approved a compromise bill in votes on Tuesday and Wednesday. It will likely head to Republican Gov. Tate Reeves for his signature after it clears a procedural motion.
The agreement between the Republican-dominated chambers followed hours of heated debate in which Democrats, almost all of whom are Black, excoriated the legislation as a setback in the long struggle to make Mississippi a fairer place for minorities. They also said the bill could bog universities down with costly legal fights and erode academic freedom.
Democratic Rep. Bryant Clark, who seldom addresses the entire House chamber from the podium during debates, rose to speak out against the bill on Tuesday. He is the son of the late Robert Clark, the first Black Mississippian elected to the state Legislature since the 1800s and the first Black Mississippian to serve as speaker pro tempore and preside over the House chamber since Reconstruction.
“We are better than this, and all of you know that we don’t need this with Mississippi history,” Clark said. “We should be the ones that say, ‘listen, we may be from Mississippi, we may have a dark past, but you know what, we’re going to be the first to stand up this time and say there is nothing wrong with DEI.'”
Legislative Republicans argued that the measure — which will apply to all public schools from the K-12 level through universities — will elevate merit in education and remove a list of so-called “divisive concepts” from academic settings. More broadly, conservative critics of DEI say the programs divide people into categories of victims and oppressors and infuse left-wing ideology into campus life.
“We are a diverse state. Nowhere in here are we trying to wipe that out,” said Republican Sen. Tyler McCaughn, one of the bill’s authors. “We’re just trying to change the focus back to that of excellence.”
The House and Senate initially passed proposals that differed in who they would impact, what activities they would regulate and how they aim to reshape the inner workings of the state’s education system. Some House leaders wanted the bill to be “semi-vague” in its language and wanted to create a process for withholding state funds based on complaints that almost anyone could lodge. The Senate wanted to pair a DEI ban with a task force to study inefficiencies in the higher education system, a provision the upper chamber later agreed to scrap.
The concepts that will be rooted out from curricula include the idea that gender identity can be a “subjective sense of self, disconnected from biological reality.” The move reflects another effort to align with the Trump administration, which has declared via executive order that there are only two sexes.
The House and Senate disagreed on how to enforce the measure but ultimately settled on an agreement that would empower students, parents of minor students, faculty members and contractors to sue schools for violating the law.
People could only sue after they go through an internal campus review process and a 25-day period when schools could fix the alleged violation. Republican Rep. Joey Hood, one of the House negotiators, said that was a compromise between the chambers. The House wanted to make it possible for almost anyone to file lawsuits over the DEI ban, while Senate negotiators initially bristled at the idea of fast-tracking internal campus disputes to the legal system.
The House ultimately held firm in its position to create a private cause of action, or the right to sue, but it agreed to give schools the ability to conduct an investigative process and potentially resolve the alleged violation before letting people sue in chancery courts.
“You have to go through the administrative process,” said Republican Sen. Nicole Boyd, one of the bill’s lead authors. “Because the whole idea is that, if there is a violation, the school needs to cure the violation. That’s what the purpose is. It’s not to create litigation, it’s to cure violations.”
If people disagree with the findings from that process, they could also ask the attorney general’s office to sue on their behalf.
Under the new law, Mississippi could withhold state funds from schools that don’t comply. Schools would be required to compile reports on all complaints filed in response to the new law.
Trump promised in his 2024 campaign to eliminate DEI in the federal government. One of the first executive orders he signed did that. Some Mississippi lawmakers introduced bills in the 2024 session to restrict DEI, but the proposals never made it out of committee. With the national headwinds at their backs and several other laws in Republican-led states to use as models, Mississippi lawmakers made plans to introduce anti-DEI legislation.
The policy debate also unfolded amid the early stages of a potential Republican primary matchup in the 2027 governor’s race between State Auditor Shad White and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann. White, who has been one of the state’s loudest advocates for banning DEI, had branded Hosemann in the months before the 2025 session “DEI Delbert,” claiming the Senate leader has stood in the way of DEI restrictions passing the Legislature.
During the first Senate floor debate over the chamber’s DEI legislation during this year’s legislative session, Hosemann seemed to be conscious of these political attacks. He walked over to staff members and asked how many people were watching the debate live on YouTube.
As the DEI debate cleared one of its final hurdles Wednesday afternoon, the House and Senate remained at loggerheads over the state budget amid Republican infighting. It appeared likely the Legislature would end its session Wednesday or Thursday without passing a $7 billion budget to fund state agencies, potentially threatening a government shutdown.
“It is my understanding that we don’t have a budget and will likely leave here without a budget. But this piece of legislation …which I don’t think remedies any of Mississippi’s issues, this has become one of the top priorities that we had to get done,” said Democratic Sen. Rod Hickman. “I just want to say, if we put that much work into everything else we did, Mississippi might be a much better place.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
House gives Senate 5 p.m. deadline to come to table, or legislative session ends with no state budget
The House on Wednesday attempted one final time to revive negotiations between it and the Senate over passing a state budget.
Otherwise, the two Republican-led chambers will likely end their session without funding government services for the next fiscal year and potentially jeopardize state agencies.
The House on Wednesday unanimously passed a measure to extend the legislative session and revive budget bills that had died on legislative deadlines last weekend.
House Speaker Jason White said he did not have any prior commitment that the Senate would agree to the proposal, but he wanted to extend one last offer to pass the budget. White, a Republican from West, said if he did not hear from the Senate by 5 p.m. on Wednesday, his chamber would end its regular session.
“The ball is in their court,” White said of the Senate. “Every indication has been that they would not agree to extend the deadlines for purposes of doing the budget. I don’t know why that is. We did it last year, and we’ve done it most years.”
But it did not appear likely Wednesday afternoon that the Senate would comply.
The Mississippi Legislature has not left Jackson without setting at least most of the state budget since 2009, when then Gov. Haley Barbour had to force them back to set one to avoid a government shutdown.
The House measure to extend the session is now before the Senate for consideration. To pass, it would require a two-thirds majority vote of senators. But that might prove impossible. Numerous senators on both sides of the aisle vowed to vote against extending the current session, and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann who oversees the chamber said such an extension likely couldn’t pass.
Senate leadership seemed surprised at the news that the House passed the resolution to negotiate a budget, and several senators earlier on Wednesday made passing references to ending the session without passing a budget.
“We’ll look at it after it passes the full House,” Senate President Pro Tempore Dean Kirby said.
The House and Senate, each having a Republican supermajority, have fought over many issues since the legislative session began early January.
But the battle over a tax overhaul plan, including elimination of the state individual income tax, appeared to cause a major rift. Lawmakers did pass a tax overhaul, which the governor has signed into law, but Senate leaders cried foul over how it passed, with the House seizing on typos in the Senate’s proposal that accidentally resembled the House’s more aggressive elimination plan.
The Senate had urged caution in eliminating the income tax, and had economic growth triggers that would have likely phased in the elimination over many years. But the typos essentially negated the triggers, and the House and governor ran with it.
The two chambers have also recently fought over the budget. White said he communicated directly with Senate leaders that the House would stand firm on not passing a budget late in the session.
But Senate leaders said they had trouble getting the House to meet with them to haggle out the final budget.
On the normally scheduled “conference weekend” with a deadline to agree to a budget last Saturday, the House did not show, taking the weekend off. This angered Hosemann and the Senate. All the budget bills died, requiring a vote to extend the session, or the governor forcing them into a special session.
If the Legislature ends its regular session without adopting a budget, the only option to fund state agencies before their budgets expire on June 30 is for Gov. Tate Reeves to call lawmakers back into a special session later.
“There really isn’t any other option (than the governor calling a special session),” Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann previously said.
If Reeves calls a special session, he gets to set the Legislature’s agenda. A special session call gives an otherwise constitutionally weak Mississippi governor more power over the Legislature.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
-

 Mississippi Today2 days ago
Mississippi Today2 days agoPharmacy benefit manager reform likely dead
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days agoYoungkin removes Ellis, appoints Cuccinelli to UVa board | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoUniversity of Alabama student detained by ICE moved to Louisiana
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed5 days agoTornado watch, severe thunderstorm warnings issued for Oklahoma
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed5 days agoGeorgia road project forcing homeowners out | FOX 5 News
-

 News from the South - West Virginia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - West Virginia News Feed6 days agoHometown Hero | Restaurant owner serves up hope
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days agoBudget cuts: Senior Citizens Inc. and other non-profits worry for the future
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoStrangers find lost family heirloom at Cocoa Beach