Kaiser Health News
Pregnancy Care Was Always Lacking in Jails. It Could Get Worse.
Renuka Rayasam
Fri, 23 Feb 2024 10:00:00 +0000
It was about midnight in June 2022 when police officers showed up at Angela Collier’s door and told her that someone anonymously requested a welfare check because they thought she might have had a miscarriage.
Standing in front of the concrete steps of her home in Midway, Texas, Collier, initially barefoot and wearing a baggy gray T-shirt, told officers she planned to see a doctor in the morning because she had been bleeding.
Police body camera footage obtained by KFF Health News through an open records request shows that the officers then told Collier — who was 29 at the time and enrolled in online classes to study psychology — to turn around.
Instead of taking her to get medical care, they handcuffed and arrested her because she had outstanding warrants in a neighboring county for failing to appear in court to face misdemeanor drug charges three weeks earlier. She had missed that court date, medical records show, because she was at a hospital receiving treatment for pregnancy complications.
Despite her symptoms and being about 13 weeks pregnant, Collier spent the next day and a half in the Walker County Jail, about 80 miles north of Houston. She said her bleeding worsened there and she begged repeatedly for medical attention that she didn’t receive, according to a formal complaint she filed with the Texas Commission on Jail Standards.
“There wasn’t anything I could do,” she said, but “just lay there and be scared and not know what was going to happen.”
Collier’s experience highlights the limited oversight and absence of federal standards for reproductive care for pregnant women in the criminal justice system. Incarcerated people have a constitutional right to health care, yet only a half-dozen states have passed laws guaranteeing access to prenatal or postpartum medical care for people in custody, according to a review of reproductive health care legislation for incarcerated people by a research group at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. And now abortion restrictions might be putting care further out of reach.
Collier’s arrest was “shocking and disturbing” because officers “blithely” took her to jail despite her miscarriage concerns, said Wanda Bertram, a spokesperson for the Prison Policy Initiative, a nonprofit organization that studies incarceration. Bertram reviewed the body cam footage and Collier’s complaint.
“Police arrest people who are in medical emergencies all the time,” she said. “And they do that regardless of the fact that the jail is often not equipped to care for those people in the way an emergency room might be.”
After a decline during the first year of the pandemic, the number of women in U.S. jails is once again rising, hitting nearly 93,000 in June 2022, a 33% increase over 2020, according to the Department of Justice. Tens of thousands of pregnant women enter U.S. jails each year, according to estimates by Carolyn Sufrin, an associate professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, who researches pregnancy care in jails and prisons.
The health care needs of incarcerated women have “always been an afterthought,” said Dana Sussman, deputy executive director at Pregnancy Justice, an organization that defends women who have been charged with crimes related to their pregnancy, such as substance use. For example, about half of states don’t provide free menstrual products in jails and prisons. “And then the needs of pregnant women are an afterthought beyond that,” Sussman said.
Researchers and advocates worry that confusion over recent abortion restrictions may further complicate the situation. A nurse cited Texas’ abortion laws as one reason Collier didn’t need care, according to her statement to the standards commission.
Texas law allows treatment of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancies, a life-threatening condition in which a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. However, different interpretations of the law can create confusion.
A nurse told Collier that “hospitals no longer did dilation and curettage,” Collier told the commission. “Since I wasn’t hemorrhaging to the point of completely soaking my pants, there wasn’t anything that could be done for me,” she said.
Collier testified that she saw a nurse only once during her stay in jail, even after she repeatedly asked jail staffers for help. The nurse checked her temperature and blood pressure and told her to put in a formal request for Tylenol. Collier said she completed her miscarriage shortly after being released.
Collier’s case is a “canary in a coal mine” for what is happening in jails; abortion restrictions are “going to have a huge ripple effect on a system already unequipped to handle obstetric emergencies,” Sufrin said.
‘There Are No Consequences’
Jail and prison health policies vary widely around the country and often fall far short of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ guidelines for reproductive health care for incarcerated people. ACOG and other groups recommend that incarcerated women have access to unscheduled or emergency obstetric visits on a 24-hour basis and that on-site health care providers should be better trained to recognize pregnancy problems.
In Alabama, where women have been jailed for substance use during pregnancy, the state offers pregnancy tests in jail. But it doesn’t guarantee a minimum standard of prenatal care, such as access to extra food and medical visits, according to Johns Hopkins’ review.
Policies for pregnant women at federal facilities also don’t align with national standards for nutrition, safe housing, and access to medical care, according to a 2021 report from the Government Accountability Office.
Even when laws exist to ensure that incarcerated pregnant women have access to care, the language is often vague, leaving discretion to jail personnel.
Since 2020, Tennessee law has required that jails and prisons provide pregnant women “regular prenatal and postpartum care, as necessary.” But last August a woman gave birth in a jail cell after seeking medical attention for more than an hour, according to the Montgomery County Sheriff’s Office.
Pregnancy complications can quickly escalate into life-threatening situations, requiring more timely and specialized care than jails can often provide, said Sufrin. And when jails fail to comply with laws on the books, little oversight or enforcement may exist.
In Louisiana, many jails didn’t consistently follow laws that aimed to improve access to reproductive health care, such as providing free menstrual items, according to a May 2023 report commissioned by state lawmakers. The report also said jails weren’t transparent about whether they followed other laws, such as prohibiting the use of solitary confinement for pregnant women.
Krishnaveni Gundu, as co-founder of the Texas Jail Project, which advocates for people held in county jails, has lobbied for more than a decade to strengthen state protections for pregnant incarcerated people.
In 2019, Texas became one of the few states to require that jails’ health policies include obstetrical and gynecological care. The law requires jails to promptly transport a pregnant person in labor to a hospital, and additional regulations mandate access to medical and mental health care for miscarriages and other pregnancy complications.
But Gundu said lack of oversight and meaningful enforcement mechanisms, along with “apathy” among jail employees, have undermined regulatory protections.
“All those reforms feel futile,” said Gundu, who helped Collier prepare for her testimony. “There are no consequences.”
Before her arrest, Collier had been to the hospital twice that month experiencing pregnancy complications, including a bladder infection, her medical records show. Yet the commission found that Walker County Jail didn’t violate minimum standards. The commission did not consider the police body cam footage or Collier’s personal medical records, which support her assertions of pregnancy complications, according to investigation documents obtained by KFF Health News via an open records request.
In making its determination, the commission relied mainly on the jail’s medical records, which note that Collier asked for medical attention for a miscarriage once, in the morning on the day she was released, and refused Tylenol.
“Your complaint of no medical care is unfounded,” the commission concluded, “and no further action will be taken.”
Collier’s miscarriage had ended before she entered the jail, argued Lt. Keith DeHart, jail lieutenant for the Walker County Sheriff’s Office. “I believe there was some misunderstanding,” he said.
Brandon Wood, executive director of the commission, wouldn’t comment on Collier’s case but defends the group’s investigation as thorough. Jails “have a duty to ensure that those records are accurate and truthful,” he said. And most Texas jails are complying with heightened standards, he said.
Bertram disagrees, saying the fact that care was denied to someone who was begging for it speaks volumes. “That should tell you something about what these standards are worth,” she said.
Last year, Chiree Harley spent six weeks in a Comal County, Texas, jail shortly after discovering she was pregnant and before she could get prenatal care, she said.
I was “thinking that I was going to be well taken care of,” said Harley, 37, who also struggled with substance use.
Jail officials put her in the infirmary, Harley said, but she saw only a jail doctor and never visited an OB-GYN, even though she had previous pregnancy complications including losing multiple pregnancies at around 21 weeks. This time she had no idea how far along she was.
She said that she started leaking amniotic fluid and having contractions on Nov. 1, but that jail officials waited nearly two days to take her to a hospital. Harley said officers forced her to sign papers releasing her from jail custody while she was having contractions in the hospital. Harley delivered at 23 weeks; the baby boy died less than a day later in her arms.
The whole experience was “very scary,” Harley said. “Afterwards we were all very, very devastated.”
Comal County declined to send Harley’s medical and other records in response to an open records request. Michael Shaunessy, a partner at McGinnis Lochridge who represents Comal County, said in a statement that, “at all times, the Comal County Jail provided Chiree Harley with all appropriate and necessary medical treatment for her and her unborn child.” He did not respond to questions about whether Harley was provided specialized obstetric care.
‘I Trusted Those People’
In states like Idaho, Mississippi, and Louisiana that installed near-total abortion bans after the Supreme Court eliminated the constitutional right to abortion in 2022, some patients might have to wait until no fetal cardiac activity is detected before they can get care, said Kari White, the executive and scientific director of Resound Research for Reproductive Health.
White co-authored a recent study that documented 50 cases in which pregnancy care deviated from the standard because of abortion restrictions even outside of jails and prisons. Health care providers who worry about running afoul of strict laws might tell patients to go home and wait until their situations worsen.
“Obviously, it’s much trickier for people who are in jail or in prison, because they are not going to necessarily be able to leave again,” she said.
Advocates argue that boosting oversight and standards is a start, but that states need to find other ways to manage pregnant women who get caught in the justice system.
For many pregnant people, even a short stay in jail can cause lasting trauma and interrupt crucial prenatal care.
Collier remembers being in “disbelief” when she was first arrested but said she was not “distraught.”
“I figured I would be taken care of, that nothing bad was gonna happen to me,” she said. As it became clear that she wouldn’t get care, she grew distressed.
After her miscarriage, Collier saw a mental health specialist and started medication to treat depression. She hasn’t returned to her studies, she said.
“I trusted those people,” Collier said about the jail staff. “The whole experience really messed my head up.”
——————————
By: Renuka Rayasam
Title: Pregnancy Care Was Always Lacking in Jails. It Could Get Worse.
Sourced From: kffhealthnews.org/news/article/pregnancy-care-jails-prisons-incarcerated-women/
Published Date: Fri, 23 Feb 2024 10:00:00 +0000
Kaiser Health News
LGBTQ+ People Relive Old Traumas as They Age on Their Own
SUMMARY: Bill Hall, a 71-year-old HIV survivor, has endured numerous health challenges, including depression, heart disease, and cancer since contracting the virus in 1986. His struggles are compounded by trauma from childhood, where he faced bullying and abuse in a government boarding school. LGBTQ+ seniors like Hall often face isolation, with many living alone and lacking social support. By 2030, the number of LGBTQ+ seniors is projected to double, increasing their vulnerability to health issues and mental struggles. Many have experienced profound loss from the AIDS crisis, leading to ongoing emotional challenges. Support services remain critical for this aging population.
The post LGBTQ+ People Relive Old Traumas as They Age on Their Own appeared first on kffhealthnews.org
Kaiser Health News
Caseworkers Coax Homeless People out of Las Vegas’ Tunnels for Treatment
SUMMARY: In Las Vegas, case manager Bryon Johnson searches the underground tunnels for homeless individuals like Jay Flanders, who suffers from health issues and substance abuse. Escaping rising housing costs and law enforcement, around 1,200 to 1,500 people live in these tunnels, which provide shelter from extreme weather but pose significant health risks, especially during monsoon season. Outreach workers emphasize the dangers of drug addiction and untreated health conditions, urging residents to seek medical care above ground. As housing costs soar, many homeless individuals, including tourists, end up in these perilous conditions, seeking cover from societal judgment and harsh weather.
The post Caseworkers Coax Homeless People out of Las Vegas’ Tunnels for Treatment appeared first on kffhealthnews.org
Kaiser Health News
In Settling Fraud Case, New York Medicare Advantage Insurer, CEO Will Pay up to $100M
SUMMARY: Independent Health Association of Buffalo and Betsy Gaffney, CEO of medical analytics firm DxID, have agreed to a settlement of up to $100 million to resolve Justice Department allegations of fraudulent Medicare billing for exaggerated or non-existent health conditions. Independent Health will pay up to $98 million, while Gaffney will contribute $2 million. Neither party admitted wrongdoing. The case was triggered by whistleblower Teresa Ross, highlighting issues of “upcoding” in Medicare Advantage plans. Ross, having faced repercussions for her allegations, will receive at least $8.2 million from the settlement. This case underscores the challenges of regulating billing practices in the Medicare system.
The post In Settling Fraud Case, New York Medicare Advantage Insurer, CEO Will Pay up to $100M appeared first on kffhealthnews.org
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed4 days agoSocial Security benefits boosted for millions in bill headed to Biden’s desk • NC Newsline
-

 Local News4 days ago
Local News4 days agoHard Rock Hotel & Casino Biloxi Honors Veterans with Wreath-Laying Ceremony and Holiday Giving Initiative
-

 Mississippi Today7 days ago
Mississippi Today7 days agoMississippi PERS Board endorses plan decreasing pension benefits for new hires
-

 Local News4 days ago
Local News4 days agoMDOT suspends work, urges safe driving for holiday travel
-
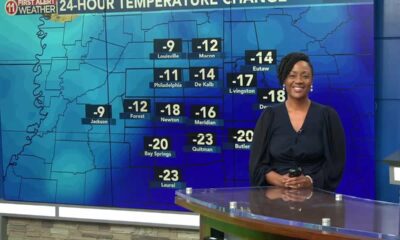
 Mississippi News Video5 days ago
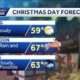
Mississippi News Video5 days ago12/19- Friday will be breezy…but FREEZING by this weekend
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days agoCould prime Albert Pujols fetch $1 billion in today's MLB free agency?
-

 Local News6 days ago
Local News6 days agoTrump calls for abolishing the debt ceiling
-

 News from the South - Texas News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Texas News Feed6 days agoAmazon workers strike at facilities around the country as Teamsters seek contract