Mississippi Today
Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann calls state pension problems ‘the major issue’ of 2024 legislative session
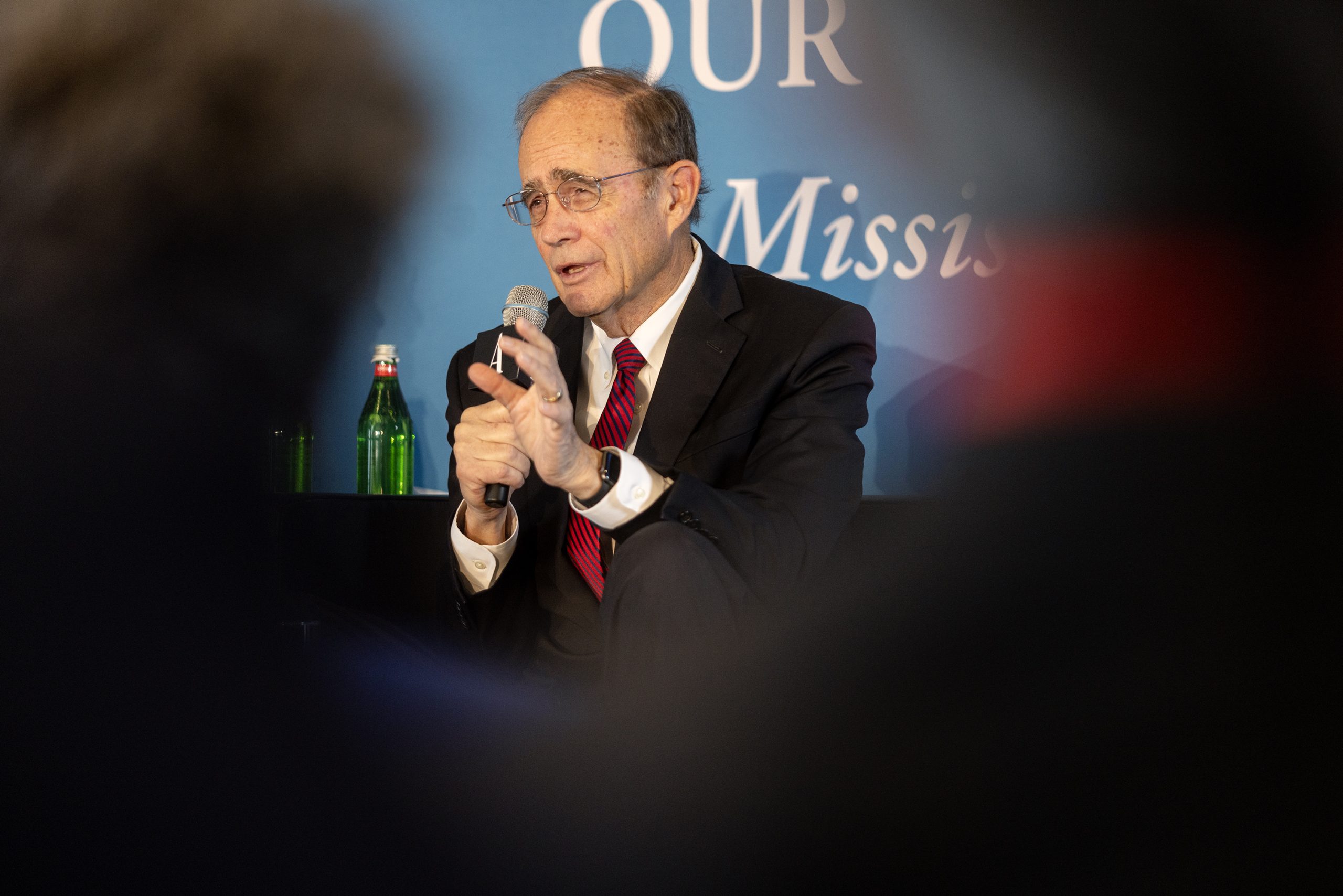

Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann said that deciding how to ensure the long-term financial solvency of the massive Mississippi Public Employees Retirement System is “the major issue” facing lawmakers during the current legislative session.
PERS provides pension benefits for more than 360,000 current and former government employees in Mississippi, including school district employees and higher education and community college staff.
The system has experienced financial problems for years that many argue have gone largely unaddressed. It has about $32 billion in assets to pay its retirees, but it is about $25 billion in long-term debt. It has a funding ratio of about 56%, meaning the system has just 56% of the revenue needed to cover its liabilities over a 30-year period.
PERS leaders this year are asking the Legislature for an infusion of cash — which lawmakers traditionally do not provide on an annual basis — to help offset the system’s uncertain financial future.
Hosemann recently said until the issues facing PERS are resolved, the Legislature cannot commit on how much to provide in funding for state agencies, schools and other programs.
“We are going to pay the retirees,” Hosemann said.
House Speaker Jason White, R-West, has also talked of the importance of addressing PERS.
“I think there has been a commitment at least around the coffee pot that we (legislators) want to fix this long term,” White said before the session began. “… For myself, I would say we are not going to just increase it (the amount of government money put into the plan) 5%, 10% and hope it gets better.”
While Hosemann and many legislative leaders appear to be locked in on PERS, the problems have not been addressed by Gov. Tate Reeves. Reeves, in the first year of his final term as governor, did not mention PERS in his recently released budget proposal. At a time when legislative leaders and local government officials are grappling with how to fund PERS, Reeves instead touted his plan to eliminate the state income tax, which would, if passed, do away with one-third of the state’s current annual general fund revenue.
Fixing the pension program, many leaders believe, will take a significant infusion of funds. Some proposed solutions could place a significant strain on city and county governments, on school districts and state agencies that currently pay into the system unless the Legislature commits to appropriating an additional amount of money.
During a recent meeting with the Senate Finance Committee, Ray Higgins, the PERS executive director, did not provide a specific amount of money that he believes the Legislature needed to contribute to the program. Hosemann has spoken of the program possibly needing an additional $360 million annually.
“When it comes down to the long-term sustainability of PERS, we should either fund it, change it, or eventually we may risk it,” Higgins wrote in a letter to lawmakers. “Revenue must increase, expenses and liabilities should decrease, or both.”
The retirement system’s revenue to pay pension benefits is generated in the following ways:
- From employees contributing 9% of their salaries to PERS.
- From employers or governmental entities contributing a sum equal to 17.4% of an employee’s paycheck to the program.
- From investment income. Investment income is key since the employee/employer contributions are not enough to cover the monthly costs.
The average annual retirement income for retirees is about $26,900.
Multiple factors are contributing to the financial uncertainty in the system, including:
- Recessions through the years that have impacted the investment earnings.
- A shrinking governmental workforce and additional retirees.
- Legislature-approved added benefits through the years, dating back to the 1990s — some of which were provided, some argue, without a revenue stream to pay for them.
Perhaps the most confusing and controversial change that placed stress on the system was the action by the 10-member board that governs PERS to change what is known as the assumed rate of return. Based on recommendations from actuaries, the board recently dropped the assumed rate of return from 7.5% to 7%, meaning that PERS’ investments will earn 7% instead of 7.5% annually. The change was made to paint what PERS officials said is a more accurate picture of the system’s financial outlook. But the lower assumed rate of return means the expectation is that the investment earnings will generate less money, thus causing more debt.
Sen. Daniel Sparks, R-Belmont, pointed out that at one point not too long ago the assumed rate of return was 8%. He said, optimistically, that each year the investment earnings exceed the assumed rate of returns means the system’s debt is decreased.
Still, the PERS board believes that strong investment earnings will not be enough to totally resolve the financial woes facing the system. The board plans to phase in a 5% increase in the employer contribution rate over a three-year period. There has been talk of phasing in a 10% increase in the employer contribution rate. The first 2% increase that will be enacted on July 1 will cost the state $60 million, not counting the cost for local and county governments. Under current law, the board has the authority to act on its own to increase the employer contribution rate, though the Legislature could change the law.
City and county officials have told legislators they cannot afford the increase.
Senate Appropriations Chair Briggs Hopson, R-Vicksburg, said he already is hearing from state agency directors about the issue.
“I guarantee they are coming to me saying whatever you do, give us enough money to pay for the PERS increase,” Hopson said. “ … Either we provide the money or they have to absorb it,” meaning they cannot provide raises or enact other programs that cost money.
Hosemann said such increases in the employer contribution would be “catastrophic” for the system since local governments would start hiring contract workers instead of full-time government employees who would be eligible for PERS pensions. That, Hosemann said, would further reduce the number of employees paying into the system.
Sen. Hob Bryan, D-Amory, pointed out that each time the Legislature privatizes a governmental function it reduces the number of state employees paying into the system.
Bryan also pointed out that years ago, a separate public retirement system for Mississippi Highway Patrol troopers faced financial difficulties. Bryan said in that instance, the Legislature passed a law to place a fee on traffic citations with the revenue earned from the fee directed to the retirement system.
Whether there is the legislative will to create a similar source of revenue dedicated to the much larger PERS system remains to be seen.
In the meantime, the Legislature is expected to act on a proposal by the PERS board to change the benefits for new governmental hires. The proposal includes eliminating the guaranteed 3% annual cost of living increase for new employees. Instead, under the proposal, new employees would get a cost of living increase when revenue is available and tied to the annual inflation rate instead of the automatic 3% cost of living increase each year. The proposal would not make any changes to the guaranteed 3% annual cost of living increase for current employees and retirees.
Both Hosemann and Hopson said they do not believe it is legal to reduce the benefits for current employees and retirees.
“I don’t think you can do that,” Hosemann said. “I am not going to do it.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Mississippi Today
Meet Willye B. White: A Mississippian we should all celebrate
In an interview years and years ago, the late Willye B. White told me in her warm, soothing Delta voice, “A dream without a plan is just a wish. As a young girl, I had a plan.”
She most definitely did have a plan. And she executed said plan, as we shall see.
And I know what many readers are thinking: “Who the heck was Willye B. White?” That, or: “Willye B. White, where have I heard that name before?”
Well, you might have driven an eight-mile, flat-as-a-pancake stretch of U.S. 49E, between Sidon and Greenwood, and seen the marker that says: “Willye B. White Memorial Highway.” Or you might have visited the Olympic Room at the Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame and seen where White was a five-time participant and two-time medalist in the Summer Olympics as a jumper and a sprinter.
If you don’t know who Willye B. White was, you should. Every Mississippian should. So pour yourself a cup of coffee or a glass of iced tea, follow along and prepare to be inspired.
Willye B. White was born on the last day of 1939 in Money, near Greenwood, and was raised by grandparents. As a child, she picked cotton to help feed her family. When she wasn’t picking cotton, she was running, really fast, and jumping, really high and really long distances.
She began competing in high school track and field meets at the age of 10. At age 11, she scored enough points in a high school meet to win the competition all by herself. At age 16, in 1956, she competed in the Summer Olympics at Melbourne, Australia.
Her plan then was simple. The Olympics, on the other side of the world, would take place in November. “I didn’t know much about the Olympics, but I knew that if I made the team and I went to the Olympics, I wouldn’t have to pick cotton that year. I was all for that.”
Just imagine. You are 16 years old, a high school sophomore, a poor Black girl. You are from Money, Mississippi, and you walk into the stadium at the Melbourne Cricket Grounds to compete before a crowd of more than 100,000 strangers nearly 10,000 miles from your home.
She competed in the long jump. She won the silver medal to become the first-ever American to win a medal in that event. And then she came home to segregated Mississippi, to little or no fanfare. This was the year after Emmett Till, a year younger than White, was brutally murdered just a short distance from where she lived.
“I used to sit in those cotton fields and watch the trains go by,” she once told an interviewer. “I knew they were going to some place different, some place into the hills and out of those cotton fields.”
Her grandfather had fought in France in World War I. “He told me about all the places he saw,” White said. “I always wanted to travel and see the places he talked about.”
Travel, she did. In the late 1950s there were two colleges that offered scholarships to young, Black female track and field athletes. One was Tuskegee in Alabama, the other was Tennessee State in Nashville. White chose Tennessee State, she said, “because it was the farthest away from those cotton fields.”
She was getting started on a track and field career that would take her, by her own count, to 150 different countries across the globe. She was the best female long jumper in the U.S. for two decades. She competed in Olympics in Melbourne, Rome, Tokyo, Mexico City and Munich. She would compete on more than 30 U.S. teams in international events. In 1999, Sports Illustrated named her one of the top 100 female athletes of the 20th century.
Chicago became White’s home for most of adulthood. This was long before Olympic athletes were rich, making millions in endorsements and appearance fees. She needed a job, so she became a nurse. Later on, she became an public health administrator as well as a coach. She created the Willye B. White Foundation to help needy children with health and after school care.
In 1982, at age 42, she returned to Mississippi to be inducted into the Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame and was welcomed back to a reception at the Governor’s Mansion by Gov. William Winter, who introduced her during induction ceremonies. Twenty-six years after she won the silver medal at Melbourne, she called being hosted and celebrated by the governor of her home state “the zenith of her career.”
Willye B. White died of pancreatic cancer in a Chicago hospital in 2007. While working on an obituary/column about her, I talked to the late, great Ralph Boston, the three-time Olympic long jump medalist from Laurel. They were Tennessee State and U.S. Olympic teammates. They shared a healthy respect from one another, and Boston clearly enjoyed talking about White.
At one point, Ralph asked me, “Did you know Willye B. had an even more famous high school classmate.”
No, I said, I did not.
“Ever heard of Morgan Freeman?” Ralph said, laughing.
Of course.
“I was with Morgan one time and I asked him if he ever ran track,” Ralph said, already chuckling about what would come next.
“Morgan said he did not run track in high school because he knew if he ran, he’d have to run against Willye B. White, and Morgan said he didn’t want to lose to a girl.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Early voting proposal killed on last day of Mississippi legislative session
Mississippi will remain one of only three states without no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting.
Senate leaders, on the last day of their regular 2025 session, decided not to send a bill to Gov. Tate Reeves that would have expanded pre-Election Day voting options. The governor has been vocally opposed to early voting in Mississippi, and would likely have vetoed the measure.
The House and Senate this week overwhelmingly voted for legislation that established a watered-down version of early voting. The proposal would have required voters to go to a circuit clerk’s office and verify their identity with a photo ID.
The proposal also listed broad excuses that would have allowed many voters an opportunity to cast early ballots.
The measure passed the House unanimously and the Senate approved it 42-7. However, Sen. Jeff Tate, a Republican from Meridian who strongly opposes early voting, held the bill on a procedural motion.
Senate Elections Chairman Jeremy England chose not to dispose of Tate’s motion on Thursday morning, the last day the Senate was in session. This killed the bill and prevented it from going to the governor.
England, a Republican from Vancleave, told reporters he decided to kill the legislation because he believed some of its language needed tweaking.
The other reality is that Republican Gov. Tate Reeves strongly opposes early voting proposals and even attacked England on social media for advancing the proposal out of the Senate chamber.
England said he received word “through some sources” that Reeves would veto the measure.
“I’m not done working on it, though,” England said.
Although Mississippi does not have no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting, it does have absentee voting.
To vote by absentee, a voter must meet one of around a dozen legal excuses, such as temporarily living outside of their county or being over 65. Mississippi law doesn’t allow people to vote by absentee purely out of convenience or choice.
Several conservative states, such as Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas and Florida, have an in-person early voting system. The Republican National Committee in 2023 urged Republican voters to cast an early ballot in states that have early voting procedures.
Yet some Republican leaders in Mississippi have ardently opposed early voting legislation over concerns that it undermines election security.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi Legislature approves DEI ban after heated debate
Mississippi lawmakers have reached an agreement to ban diversity, equity and inclusion programs and a list of “divisive concepts” from public schools across the state education system, following the lead of numerous other Republican-controlled states and President Donald Trump’s administration.
House and Senate lawmakers approved a compromise bill in votes on Tuesday and Wednesday. It will likely head to Republican Gov. Tate Reeves for his signature after it clears a procedural motion.
The agreement between the Republican-dominated chambers followed hours of heated debate in which Democrats, almost all of whom are Black, excoriated the legislation as a setback in the long struggle to make Mississippi a fairer place for minorities. They also said the bill could bog universities down with costly legal fights and erode academic freedom.
Democratic Rep. Bryant Clark, who seldom addresses the entire House chamber from the podium during debates, rose to speak out against the bill on Tuesday. He is the son of the late Robert Clark, the first Black Mississippian elected to the state Legislature since the 1800s and the first Black Mississippian to serve as speaker pro tempore and preside over the House chamber since Reconstruction.
“We are better than this, and all of you know that we don’t need this with Mississippi history,” Clark said. “We should be the ones that say, ‘listen, we may be from Mississippi, we may have a dark past, but you know what, we’re going to be the first to stand up this time and say there is nothing wrong with DEI.'”
Legislative Republicans argued that the measure — which will apply to all public schools from the K-12 level through universities — will elevate merit in education and remove a list of so-called “divisive concepts” from academic settings. More broadly, conservative critics of DEI say the programs divide people into categories of victims and oppressors and infuse left-wing ideology into campus life.
“We are a diverse state. Nowhere in here are we trying to wipe that out,” said Republican Sen. Tyler McCaughn, one of the bill’s authors. “We’re just trying to change the focus back to that of excellence.”
The House and Senate initially passed proposals that differed in who they would impact, what activities they would regulate and how they aim to reshape the inner workings of the state’s education system. Some House leaders wanted the bill to be “semi-vague” in its language and wanted to create a process for withholding state funds based on complaints that almost anyone could lodge. The Senate wanted to pair a DEI ban with a task force to study inefficiencies in the higher education system, a provision the upper chamber later agreed to scrap.
The concepts that will be rooted out from curricula include the idea that gender identity can be a “subjective sense of self, disconnected from biological reality.” The move reflects another effort to align with the Trump administration, which has declared via executive order that there are only two sexes.
The House and Senate disagreed on how to enforce the measure but ultimately settled on an agreement that would empower students, parents of minor students, faculty members and contractors to sue schools for violating the law.
People could only sue after they go through an internal campus review process and a 25-day period when schools could fix the alleged violation. Republican Rep. Joey Hood, one of the House negotiators, said that was a compromise between the chambers. The House wanted to make it possible for almost anyone to file lawsuits over the DEI ban, while Senate negotiators initially bristled at the idea of fast-tracking internal campus disputes to the legal system.
The House ultimately held firm in its position to create a private cause of action, or the right to sue, but it agreed to give schools the ability to conduct an investigative process and potentially resolve the alleged violation before letting people sue in chancery courts.
“You have to go through the administrative process,” said Republican Sen. Nicole Boyd, one of the bill’s lead authors. “Because the whole idea is that, if there is a violation, the school needs to cure the violation. That’s what the purpose is. It’s not to create litigation, it’s to cure violations.”
If people disagree with the findings from that process, they could also ask the attorney general’s office to sue on their behalf.
Under the new law, Mississippi could withhold state funds from schools that don’t comply. Schools would be required to compile reports on all complaints filed in response to the new law.
Trump promised in his 2024 campaign to eliminate DEI in the federal government. One of the first executive orders he signed did that. Some Mississippi lawmakers introduced bills in the 2024 session to restrict DEI, but the proposals never made it out of committee. With the national headwinds at their backs and several other laws in Republican-led states to use as models, Mississippi lawmakers made plans to introduce anti-DEI legislation.
The policy debate also unfolded amid the early stages of a potential Republican primary matchup in the 2027 governor’s race between State Auditor Shad White and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann. White, who has been one of the state’s loudest advocates for banning DEI, had branded Hosemann in the months before the 2025 session “DEI Delbert,” claiming the Senate leader has stood in the way of DEI restrictions passing the Legislature.
During the first Senate floor debate over the chamber’s DEI legislation during this year’s legislative session, Hosemann seemed to be conscious of these political attacks. He walked over to staff members and asked how many people were watching the debate live on YouTube.
As the DEI debate cleared one of its final hurdles Wednesday afternoon, the House and Senate remained at loggerheads over the state budget amid Republican infighting. It appeared likely the Legislature would end its session Wednesday or Thursday without passing a $7 billion budget to fund state agencies, potentially threatening a government shutdown.
“It is my understanding that we don’t have a budget and will likely leave here without a budget. But this piece of legislation …which I don’t think remedies any of Mississippi’s issues, this has become one of the top priorities that we had to get done,” said Democratic Sen. Rod Hickman. “I just want to say, if we put that much work into everything else we did, Mississippi might be a much better place.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
-

 Mississippi Today3 days ago
Mississippi Today3 days agoPharmacy benefit manager reform likely dead
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days ago
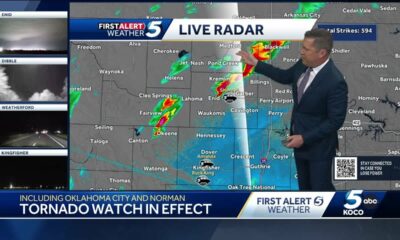
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days agoTornado watch, severe thunderstorm warnings issued for Oklahoma
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days agoGeorgia road project forcing homeowners out | FOX 5 News
-

 News from the South - West Virginia News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - West Virginia News Feed7 days agoHometown Hero | Restaurant owner serves up hope
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days agoTornado practically rips Bullitt County barn in half with man, several animals inside
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed7 days agoBudget cuts: Senior Citizens Inc. and other non-profits worry for the future
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days agoStrangers find lost family heirloom at Cocoa Beach
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoRepublicans look to maintain majority in Congress ahead of Florida special election