Mississippi Today
They Were Prosecuted for Using Drugs While Pregnant. But It May Not Have Been a Crime
This article was published in partnership with The Marshall Project, a nonprofit news organization covering the U.S. criminal justice system. Sign up for their newsletters, and follow them on Instagram, TikTok, Reddit and Facebook.
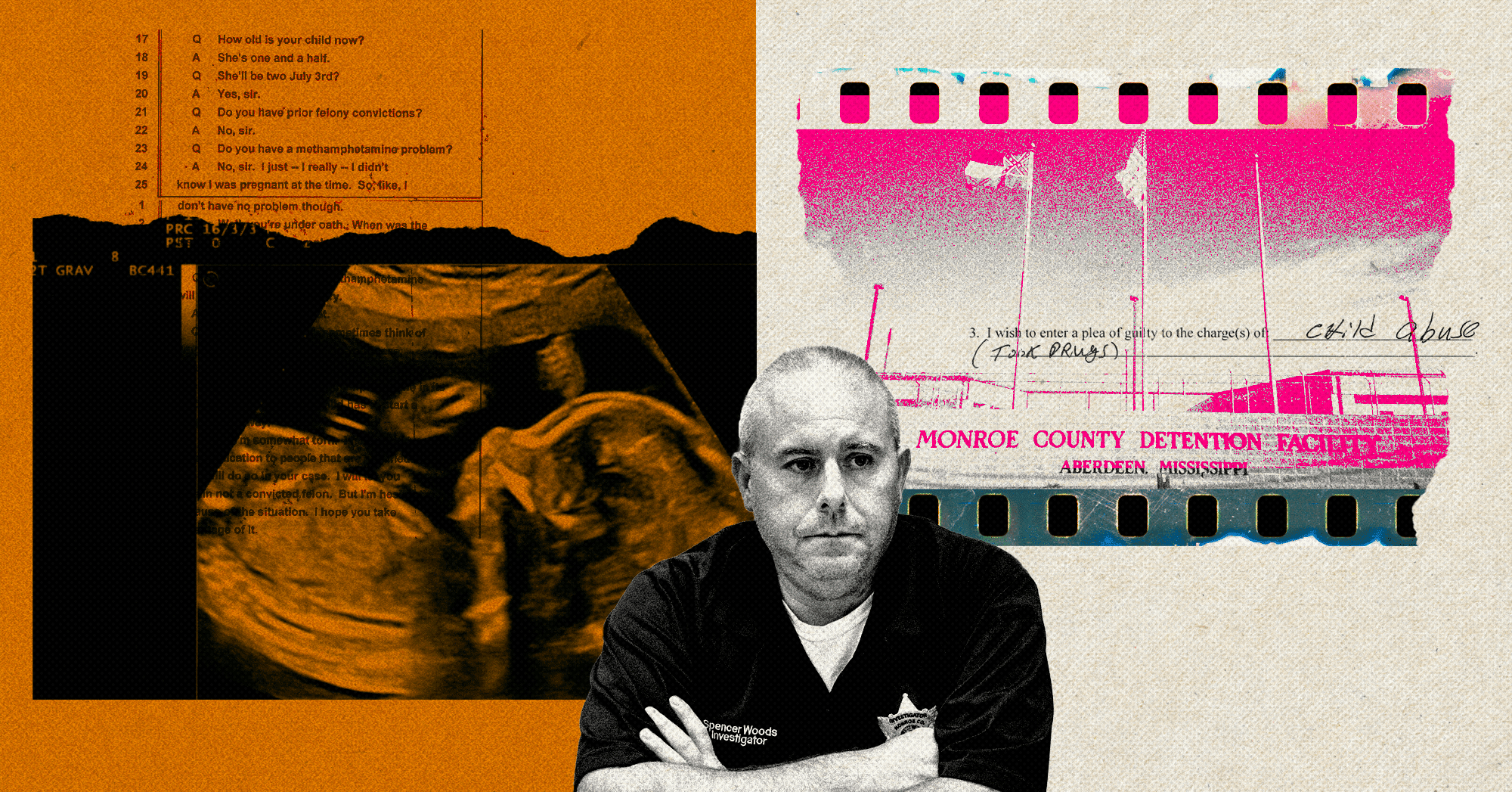
Spencer Woods wanted to fight a crime that didn’t exist.
As a sheriff’s investigator in Monroe County, Mississippi, near the Alabama border, he would occasionally receive reports from his state’s child protection agency that a baby had tested positive for illegal drugs at birth.
To Woods, the mothers had endangered their fetuses and should face criminal charges. But unlike some other southern states, Mississippi law doesn’t define a fetus as a person; in fact, voters had rejected a ballot measure to do just that more than a decade ago.
So when Woods would receive these referrals, he had to effectively place them in the trash.
“We were coming across those type [of] things that I considered to be child abuse, but as far as the statute, the state wasn’t recognizing that as actual child abuse,” Woods said in an interview.
That’s until 2019, when Woods decided that his office would take matters into its own hands and pursue child endangerment cases against the women anyway. He argued that child abuse can, in fact, take place inside the womb, challenging anyone to prove otherwise.
Through news reports and court records, Mississippi Today identified 44 cases in which law enforcement officers in Mississippi have arrested women for a crime that, based on existing state law, they may not have actually committed.
“The state of Mississippi does not look at a child as being a child until it draws its first breath,” Woods said. “Well, when that child tests positive when it’s born, the abuse has already happened, and it didn’t happen to a ‘child.’ So it was a crack in the system, the way I looked at it. And that’s where we’re kind of playing.”
While medical experts warn against drug use during pregnancy, they point out that not all babies exposed to drugs in the womb are born with medical problems. But Woods said that he doesn’t need evidence of harm to the fetus — just a positive drug test — to pursue a child endangerment case.
Monroe County has accounted for 12 of the 44 cases we found. Woods said he was unaware that 200 miles to the south of his jurisdiction, officials in Jones County had already been filing similar charges against mothers for years, Mississippi Today reported in 2019. All but three of the cases Mississippi Today identified from 2015 to 2023 came from Monroe and Jones, two small rural counties.
While Monroe County has offered leniency in keeping these women out of prison, Jones County’s lone judge, Circuit Court Judge Dal Williamson, has given at least six women long prison sentences for using drugs while pregnant. The difference in sentencing stems in part from the counties charging women under different sections of the child abuse law. Monroe County has utilized the child endangerment section that bars parents from allowing their children to be present around drugs, such as in meth labs. Meanwhile, Jones County has charged women in similar circumstances with poisoning their fetuses. Williamson ordered the women to serve between two and 15 years in prison.

“I don’t understand how in the world a mother expecting a child would continue to pour this poison in their body,” Williamson said at a sentencing last year, according to the local newspaper Laurel Leader-Call. “Your baby can’t say, ‘No, mama, stop.’”
Some local investigators and prosecutors are pursuing similar cases in Alabama, Oklahoma and South Carolina. They are policing pregnant people under an expanded interpretation of child abuse and neglect laws — even if parents birthed healthy babies, according to an investigation by The Marshall Project, Mississippi Today, AL.com, The Frontier and The Post & Courier.
Officials in Etowah County, Alabama, 185 miles to the east of Woods, are perhaps the champions of this approach, having arrested hundreds of women in the past several years.
Woods’ strategy has never been tested in court, because each of the 12 women his office has arrested have pleaded guilty under diversion or probation deals that keep them out of prison.
Defense lawyers said they would like to take a case to trial, but their clients are reluctant. “They’re not wanting to take that risk of going to trial and getting convicted because they’re all fighting to get their kids back,” said Luanne Thompson, one of two public defenders in Monroe County who has handled these cases. “That is the dilemma that they’re in.”
Most of Thompson’s clients have received “non-adjudicated” sentences, meaning they avoid prison and their records will be cleared if they satisfy the terms of their probation.
Public health experts fear that the threat of prosecution could dissuade pregnant people from seeking prenatal care at a time when the state is facing growing threats to the health of newborns. Mississippi has the highest infant mortality rate in the nation, at roughly 9 deaths per 1,000 live births.
Cases of infant hospitalizations in Mississippi related to drug exposure in the womb have skyrocketed from more than 300 cases in 2015, when Jones County began prosecuting these cases, to four times that in 2021, at a high of more than 1,200.
State Health Officer Daniel Edney has vowed to address these issues. His department compiled a recent report that identified the uptick in drug-exposed newborns. The report blamed the increase on changes in diagnostic coding at hospitals, as well as rising substance abuse due to the isolation and reduced access to therapy people experienced during the coronavirus pandemic.
But Edney, a longtime addiction specialist, was shocked to learn from recent reporting by The Marshall Project and Mississippi Today about local prosecutions of mothers not unlike his own patients.
“I thought, ‘This is archaic,’” Edney said. “There are a lot of medical conditions that if a pregnant mom doesn't take care of herself, it hurts the baby. This is the one disease that we’ll incarcerate a woman for.”
He warns that prosecuting moms with substance use disorders as child abusers will only deter them from seeking care, making it harder for the medical community to do its job.
“We don't need law enforcement going in to arrest women who are trying to get help,” Edney said. “It has a chilling effect on the women out there who are trying to decide what they need to do.”
Though Mississippi officials enacted and defended the state abortion prohibition that ultimately led to the U.S. Supreme Court overturning Roe v. Wade last year, the state does not recognize “fetal personhood.” In 2011, Mississippi voters rejected an amendment to the state constitution proposed by anti-abortion activists that would have defined a fertilized egg as a person.
The Mississippi Supreme Court has twice taken up the issue — through two cases in which local officers charged women with murder or manslaughter after losing their pregnancies in 2006 and 2009. Both times, justices wrote ambiguous opinions, and the lower courts ultimately threw charges out in both cases.
Mississippi’s abortion prohibition doesn’t criminalize pregnant people, nor does it treat abortion as murder. The law stipulates prison terms only for the person who performed the abortion, not the woman who sought it. Bills filed in the Mississippi Legislature to criminalize drug use while pregnant under the state’s child abuse statute have died with little attention. Despite those failed efforts, the sheriff’s investigator in Monroe County decided his department needed to act.
“We're eventually gonna have to deal with possibly the Supreme Court or possibly the state Legislature on changing the law, hopefully,” Woods said.
He said he realizes that his tactic may have implications for reproductive rights.
“I always had to keep that in the back of my mind, the Roe v. Wade type stuff, what women can do with their bodies,” Woods said. “That was never my argument. My argument was always what was best for the child. I discussed it with my assistant district attorney, who is a woman, and she had my back on this, and we went forward with it.”
But a growing body of research shows that what’s best for the health of newborns is critical bonding with their mother.
“We have to balance the health and safety of that baby while also trying to make sure that family stays connected,” said Dr. Anita Henderson, a Hattiesburg pediatrician and president of the Mississippi chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics. “If you’re trying to reunify families or make that mom or that family as healthy as possible, then the goal should be treatment. ... Incarceration and the threat of incarceration have proven to be ineffective.”
Christina Dent, who has cared for children in Mississippi’s foster care system as a result of their mothers’ drug addictions, supports the concept of fetal personhood and is personally against abortion. She’s also the founder of End It For Good, a nonprofit that advocates for the legalization of drugs. Dent’s group argues that criminalizing drugs only increases harm to people and society. She said that treating these mothers as criminals is “opposed to a pro-life ethic” and leads to worse outcomes for both the mother and baby.
“I would say, yes, that [fetus] is a child,” Dent said, speaking for herself and not on behalf of her organization. “And because of that, shouldn’t we do everything possible to protect that child from further harm, help the mother access prenatal care, and protect the bond of this little family?”
Monroe County Sheriff Kevin Crook has earned a reputation for taking a compassionate approach to drug offenses, placing an emphasis on treatment and rehabilitation. In Crook’s view, though, the threat of prison motivates people to take recovery seriously.
“We gotta have something for these people to run into,” Crook said, “or they're not just gonna stop on their own.”
Woods agreed. “I'm not really trying to put these women in prison,” he said. “What I'm trying to do is correct the issue. We do offer counseling and rehab and those types of things.”
But the investigator acknowledged there’s never enough mental health services to cover the need. He also couldn’t say how effective his strategy is; he doesn’t have any data to show how many mothers he’s arrested have gotten clean or reunited with their children.
Woods said he also believes that smoking or drinking alcohol while pregnant — which can produce similar if not more harmful effects as controlled substances on a fetus’ development — constitutes child abuse.
He’s aware his approach could be applied to other activities that might endanger a fetus. “Of course, you keep going, ‘You're eating too much sugar. You’re ingesting too much caffeine.’ Where do you stop with it?” Woods said.
He draws the line at illegal substances. “I have to go by statutes,” he said. “I can’t just decide what I want to.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1873, La. courthouse scene of racial carnage
April 13, 1873

On Easter Sunday, after Reconstruction Republicans won the Louisiana governor’s race, a group of white Democrats vowed to “take back” the Grant Parish Courthouse from Republican leaders.
A group of more than 150 white men, including members of the Ku Klux Klan and the White League, attacked the courthouse with a cannon and rifles. The courthouse was defended by an all-Black state militia.
The death toll was staggering: Only three members of the White League died, but up to 150 Black men were killed. Of those, nearly half were killed in cold blood after they surrendered.
Historian Eric Foner called the Colfax Massacre “the bloodiest single instance of racial carnage in the Reconstruction era,” demonstrating “the lengths to which some opponents of Reconstruction would go to regain their accustomed authority.”
Congress castigated the violence as “deliberate, barbarous, cold-blooded murder.”
Although 97 members of the mob were accused, only nine went to trial. Federal prosecutors won convictions against three of the mob members, but the U.S. Supreme Court tossed out the convictions, helping to spell the end of Reconstruction in Louisiana.
A state historical marker said the event “marked the end of carpetbag misrule in the South,” and until recent years, the only local monument to the tragedy, a 12-foot tall obelisk, honored the three white men who died “fighting for white supremacy.”
In 2023, Colfax leaders unveiled a black granite memorial that listed the 57 men confirmed killed and the 35 confirmed wounded, with the actual death toll presumed much higher.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Lawmakers used to fail passing a budget over policy disagreement. This year, they failed over childish bickering.
It is tough to determine the exact reason the Mississippi Legislature adjourned the 2025 session without a budget to fund state government, which will force lawmakers to return in special session to adopt a spending plan before the new fiscal year begins July 1.
In a nutshell, the breakdown seemed to have occurred when members of the Senate got angry at their House counterparts because they were not being nice to them. Or maybe vice versa.
Trying to suss this reasoning out is too difficult. The whole breakdown is confusing. It’s adolescent.
Perhaps there’s no point in trying to determine a reason. After all, when preteen children get mad at each other on the playground and start bickering, does it serve any purpose to ascertain who is right?
During a brief time early in the 2000s, when the state had the semblance of a true two-party system, the Legislature often had to extend the session or be called back in special session to finish work on the budget.
During those days, though, the Democrat-led House, the Republican-controlled Senate and the Republican governor were arguing about policy issues. There were often significant disagreements then over, say, how much money would be appropriated to the public schools or how Medicaid would be funded.
Now, with Republicans holding supermajorities over both the House and the Senate and a Republican in the Governor’s Mansion, the disagreements do not seem to rise to such legitimate policy levels.
It appears the necessity of a special session this summer is the result of House leaders not wanting to work on a weekend. And actually, that seemed like a reasonable request. It has always been a mystery why the Legislature could not impose earlier budget deadlines keeping lawmakers from having to work every year on a weekend near the end of the session.
But there were rumblings that if the House members did not want to work on the weekend, they should have been willing to begin budget negotiations with senators earlier in the session.
In fairness and to dig deeper, there also was speculation that the budget negotiations stalled because senators were angry that the House leadership was unwilling to work with them to fix mistakes in the Senate income tax bill. Instead of working to fix those mistakes in the landmark legislation, the House opted to send the error-riddled bill to the governor to be signed into law — because after all, the mistakes in the bill made it closer to the liking of the House leadership and Gov. Tate Reeves.
In addition, there was talk that House leaders were slowing budget negotiations by trying to leverage the Senate to pass a litany of bills ranging from allowing sports betting outside of casinos to increasing school vouchers to passing a traditional pet projects or “Christmas tree” bill.
The theory was that the House was mad that the Senate was balking on agreeing to pass the annual projects bill that spends state funds for a litany of local projects. For many legislators, particularly House members, their top priority each year is to bring funds home to their district for local projects, and not having a bill to do so was a dealbreaker for those rank-and-file House members.
To go another step further, some claimed senators were balking on the projects bill because of anger over the aforementioned tax bill. Another theory was that the Senate was fed up with House Ways and Means Chair Trey Lamar sneaking an inordinate number of projects in the massive bill for his home county of Tate.
But as stated earlier, does the reason for the legislative impasse really matter? The bottom line is that it appears that the reason for legislators not agreeing on a budget had nothing to do with the budget itself or disagreement over how much money to appropriate for vital state services.
House and Senate budget negotiators apparently did not even meet at the end of the session to fulfill the one task the Mississippi Constitution mandates the Legislature to fulfill: fund state government.
As a result, lawmakers will have to return to Jackson this summer in a costly special session not because of big policy issues, such as how to fund health care or how much money to plow into the public schools, but because “somebody done somebody wrong.”
Those big fights of previous years are less likely today because of the Republican Party grip on state government. The governor, the speaker and the lieutenant governor agree philosophically on most issues.
But in the democratic process, people who are like-minded can still have major disagreements that derail the legislative train — even if those disagreements are over something as simple as whether members are going to work during a weekend.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1864, Confederates kill up to 300 in massacre
The post On this day in 1864, Confederates kill up to 300 in massacre appeared first on mississippitoday.org
-

 News from the South - Louisiana News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed7 days agoNew Orleans police investigating hit-and-run crash in Seventh Ward; family says grandmother was hurt
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed7 days agoVersailles asked to conserve water, county steps in to help
-

 News from the South - Louisiana News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Louisiana News Feed6 days agoCrime scene shocks St. Tammany Trace residents as sheriff's investigation continues
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed5 days agoLocals react to Cara Spencer winning mayoral race
-

 News from the South - Arkansas News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed4 days agoArkansas State Police launches new phone-free campaign
-

 Mississippi Today6 days ago
Mississippi Today6 days agoOn this day in 1918, Harlem Hellfighters joned France in WWI
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoInvestigators continue search for Florida child missing since 2006
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed5 days agoProposal: Farm property tax break on solar from 80% to zero | North Carolina