Mississippi Today
Mississippi Medical Association has not always been out front on state’s health care issues

In 2002, during the 83-day special session, the longest in state history, members of the Mississippi Medical Association were out in full force in favor of legislation to provide health care providers more protection from lawsuits.
The Medical Association, the largest organization of physicians in the state, had members in their white coats at the Mississippi Capitol aggressively lobbying lawmakers.
They won.
A few years later, the white-coated members were nowhere to be seen at the Capitol as various groups ranging from the American Cancer Society to the American Heart Association and many more were lobbying lawmakers for an increase in the 18-cent per pack tax on cigarettes, which was the third lowest in the nation and significantly below the national average.
The groups argued that multiple studies had found it was good for the state’s public health to increase the tax on cigarettes. And various studies had confirmed that higher taxes on cigarettes were a deterrent to smoking, especially among teenagers.
Then-Gov. Haley Barbour, a former tobacco lobbyist, blocked all efforts to increase the cigarette tax — and even the bipartisan effort led by Republican Lt. Gov. Amy Tuck to reduce the grocery tax to offset that lost revenue by increasing the cigarette tax.
The Medical Association, which was quiet on the issue, had long supported Barbour.
In Barbour’s second term, he finally acquiesced to an increase in the cigarette tax, but not a reduction in the grocery tax. But at a meeting of legislative leaders where the cigarette tax increase was announced, the head of the Mississippi Medical Association was sitting front and center.
When asked what he was doing at the meeting, he replied his group had been working for years to increase the cigarette tax. As the old saying goes, nobody knows what goes on behind closed doors, but members of the Medical Association were far from front and center on the issue like they had been on efforts to garner themselves more protection from lawsuits.
This year the Medical Association — or at least its political action committee — has endorsed Tate Reeves for governor. Reeves, like Barbour in the early 2000s, is blocking a proposal that many other health care groups argue would help improve health care in the state.
Reeves has adamantly rejected pleas from numerous groups to expand Medicaid with the federal government paying at least 90% of the costs to provide health care to primarily the working poor. Heck, while not uttering the words Medicaid expansion, even the aforementioned Mississippi Medical Association has voiced support for expanding Medicaid.
In January 2002, the Medical Association wrote: “The fact is, there is a sizable gap that exists for working Mississippians who cannot afford private health insurance, yet whose income is too much to qualify for Mississippi Medicaid. When these individuals need healthcare, hospitals are required to treat them regardless of their ability to pay. And because these individuals are uninsured, the hospital is not compensated for this necessary care. Such an economical strain on hospitals is one that even the most successful private business could not endure.”
In the same opinion piece, the Medical Association offered some “considerations” it said should be enacted.
They include a “raise the income eligibility for Medicaid.” Raising the income level is the very definition of expanding Medicaid. And if that is not enough, the Medical Association also proposed considering “the Arkansas model to provide access to care for working Mississippians through the purchase of private insurance for qualified recipients.” The Arkansas model has been approved by the federal government, which pays the bulk of the costs as a form of Medicaid expansion.
When asked if the endorsement of Reeves meant the Medical Association was giving up on Medicaid expansion, Dr. James Rish, chair of the Medical Association’s political action committee, replied via email: “We look forward to further discussion and engagement with Gov. Reeves to address the many healthcare challenges in our state, including improving accessibility, affordability, and the overall statewide healthcare delivery system for all Mississippians.”
If history is an indicator, one thing is for sure: members of the Medical Association will be sitting front and center when and if Medicaid is ever expanded, just as they were when the cigarette tax was finally increased.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
On this day in 1947, Jackie Robinson broke MLB color barrier
April 15, 1947

Jackie Robinson broke through the color barrier in Major League Baseball, becoming the first Black player in the 20th century.
Born in Cairo, Georgia, Robinson lettered in four sports at UCLA – football, basketball, baseball and track. After time in the military, he played for the Kansas City Monarchs in the Negro Leagues. After his success there, Dodgers general manager Branch Rickey signed Robinson, and the legendary baseball player started for Montreal, where he integrated the International League.
In addition to his Hall of Fame career, he was active in the civil rights movement and became the first Black TV analyst in Major League Baseball and the first Black vice president of a major American corporation.
In recognition of his achievements, Robinson was posthumously awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom and the Congressional Gold Medal.
Major League Baseball retired his number “42,” which became the title of the movie about his breakthrough.
Ken Burns’ four-hour documentary reveals that Robinson did more than just break the color barrier — he became a leader for equal rights for all Americans.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Mississippians highlight Black Maternal Health Week
Advocates and health care leaders joined lawmakers Monday morning at the Capitol to recognize Black Maternal Health Week, which started Friday.
The group was highlighting the racial disparities that persist in the delivery room, with Black women three times more likely to die of a pregnancy-related cause than white women.
“The bond between a mother and her baby is worth protecting,” said Cassandra Welchlin, executive director of the Mississippi Black Women’s Roundtable.
Rep. Timaka James-Jones, D-Belzoni, spoke about her niece Harmony, who suffered from preeclampsia and died on the side of the road in 2021 along with her unborn baby, three miles from the closest hospital in Yazoo City.
“It’s utterly important that stories are shared – but realize these are not just stories. This is real life,” she said.
The tragedy inspired James-Jones to become a lawmaker. She says she is working on gaining support to appropriate the funds needed to build a standalone emergency room in Belzoni.
But it isn’t just emergency medical care that’s lacking for some mothers. Mental health conditions are a leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, defined as deaths up to one year postpartum from associated causes.
And more than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable – making the issue ripe for policy change, advocates said.
“About 20 years ago, I was almost a statistic,” said Lauren Jones, a mother who founded Mom.Me, a nonprofit seeking to normalize the struggles of motherhood through community support. “I contemplated taking my life, I severely suffered from postpartum depression … None of my physicians told me that the head is connected to the body while pregnant.”
With studies showing “mounting disparities” in women’s health across the United States – and Mississippi scoring among the worst overall – more action is needed to halt and reverse the inequities, those at the press conference said.
The Mississippi Legislature passed four bills related to maternal health between 2018 and 2023, according to a study by researchers at the University of Mississippi Medical Center.
“How many times are we going to have to come before committees like this to share the statistics before the statistics become a solution?” Jones asked.
A bill that would require health care providers to offer postpartum depression screenings to mothers is pending approval from the governor.
Rep. Zakiya Summers, D-Jackson, the organizer of the press conference, commended the Legislature for passing presumptive eligibility for pregnant women this year. The policy will allow women to receive health care covered by Medicaid as soon as they find out they are pregnant – even if their Medicaid application is still pending. It was spearheaded by Rep. Missy McGee, R-Hattiesburg.
Summers also thanked Rep. Kevin Felsher, R-Biloxi, for pushing paid parental leave for state employees through the finish line this year.
Speakers emphasized the importance of focusing Black Maternal Health Week not just on mitigating deaths but on celebrating one of life’s most vulnerable and meaningful events.
“Black Maternal Health Week is a celebration of life, since Black women don’t often get those opportunities to celebrate,” said Nakeitra Burse, executive director of Six Dimensions, a minority women-owned public health research agency. “We go into our labor and delivery and pregnancy with fear – of the unknown, fear of how we’ll be taken care of, and just overall uncertainty about the outcomes.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Trump to appoint two Northern District MS judges after Aycock takes senior status
President Donald Trump can now appoint two new judges to the federal bench in the Northern District of Mississippi.
U.S. District Judge Sharion Aycock announced recently that she was taking senior status effective April 15. This means she will still hear cases as a judge but will have a reduced caseload.
“I have been so fortunate during my entire legal career,” Aycock said in a statement. “As one of only a few women graduating in my law school class, I had the chance to break ground for the female practitioner.”
A native of Itawamba County, Aycock graduated from Tremont High School and Mississippi State University. She received her law degree from Mississippi College, where she graduated second in her class.
Throughout her legal career, she blazed many trails for women practicing law and female jurists. She began her career as a judge when she was elected as a Mississippi Circuit Court judge in northeast Mississippi in 2002, the first woman ever elected to that judicial district.
She held that position until President George W. Bush in 2007 appointed her to the federal bench. After the U.S. Senate unanimously confirmed her, she became the first woman confirmed to the federal judiciary in Mississippi.
This makes Aycock the second judge to take senior status in four years. U.S. District Judge Michael Mills announced in 2021 that he was taking senior status, but the U.S. Senate still has not confirmed someone to replace him.
President Joe Biden appointed state prosecutor Scott Colom to fill Mills’ vacancy in 2023. U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker approved Colom’s appointment, but U.S. Sen. Cindy Hyde-Smith blocked his confirmation through a practice known as “blue slips,” where senators can block the confirmation of judicial appointees in their home state.
This means President Trump will now have the opportunity to appoint two federal judges to lifetime appointments to the Northern District. U.S. District Judge Debra Brown will soon be the only active federal judge serving in the district. Aycock, Mills, and U.S. District Judge Glen Davidson will all be senior-status judges.
Federal district judges provide crucial work to the federal courts through presiding over major criminal and civil trials and applying rulings from the U.S. Supreme Court and the U.S. Court of Appeals in the local districts.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
-

 News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed7 days agoArkansas State Police launches new phone-free campaign
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed7 days ago
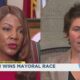
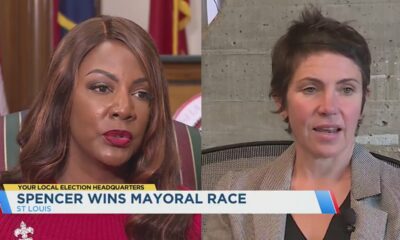
News from the South - Missouri News Feed7 days agoLocals react to Cara Spencer winning mayoral race
-

 News from the South - Arkansas News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Arkansas News Feed5 days agoMeasles cases confirmed in Arkansas children after travel exposure
-

 News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Missouri News Feed6 days agoSleeping 14-year-old critically injured by bullet in Ferguson home; father flees scene
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days agoImpacts of Overdraft Fees | April 11, 2025 | News 19 at 10 p.m.
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed6 days agoTax Day of April 15 is essentially May 1 in North Carolina | North Carolina
-

 Mississippi Today5 days ago
Mississippi Today5 days agoA self-proclaimed ‘loose electron’ journeys through Jackson’s political class
-

 News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days agoKSAT's Patty Santos speaks with Poteet Strawberry Festival court members, organization VP