Mississippi Today
Months after a sacred site was vandalized, Choctaw officials still seek answers

Earlier this year, Amanda Bell and her family planned a visit to Nanih Waiya.
Located in southern Winston County between the Crystal Ridge and Bogue Chitto Choctaw communities, the Nanih Waiya mound is “the heartbeat of the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians,” said Bell, who is manager and Choctaw archivist of the Chahta Immi Cultural Center in Philadelphia.
The trip to the mound was meant to be a moment for reflection and family, but it quickly devolved into a horrific and saddening day instead.
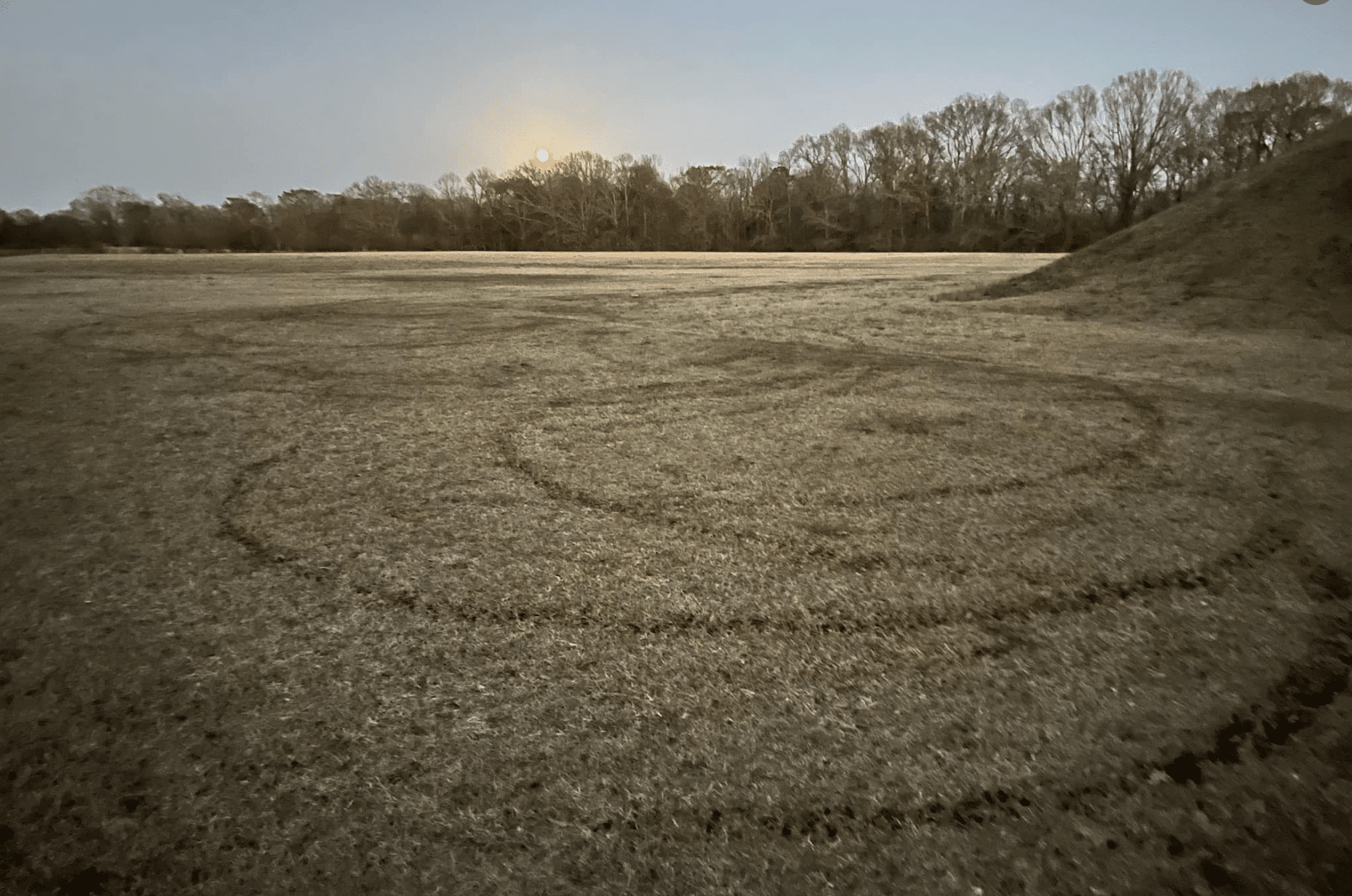
As they arrived at the site in February, Bell and her family found destruction: donut tire tracks on and around the mount, litter and bottles of alcohol strewn around the sacred site.
The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians Department of Public Safety posted photos of the vandalism, along with a request for information on Facebook after Bell and her family discovered what happened.
“Nanih Waiya Mound is a sacred and important landmark of the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians,” the post reads. “It is an area that should be respected by all people who visit. We are saddened to hear that our sacred Mound grounds was vandalized recently.”
Months later, the search for the vandals continues.

‘The Mother Mound‘
Nanih Waiya, which means “leaning hill,” is 25 feet high, 618 feet long and 140 feet wide, roughly matching the earliest recorded descriptions of the site.
Originally, the mound also included a ramp, which has now been destroyed. While Nanih Waiya itself has received only minimal damage across the centuries, the entire site has not been as fortunate. Several small burial mounds, which have now been nearly leveled by plowing, are several yards from Nanih Waiya, while a raised embankment and a moat once circled the site.
Nanih Waiya is prominently featured in the two Choctaw creation stories.
In one, each of the Southeastern Indigenous nations emerged from Nanih Waiya. After spending some time near the mound, they eventually went in their various directions, becoming the Creek, Cherokee and Chickasaw Nations. The Choctaw were the last to emerge from the mound. Once they did so, unlike the other nations, they saw that the “Mother mound,” had birthed them in a good place. They decided not to leave.
In the other legend, Choctaw ancestors came from the West, looking for a place to resettle. Each night of their travels, a Miko, or chief, placed a pole in the ground. The group would continue on in the direction in which the pole leaned the next day. When they reached Nanih Waiya, the pole remained upright, thus it was determined by the Choctaw ancestors that this is where they would remain.
Nanih Waiya represents not only the MBCI’s history but its resiliency. Despite its status as a sacred site — one Choctaw people fought to protect and retain even as early European settlers took more and more of their land — the U.S. took Nanih Waiya, along with about 11 million acres of what is now Mississippi, from the Choctaw people in 1830 with the signing of the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek.
After eight previous treaties between the Choctaw and the United States, the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was the last. It was also the first removal treaty, carried into effect under the Indian Removal Act, sparking the Trail of Tears. In exchange for their home, the Choctaw received about 15 million acres in what is now Oklahoma. About 15,000 Choctaws left Mississippi for Oklahoma.
But not all Choctaws participated in the Trail of Tears.
Several thousand stayed in Mississippi and, in doing so, experienced decades of retaliation and intimidation. In 1945, those who stayed behind formed the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, the only federally recognized American Indian tribe in Mississippi. In 2007, with one nay vote in the House, the Mississippi Legislature passed SB 2732, returning Nanih Waiya to the MBCI after nearly 200 years.
Miko Beasley Denson and 17 Tribal Council members signed a proclamation in 2008, saying that the mound was never to be taken from the Choctaw people again, Bell said. In celebration of this, the MBCI celebrates Nanih Waiya Day the second Friday in August.

‘I hope they learn their lesson’
Once they arrived at the site, Bell said they noticed tire tracks in the shape of a donut on the left side of the mound. In one area, it seemed as if someone had attempted to drive up the side of the mound. Trash, including a cardboard box, liquor bottles, beer cans and cigarettes, were scattered about the sacred site. The “Mother Mound” seemed to have been used not for ceremony or contemplation, but for debauchery.
Months later, Bell is still seeped in sadness when recalling the vandalism.
“How could they disrespect this sacred site? To this day, they haven’t found the person or persons that committed that,” she said.
But Bell is hopeful that the story doesn’t end there.
She hopes that bringing attention to the harm the vandals caused will prevent similar instances in the future, and that it will encourage all Mississippians to learn about the state’s first inhabitants.
“It was sad and a bit of a heartbreak,” she said. “The person that did this, well, they’ve gotten away with it. I hope that they learn their lesson that this is a sacred site … I hope it will open eyes to others that it needs to be respected. It’s not just a hill, it’s a mound. It’s the Mother mound and a sacred space where the early Choctaws settled.”
Note: If you have any information about the vandalism, contact the Choctaw Police Department at 601-656-5711 or the Attorney General’s Office at 601-656-4507. You can anonymously share information by calling or texting 844-601-1308.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Did you miss our previous article…
https://www.biloxinewsevents.com/?p=274830
Mississippi Today
Program helps students with disabilities forge paths to careers
‘I wouldn’t have found them otherwise’: Program helps students with disabilities forge paths to careers
Matthew Devers, 18, describes his current job as “very brute force.” He’s in a welding program, working part time while completing his associates degree at Mississippi Gulf Coast Community College.
He says it wouldn’t have been possible without the pre-employment training and services program he joined after high school. Pre-ETS is a program that provides students with disabilities education and experience to help them enter post-secondary education and/or the workforce. Devers, who is autistic, says “I wouldn’t have found them otherwise.”
People with disabilities make up 13% of the country’s population as of 2024. The employment rate for people with disabilities is lower than for people without. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the 2024 employment-population ratio for disabled people between 16 to 24 years old is 37.4%. By comparison, the employment rate for non-disabled people is 65.8%.
Pre-ETS provides job exploration and counseling, work-based learning experiences, counseling opportunities for enrollment in comprehensive transition or postsecondary education programs, workplace readiness training, and instruction in self-advocacy.
In 2014, Congress amended The Rehabilitation Act of 1973 through the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act, expanding the population of students with disabilities that vocational rehabilitation agencies may serve. This gave birth to the pre-ETS program, which is funded by state vocational rehabilitation agencies.
Nationally, pre-ETS services are underutilized. The Hechinger Report found that in 2023, 295,000 students were using pre-ETS when it’s estimated that 3.1 million were eligible. Often, the report found, parents are even aware it exists.
The Office of Vocational Rehabilitation is currently serving 3,382 students, 2,053 of whom are in the pre-ETS program. How many it could potentially serve isn’t known, but the Mississippi Department of Education said there are 20,994 students between the ages of 14 and 21 in special education. That’s the age group pre-ETS serves.
If aware of pre-ETS, families can request thatfor their child to join the program through a school counselor or school transition staff. If the student doesn’t have an open vocational rehabilitation case, they can reach out to a local VR transition counselor or vocational rehabilitation for the blind counselor.
Jennifer Jackson, the executive director of the Office of Vocational Rehabilitation, said she is optimistic about the direction of pre-ETS in Mississippi. “I feel like our state is constantly improving and constantly seeking out ways to help these individuals be successful,” she said.
The recent cost-cutting measures from the Trump administration have alarmed some disability rights advocates. As part of its sweeping cost-cutting spree, the Department of Government Efficiency, or DOGE, canceled at least two grants researching school-to-work transition services for youth with disabilities, including two multimillion-dollar contracts for studies on outcomes for students with disabilities after high school graduation.
“While we are aware that staffing changes have taken place within the Department of Education (DE), where RSA is housed, we have not been informed of any direct impact to Vocational Rehabilitation (VR) funding at this time,” Jackson said in a statement. RSA refers to the Rehabilitation Services Administration.
Jackson said these services provide essential help for young people with disabilities who often struggle learning skills that people are not disabled can take for granted. She said they’re also key for improving employment outcomes for people with disabilities.

To be eligible, a student must: be between ages 14 to 21; have a documented disability, 504 plan to ensure the child receives accommodations and access to the learning environment; or Individualized Education Program plan; and be enrolled in a recognized educational program. Applicants must complete a Pre-ETS Referral Form, have a parent or guardian sign a release of information, and have a copy of the student’s documented disability, 504 plan, or IEP plan.
OVR partners with 13 organizations and nonprofits across Mississippi to deliver pre-ETS programs. One of them is the Transition to Adulthood Center on Learning, the same program Devers was in. The center is part of the Institute for Disability Studies at the University of Southern Mississippi.
Beth Robertson, the center’s executive coordinator for transition, described the program as a collaboration between families, schools and state agencies. “We can always work together even more, increase our involvement more, we would love to see that,” she said.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Government secrecy tends to bite Mississippi in the butt. It’s happened again
The state Senate Republican leadership didn’t plan to fail on a Mississippi tax overhaul. It failed to plan.
And when pressed late in the 2025 legislative session to come up with a proposal to counter the House Republican leadership’s sweeping bill, Senate leaders did so behind closed doors and hurriedly.
The result: a majority of legislators passing a tax overhaul bill full of math errors that accidentally did what Senate leaders didn’t want. And it stripped out safeguards for taxpayers that both the House and Senate leadership said were prudent.
No matter how much Gov. Tate Reeves praises House Bill 1 as “one big, beautiful bill,” borrowing a phrase from President Trump as he signed it into law, it was passed through secrecy, subterfuge and error, not representative democracy.
Had the Senate perhaps taken a little more time, allowed more input from and access to its strategizing from rank-and-file lawmakers, and who knows, maybe even a little crowd-sourcing allowing the public to scrutinize the bill before passing it, maybe the blunder could have been prevented.
READ MORE: OOPS! Senate sent House an income tax bill with typos. House ran with it. What’s next?
And while House leaders should receive praise for coming up with an initial public-facing tax overhaul plan through months of public hearings and forums, that’s not what was passed into law. House leaders played a game of secret squirrel to pass the Senate’s mistakes into law. Then instead of negotiating in good faith to fix the problems, House leaders tried to shanghai the Senate in backroom negotiations to pass a few plums they wanted, such as legalized online sports betting and a sales tax increase.
The end result: Historically bitter infighting among state GOP leaders to the point they couldn’t even pass a state budget, their main job. And we have communications between Mississippi’s top legislative leaders and governor, all Republicans, that these days are often reduced to mean tweets or Facebook posts about each other, not earnest negotiations.
READ MORE: The Typo Tax Swap Act of 2025 may be the most Mississippi thing ever
Mississippi government’s default setting is secrecy, from public records and meetings to access to elected officials, and it has never served our citizens well. From a black-ops agency that spied on its citizens for nearly two decades to festering, generational government corruption that has cost taxpayers hundreds of millions of dollars, secrecy is neither good politics nor good policy.
Major, sweeping state policy should be conducted in the open and with public input. But as the national and world economies plunge into turmoil that is sure to impact Mississippi, our new tax code lacks safeguards that both House and Senate leaders said were needed — all because of secrecy and lack of planning and communication.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Mississippi Today
Ward 6 council candidates face the image of south Jackson versus the reality
Driving down roads in south Jackson in recent weeks, residents were inundated with placards of smiling faces and names in bright, bold fonts of people hoping to be the next Ward 6 councilman.
In some neighborhoods, the streets were as littered with campaign signs as they are overgrown lots and abandoned properties in between neatly kept homes.
“The homes in the surrounding area and businesses in Ward 6 have been decimated. It looks like a bomb went off,” said Sylvia Walker, Ward 6 board member for the Jackson Association of Neighborhoods. “We’ve seen the businesses hollow out and nothing come back in. It’s disheartening. It’s sad.”
Walker said the image of south Jackson must be interrogated. Not enough people are talking about the good happening in Ward 6, she said.
“South Jackson is very diverse and not just one specific area,” said Walker. “I think the biggest misconception is that south Jackson is just full of dilapidated homes, and the people are poverty-stricken and destitute, and that’s not true.”
Ward 6 has the largest population of Jacksonians, with just over 23,000 people. It also has the highest number of Black residents, according to data from the City of Jackson’s website.
Jackson also has a high number of abandoned properties owned by the state. According to data from the Secretary of State’s office, there are about 1,900 tax-forfeited properties in the City of Jackson.
There will be a Democratic runoff on April 22 between two candidates for the Ward 6 city council seat. Emon Thompson Sr. garnered 714 votes and Lashia Brown-Thomas came in second with 652 votes. Voter turnout was low, with less than 3,200 votes cast in a ward with a voting age population of more than 16,000. There were nine contenders for the coveted council seat, more than any other council race.
Candidates for the coveted Ward 6 seat envision a more beautiful, thriving south Jackson. After a stacked primary, two candidates have made it to the runoff to replace Aaron Banks, former council person who faces criminal charges for allegedly accepting cash bribes in exchange for his vote on a development project. He pleaded not guilty.
Banks is familiar with the image problem in south Jackson. He said he’s made progress with more demolitions and landscaping work done than others in the past. This includes the demolition of Casa Grande Apartments and Appleridge Shopping Center.
“I’ve always said that I would serve two terms, and we got a lot of work done,” Banks said in a recent interview with Mississippi Today.
Brown-Thomas said that crime and blight are the biggest issues affecting Ward 6. The law enforcement officer wants to hold people accountable for their part in the perceived image of a decaying south Jackson.
“The city has codes, and if these people are not holding up to the codes, they need whatever punishment there is,” Brown-Thomas said. “If they aren’t holding the property up, then they should not have the property.”
She said that if she’s elected, she’ll work to get police officers higher wages, and will remain transparent and available to constituents.
“It’s not going to happen overnight, but it will take some time,” Brown-Thomas said. “I’m not saying it’s going to come in a year, not even two years, but we have to address the issues first, then everything else will fall in line.”

Thompson Sr., a business owner and retired veteran, said that a lot of the issues with blight comes down to enforcement.
“We need to, first of all, clean up our blighted properties by using the laws that we already have,” Thompson said. “The city already has ordinances with enough teeth to deal with blight.”
South Jackson voters don’t turn out like they should, he said, which can lead to a distrust in the system. He hopes, if elected, to be able to reach constituents where they are and keep them a part of the process in restoring their communities, like water improvement or curbing crime.
“Out of the 40 something thousand people that’s in south Jackson, maybe 3,900 people vote in the municipal elections,” he said. “They don’t have faith in the government anymore.”
“…If there’s a reason why we’re not getting any services out here, then I want to make sure I communicate that with a constituent so they can continue to have hope,” he said.
Representative Ronnie Crudup, Jr., D-Jackson, said that residents’ migration out of Jackson creates bigger issues for communities.
“To me, blight is just a symptom of a larger problem. The people are leaving the city of Jackson, and the population is decreasing,” Crudup said. “When people leave the properties, you end up with squatters and vagrants who move into these properties and tear them up.”
Crudup has been renovating and demolishing blighted properties in south and west Jackson for nearly eight years. So far, he said he’s renovated about 35 homes.
“Even though we are demoing and tearing down one or two properties, when people leave, that leaves other ones there,” he said. “You got all these blighted properties all around south and west Jackson, and some even in parts of north Jackson now, because people are leaving.”
He said the one thing that’s needed most: more funding from all levels of government for blight mitigation work.
“There needs to be more money from the legislature, but there needs to be more money allocated from the city council too,” Crudup said. “I think the city is going to have to take clean up efforts to a higher circumstance, and let the legislature see that they’re serious about this, and also get the county involved and let them know ‘Hey, we need all the help we can get.’”
And, the perception that city leaders have abandoned south Jackson is not necessarily right. Former Jackson Mayor Harvey Johnson said that blight is an issue that affects not only south Jackson but all parts of the city. Mitigating blight is going to take an intergovernmental approach, he said.
“I know that in some cases, some people feel they’ve been sort of abandoned, but I don’t think that’s the case,” Johnson said. “It may be a lack of resources to attack the problem and it’s going to require all governments to work together.”
Walker said she remembers when the city’s southern boundary changed and her neighborhood, which had been part of Byram, came inside Jackson city limits. A small portion of her ward was annexed by the city of Jackson in 2006 as part of Byram’s reincorporation. In the last couple of decades, she said she’s seen people be forced out of their homes due to the recession. Others simply chose to leave.
“We’ve had a turnover, but the neighborhood is still relatively stable,” Walker said. “When we moved in, a lot of people moved out.”
Walker said that while her neighborhood isn’t struck by blight, she sees abandoned properties while making her way through the community and near her church.
When thinking of a candidate that she would want to vote for, Walker said she’s looking for a good communicator who can be an advocate for the ward.
“We need someone that’s forward thinking. Someone that has the best interests of the residents of south Jackson and an understanding of the vast diversity of the ward,” she said. “Someone that’s able to work with other members of the City Council. Someone able to work with our board of supervisors and state legislators to find solutions to some of these issues.”
Banks said that his greatest achievement as city councilman was hosting quarterly town hall meetings to inform his constituents on the importance of ordinances and legislation created to better their lives.
“There’s one piece of legislation that deals with overhanging tree limbs and limbs. That idea came from a constituent,” he said. “When you see constituents being able to give informed ideas on legislation, which is the job of a council member, I think that’s an achievement because then what that says is there’s involvement in the process.”
“I hope the next person will understand that communicating with the people is key, and that the people of Ward 6 are resilient,” Banks said. “As long as they continue to communicate and stay in the scope of their job and work with the administration, there’s a lot that can be done.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
-

 The Center Square6 days ago
The Center Square6 days agoCA fails audit of federal programs, 66% of COVID unemployment benefits in question | California
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days agoAlabama House passes public school cell phone ban
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago‘Hands Off!’ Protest Held in Huntsville Saturday | April 5, 2025 | News 19 @ 9 P.M.
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days agoFlorida student accused of punching deputy in the face
-

 News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - North Carolina News Feed7 days agoState appeals court finds merit in protests of nation’s last unsettled election | North Carolina
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoSouth Florida dad shares update on daughter severely burned in Molotov cocktail attack
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoFour people rescued, two taken to hospital after Birmingham apartment fire
-

 Mississippi Today7 days ago
Mississippi Today7 days agoMeet Willye B. White: A Mississippian we should all celebrate