Mississippi Today
These states are using fetal personhood to put women behind bars

This article was published in partnership with The Marshall Project, a nonprofit news organization covering the U.S. criminal justice system, AL.com, The Frontier, The Post and Courier and The Guardian. Sign up for The Marshall Project’s newsletters, and follow them on Instagram, TikTok, Reddit and Facebook.
When Quitney Armstead learned she was pregnant while locked up in a rural Alabama jail, she made a promise — to God and herself — to stay clean.
She had struggled with addiction and post-traumatic stress disorder for nearly a decade, since serving in the Iraq War. But when she found out she was pregnant with her third child, in October 2018, she resolved: “I want to be a mama to my kids again.”
Armstead says she did stay clean before delivering a baby girl in January 2019. Records show that hospital staff performed initial drug tests, and Armstead was negative.
Armstead didn’t know that Decatur Morgan Hospital also sent her newborn’s meconium — the baby’s first bowel movement — to the Minnesota-based Mayo Clinic for more advanced testing. Those test results showed traces of methamphetamine — drugs Armstead says she took before she knew she was pregnant. Because meconium remains in the fetus throughout pregnancy, it can show residue of substances from many months before that are no longer in the mother’s system.
Child welfare workers barred Armstead from seeing her daughter, Aziyah, while they investigated, and Armstead’s mother stepped in to care for the newborn.

The hospital shared the meconium test results with local police, who then combed through months of medical records for Armstead and her baby to build a criminal case. Prosecutors alleged that the drugs she had taken much earlier in the pregnancy could have put the fetus at risk. Nearly a year after she’d delivered a healthy baby, Armstead was arrested and charged with chemical endangerment of a child.
She is one of hundreds of women prosecuted on similar charges in Alabama, Mississippi, Oklahoma and South Carolina. Law enforcement and prosecutors in those states have expanded their use of child abuse and neglect laws in recent years to police the conduct of pregnant women under the concept of “fetal personhood,” a tenet promoted by many anti-abortion groups that a fetus should be treated legally the same as a child.
These laws have been used to prosecute women who lose their pregnancies. But prosecutors are also targeting people who give birth and used drugs during their pregnancy. This tactic represents a significant shift toward criminalizing mothers: In most states, if a pregnant woman is suspected of using drugs, the case could be referred to a child welfare agency, but not police or prosecutors.
Medical privacy laws have offered little protection. In many cases, health care providers granted law enforcement access to patients’ information, sometimes without a warrant. These women were prosecuted for child endangerment or neglect even when they delivered healthy babies, an investigation by The Marshall Project, AL.com, The Frontier, The Post & Courier and Mississippi Today found.
In these cases, whether a woman goes to prison often depends on where she lives, what hospital she goes to and how much money she has, our review of records found. Most women charged plead guilty and are separated from their children for months, years — or forever. The evidence and procedures are rarely challenged in court.
Prosecutors who pursue these criminal cases say they’re protecting babies from potential harm and trying to get the mothers help in some cases.
But medical experts warn that prosecuting pregnant people who seek health care could cause them to avoid going to a doctor or hospital altogether, which is dangerous for the mother and the developing fetus. Proper prenatal care and drug treatment should be the goal, they argue — not punishment.
Dr. Tony Scialli, an obstetrician/gynecologist who specializes in reproductive and developmental toxicology, said the prosecutions are an abuse of drug screenings and tests designed to assess the medical needs of the mother and infant. He said that drug use doesn’t necessarily harm a fetus. “Exposure does not equal toxicity,” Scialli said.
But prosecutors in these states aren’t required to prove harm to the fetus or newborn — simply exposure at some point during the pregnancy.
Legal experts say that under this expanded use of child welfare laws, prosecutors could also pursue criminal charges for a pregnant person who drinks wine or uses recreational marijuana — even where it’s legal. Police could also comb through medical records to investigate whether a life-saving abortion was medically necessary or to allege that a miscarriage was actually the result of a self-managed abortion.
Because of concerns about people being criminally punished for seeking reproductive healthcare after last year’s reversal of Roe v. Wade, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is working to strengthen privacy rules under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, or HIPAA.
Scialli said the prosecutions ignore the effects of separating a newborn from a mother, which research has shown harms the child. Several studies have shown that even when newborns exhibit signs of drug withdrawal at birth, keeping them in hospital rooms with their mothers improves their health outcomes.
Just because a person struggles with addiction doesn’t necessarily mean she is an unfit mother, Scialli said. “Even women who are using illicit drugs, they’re usually highly motivated to take care of their children. Unless the mother is being neglectful, separating the baby and mother is not healthy for either of them.”

Armstead grew up Quitney Butler in Town Creek, about two hours northwest of Birmingham. She watched as her town lost its Dairy Queen, grocery store, and eventually even the high school she graduated from in 2006.
She was deployed to Iraq in 2009, the same year her school closed. By then, she was 21 with one young daughter, Eva, with her boyfriend, Derry Armstead.
In Iraq, she drove trucks and made sure fellow soldiers got their mail. She was stationed at Forward Operating Base Hammer, in a stretch of desert east of Baghdad that was often the target of attacks.
Armstead came back from war in 2010 “a completely different person,” said her mother, Teresa Tippett. She was argumentative and temperamental.
Her family members “all said I changed when I went over there,” Armstead recalled. “I was like, ‘Mama, we were getting bombed all day, every day.’”
Armstead came home looking for an escape. She found drugs and trouble.
After her boyfriend returned from his deployment to Afghanistan, they married in 2012 and had a second daughter, Shelby. But their relationship became tumultuous, records show.
Both were arrested after a 2014 fight where he claimed she damaged his property, and she claimed he struck her on the leg, court records show. The following year, police records allege her husband drove his pickup past railroad barricades and into the side of a moving train, with his wife in the passenger seat.
Because of the couple’s fighting and arrests, her mother had custody of both Eva and Shelby. Quitney Armstead picked up two drug possession charges, and a misdemeanor charge for throwing a brick at the car her husband was in. Their divorce was granted in 2018, court records show.

In October 2018, she ended up back in jail after she was arrested on a drug possession charge during a police raid of a relative’s house, according to court records.
That’s when she found out she was pregnant with Aziyah, and promised herself she would get clean.
Not long before Armstead’s legal troubles began, some prosecutors in Alabama started to use a chemical endangerment statute — originally designed to protect children from chemical exposures in home meth labs — to punish women whose drug use potentially exposed their fetuses in the womb.
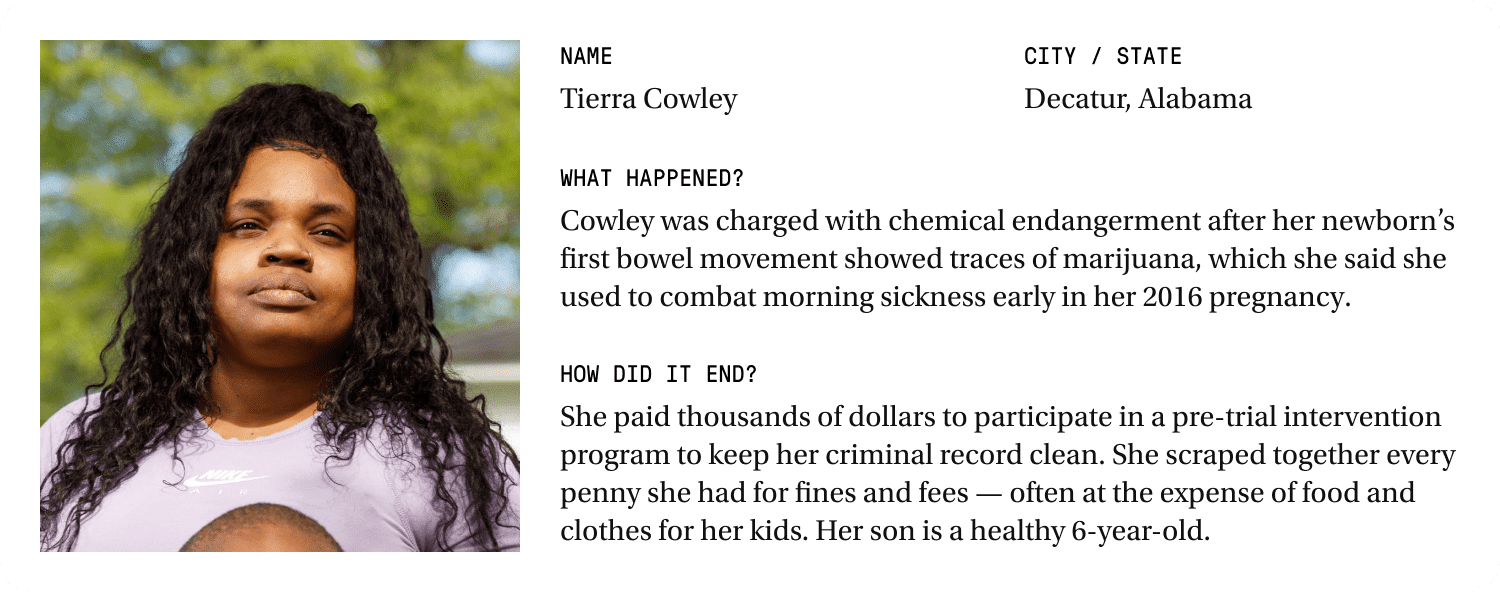
Prosecutions vary widely from county to county. In some areas, district attorneys choose not to pursue these charges, while one county has charged hundreds of women. In 2016, lawmakers carved out an exemption for exposure to prescription drugs, which can also be harmful to a fetus.
Morgan County District Attorney Scott Anderson said he does not discuss details and facts about pending cases.
“However, I will tell you that my position of being willing to allow mothers charged with chemical endangerment into diversion programs has not changed. I am willing to do that and, if at all possible, I favor that approach in resolving these type cases,” he wrote in an email. “I think that Ms. Armstead needs treatment for drug dependency and am in favor of her getting it.”
Some Alabama women we interviewed avoided a felony conviction and prison time by participating in pre-trial intervention programs run by prosecutors, which offer some treatment options. In some counties, the cost is $700 just to apply. Participants must keep making payments to remain enrolled. If they can’t afford to keep up, they face an automatic guilty plea.
In his email, Anderson said poverty does not prevent a person from entering diversion programs in his county.
In several Alabama cases, including Armstead’s, the mother and her newborn initially tested negative for drugs — but the hospital sent the baby’s meconium to a lab for more extensive testing.
Armstead said she never granted permission specifically for the test and had no idea her newborn’s meconium was being sent to the Mayo Clinic. A spokesperson for Decatur Morgan Hospital, where Armstead gave birth, wrote in an email statement that the hospital drug tests “all mothers who are admitted to our hospital for labor and delivery. Our hospital follows Alabama law regarding any required reporting of test results to state authorities.”
A federal law requires each state to have a policy on how to report and examine cases of drug-exposed newborns — but the federal statute doesn’t require states to conduct criminal investigations. About half the states stipulate that healthcare providers report to child welfare agencies when a newborn or mother tests positive for drugs, but only a handful pursue criminal prosecutions of the mothers.
Some prosecutors in Alabama, South Carolina and Oklahoma have determined that under those states’ laws and court rulings establishing fetal personhood, child welfare statutes can apply to a fetus. Mississippi doesn’t have a fetal personhood law, but that hasn’t stopped prosecutors in at least two counties from filing criminal charges against women who tested positive for drugs while pregnant.
In northeast Mississippi’s Monroe County, Sheriff’s Investigator Spencer Woods said he spearheaded the effort to begin prosecuting women under the concept of fetal personhood in 2019. Before that, Woods said, when the sheriff’s office received a referral from Child Protection Services about a newborn testing positive for drugs, officers wouldn’t investigate.
“It wouldn’t be handled because it did not fall under the statute. It still does not fall under the statute,” he said. “Because the state of Mississippi does not look at a child as being a child until it draws its first breath. Well, when that child tests positive when it’s born, the abuse has already happened, and it didn’t happen to a ‘child.’ So it was a crack in the system the way I looked at it. And that’s where we’re kind of playing.”
There are several ways law enforcement can learn of alleged drug use. Sometimes, child welfare workers inform police. Occasionally, women themselves admit drug use to an investigator; other times doctors, nurses or hospital staff pass test results to law enforcement or grant officers access to medical records without a warrant.
The cases demonstrate how existing privacy laws don’t protect women’s medical records from scrutiny by law enforcement, said Ji Seon Song, a law professor at the University of California, Irvine, who studies how law enforcement infringe on patients’ privacy.
Child abuse allegations shouldn’t be a “carte blanche to access someone’s private health information, but that’s how it’s being used,” Song said. “When the loyalty to the patient completely disappears, that’s an institutional problem the hospitals need to deal with.”
Because this surveillance system could also be used to police women who seek abortions, federal authorities have proposed a privacy rule addition for HIPAA. Among other changes, it would prohibit disclosure of private health information for criminal, civil or administrative investigations against people seeking lawful reproductive health care. The agency sought public comment on the proposed rule through June 16, and is expected to complete the changes in coming months.
Medical groups supporting the changes argue that using private health information to punish people criminally harms the physician-patient relationship and results in substandard care. But several state attorneys general — including the AGs for Alabama, Mississippi and South Carolina — wrote a statement opposing the change.
As proposed, the HIPAA changes could require law enforcement to provide documentation, such as a search warrant or subpoena, when seeking records related to someone’s reproductive healthcare — and medical providers could still refuse, said Melanie Fontes Rainer, director of the Office for Civil Rights in the Department of Health and Human Services.
“It’s very much real that your information is being used inappropriately sometimes; and then that information is then being used to seek out criminal, civil and administrative prosecution of people,” Fontes Rainer said. “We’re in this new era — of unfortunately targeting populations for the kinds of health care they seek.”
In some cases, women were arrested and prosecuted after being honest with their doctors about their struggles with substance abuse. At one South Carolina hospital, a new mother admitted to occasional drug use while pregnant, only to have hospital staff call police who arrested her after a nurse handed over her medical records.
A few women have even been prosecuted after seeking treatment.
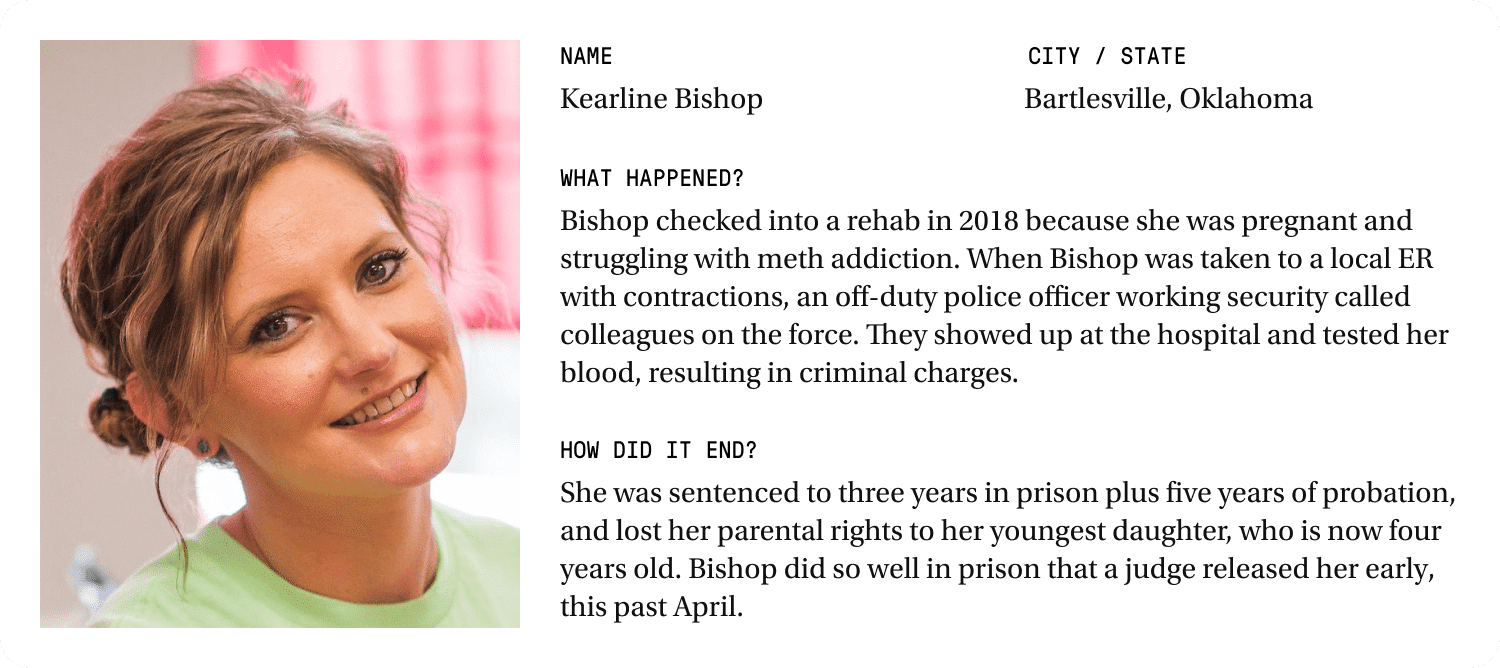
In 2018, Kearline Bishop was pregnant and struggling with meth addiction. She said she checked herself into a rehab program in northeast Oklahoma because she knew she needed help.
When Bishop appeared to have contractions, the rehab transferred her to a local hospital. A doctor at Hillcrest Hospital Claremore determined that she wasn’t yet in labor, and that despite her past drug use, her fetus was healthy.

Then two men Bishop didn’t know walked in. They were police detectives in plain clothes, who demanded a hospital worker draw her blood for testing, according to court records. It turned out that an off-duty police officer working security at the hospital had called his police department supervisor because he’d heard that a pregnant woman admitted to drug use.
The detectives didn’t have a search warrant, so they handed Bishop a “Consent to Search” property form with blank spaces on it. The officers crossed out the line where they would normally list the property to be searched and instead simply wrote “Blood Draw.” Police testified later in court that they didn’t advise Bishop she could talk to a lawyer first.
Bishop had told the cops she “was in a dark place, and needed help,” according to an affidavit.
The blood tests showed traces of drugs in her system. Officers handcuffed Bishop and took her from the hospital to jail. She stayed there until right before she delivered her baby, when she was allowed to go to a treatment house for pregnant women for a few days. When Bishop’s daughter was born, she was healthy. But child welfare workers took her from Bishop the next day.
The District Attorney in Rogers County, northeast of Tulsa, charged Bishop with child neglect. After an initial hearing, a county judge dismissed the charge, ruling the state couldn’t apply its child welfare codes to a fetus.
But the district attorney appealed. Then a 2020 decision in a separate case by the Oklahoma Court of Criminal Appeals ruled that the state’s child neglect law could be applied to fetuses — even ones that didn’t display harm from drug use. The court later ruled that the prosecutor could continue the case against Bishop.
District Attorney Matt Ballard celebrated on Twitter: “My office scored a big victory today fighting for unborn children. I’m proud of all the work that went into this. #ProtectingUnbornChildren”
Through a spokeswoman, Ballard declined an interview request.
Bishop ultimately opted for a blind plea — a form of guilty plea that leaves the sentence entirely up to a judge — in January 2022. She was sentenced to three years in prison, plus five years of probation. A court terminated her parental rights to her youngest daughter.
Bishop did so well in prison that a judge reviewed her case and agreed to her release this past March, after just one year. Her daughter is now a healthy 4-year-old, adopted by a family member. Bishop has no contact with her youngest but saves up the money she makes working to buy clothes to send to her daughter.
Part of Bishop’s motivation to secure an early release, she said, was to prove that the prosecutors and judge who sent her to prison were wrong about her. She said that they never gave her a chance to show she’d be a caring mother.
“They looked at me like I wasn’t even human,” she said.
The cloud of cigarette smoke in Kevin Teague’s Decatur law office is almost as thick as his north Alabama accent. Teague is Armstead’s court-appointed lawyer. He defends a number of women in Morgan County charged with chemical endangerment of a child.
Many of his clients — like most of the women charged in Alabama and other states — reach plea deals, rarely challenging the cases against them. Teague said he had intended to help Armstead plead guilty too, but something about her case gnawed at him.
“She’s just had a hell of a life. I mean, she fought for her country,” he said. “I truly believe she has some serious PTSD.”
Her country — and the state of Alabama — owed her something better, he said. It seems unfair that poor people who can’t afford pre-trial diversion programs get felony convictions and prison time, while people who could afford thousands of dollars in fees can get different outcomes, Teague said.
Armstead missed an October 2022 court hearing — she said she didn’t receive a notice or have transportation. The absence landed her back in jail in December, and, lacking the money for bail, she’s remained behind bars since.
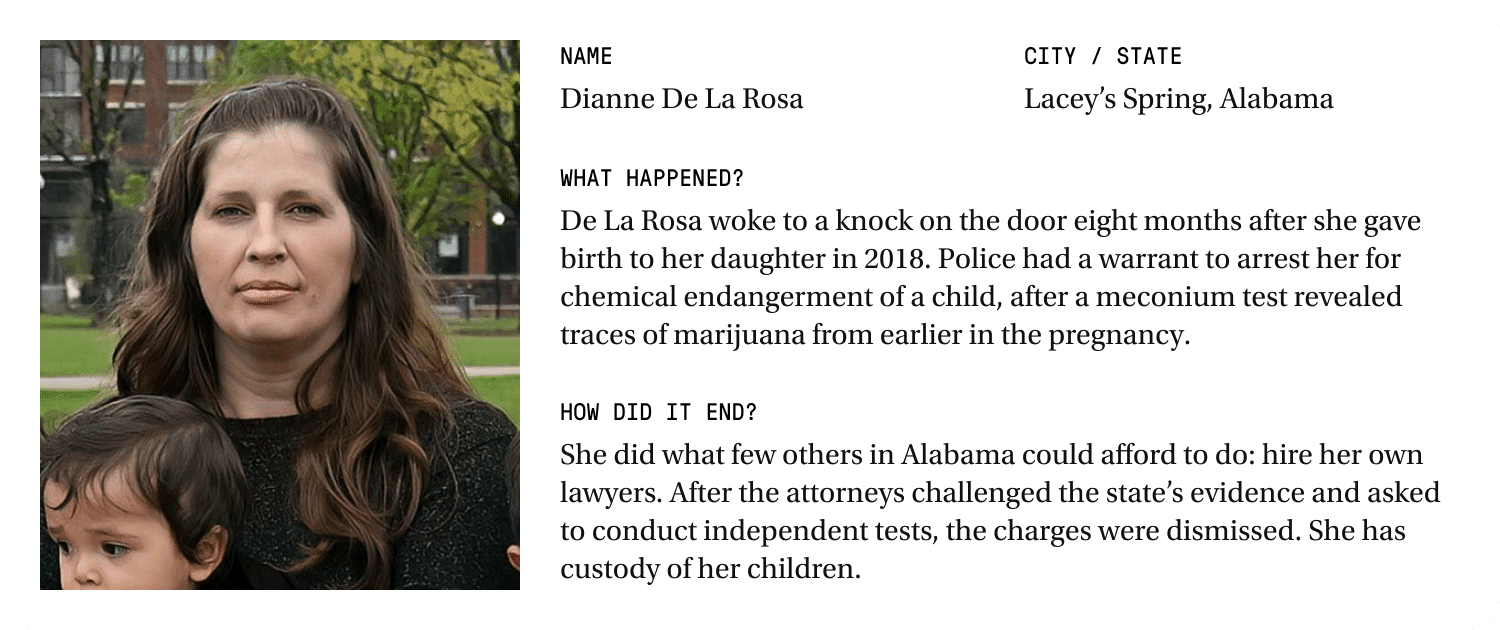
Meanwhile, Teague heard about a chemical endangerment case similar to Armstead’s in which the defendant challenged the evidence and the charges were dismissed: Dianne De La Rosa.
Eight months after De La Rosa’s daughter was born in 2018 in Huntsville, she and her family woke to a knock at the door at 2 a.m. The police had a warrant for her arrest for chemical endangerment. A meconium test allegedly showed traces of marijuana from earlier in the pregnancy.
De La Rosa did something that many women in Morgan County couldn’t afford. She scraped together thousands of dollars to hire her own attorney — John Brinkley.
Brinkley is a father of nine, with another on the way. He had waited in many delivery rooms over the years, and he remembered a key detail: The hospital doesn’t preserve everything it collects when a baby is born.
So Brinkley and his law partner Justin Nance did something unusual: They asked to conduct their own independent drug tests of the meconium in De La Rosa’s case. Defendants in Alabama have the right to request independent testing of evidence. But since so many women plead guilty, it rarely happens.
“It’s unclear the criteria they have for when they do these tests,” Nance said. “They claim they’re doing them on everybody, but I don’t think that is true.”
Prosecutors admitted that the evidence wasn’t preserved, and the charges against De La Rosa were dismissed. That took nearly three years.
Many women charged with chemical endangerment in Alabama can’t afford their own lawyer to fight a criminal case for years, Brinkley said. “They pick on these less fortunate women, and then they just railroad them.”
After hearing about De La Rosa’s case, Teague filed a motion in late March to have the meconium evidence in Armstead’s case independently tested. Prosecutors never responded in a written filing, nor they did not turn over the sample within 14 days, as the court had ordered, Teague said. Armstead’s trial was set for August.
When Teague told Armstead about filing that motion — in hopes of getting her case dismissed — she broke down sobbing.

Teague reminded her it would be a long road, and she would need to work on her sobriety and fulfill the requirements for a veterans’ court program she was offered for a synthetic marijuana possession charge in a nearby county. But it was a glimmer of hope she could hold on to.
“I am not the mistakes I’ve made,” Armstead said. “My kids were my world.”
Her incarceration has isolated her from family. Her jail doesn’t allow in-person visits from anyone but her lawyer, and she barely has the funds to make phone calls.
Her daughter Aziyah is 4 years old now. She and her older sisters only see Armstead on occasional video calls from the county jail, when the family can afford to put money in her jail account.
Armstead recalled that during a recent video chat, Aziyah asked her: “Mommy, can you just sneak out of jail for one night?”
She explained to Aziyah that if she did, she would be there even longer.
“It tore me up,” Armstead said.
Last week, Teague visited her at the jail with news: Morgan County was now offering her a better plea deal. If she successfully completes veterans’ court in nearby Lauderdale County, both her drug possession charge and chemical endangerment charge will be dismissed, he told her. There would be no conviction for either felony, as long as she didn’t screw up.
Armstead knew this meant the state probably didn’t have the meconium evidence. But taking the plea deal meant getting out of jail sooner and hugging her girls. Maybe she would be home in time for back-to-school.
She couldn’t afford to say no.
Additional reporting contributed by Anna Wolfe, Mississippi Today; Amy Yurkanin, AL.com; Brianna Bailey, The Frontier; and Jocelyn Grzeszczak, The Post and Courier.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Meet Willye B. White: A Mississippian we should all celebrate
In an interview years and years ago, the late Willye B. White told me in her warm, soothing Delta voice, “A dream without a plan is just a wish. As a young girl, I had a plan.”
She most definitely did have a plan. And she executed said plan, as we shall see.
And I know what many readers are thinking: “Who the heck was Willye B. White?” That, or: “Willye B. White, where have I heard that name before?”
Well, you might have driven an eight-mile, flat-as-a-pancake stretch of U.S. 49E, between Sidon and Greenwood, and seen the marker that says: “Willye B. White Memorial Highway.” Or you might have visited the Olympic Room at the Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame and seen where White was a five-time participant and two-time medalist in the Summer Olympics as a jumper and a sprinter.
If you don’t know who Willye B. White was, you should. Every Mississippian should. So pour yourself a cup of coffee or a glass of iced tea, follow along and prepare to be inspired.
Willye B. White was born on the last day of 1939 in Money, near Greenwood, and was raised by grandparents. As a child, she picked cotton to help feed her family. When she wasn’t picking cotton, she was running, really fast, and jumping, really high and really long distances.
She began competing in high school track and field meets at the age of 10. At age 11, she scored enough points in a high school meet to win the competition all by herself. At age 16, in 1956, she competed in the Summer Olympics at Melbourne, Australia.
Her plan then was simple. The Olympics, on the other side of the world, would take place in November. “I didn’t know much about the Olympics, but I knew that if I made the team and I went to the Olympics, I wouldn’t have to pick cotton that year. I was all for that.”
Just imagine. You are 16 years old, a high school sophomore, a poor Black girl. You are from Money, Mississippi, and you walk into the stadium at the Melbourne Cricket Grounds to compete before a crowd of more than 100,000 strangers nearly 10,000 miles from your home.
She competed in the long jump. She won the silver medal to become the first-ever American to win a medal in that event. And then she came home to segregated Mississippi, to little or no fanfare. This was the year after Emmett Till, a year younger than White, was brutally murdered just a short distance from where she lived.
“I used to sit in those cotton fields and watch the trains go by,” she once told an interviewer. “I knew they were going to some place different, some place into the hills and out of those cotton fields.”
Her grandfather had fought in France in World War I. “He told me about all the places he saw,” White said. “I always wanted to travel and see the places he talked about.”
Travel, she did. In the late 1950s there were two colleges that offered scholarships to young, Black female track and field athletes. One was Tuskegee in Alabama, the other was Tennessee State in Nashville. White chose Tennessee State, she said, “because it was the farthest away from those cotton fields.”
She was getting started on a track and field career that would take her, by her own count, to 150 different countries across the globe. She was the best female long jumper in the U.S. for two decades. She competed in Olympics in Melbourne, Rome, Tokyo, Mexico City and Munich. She would compete on more than 30 U.S. teams in international events. In 1999, Sports Illustrated named her one of the top 100 female athletes of the 20th century.
Chicago became White’s home for most of adulthood. This was long before Olympic athletes were rich, making millions in endorsements and appearance fees. She needed a job, so she became a nurse. Later on, she became an public health administrator as well as a coach. She created the Willye B. White Foundation to help needy children with health and after school care.
In 1982, at age 42, she returned to Mississippi to be inducted into the Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame and was welcomed back to a reception at the Governor’s Mansion by Gov. William Winter, who introduced her during induction ceremonies. Twenty-six years after she won the silver medal at Melbourne, she called being hosted and celebrated by the governor of her home state “the zenith of her career.”
Willye B. White died of pancreatic cancer in a Chicago hospital in 2007. While working on an obituary/column about her, I talked to the late, great Ralph Boston, the three-time Olympic long jump medalist from Laurel. They were Tennessee State and U.S. Olympic teammates. They shared a healthy respect from one another, and Boston clearly enjoyed talking about White.
At one point, Ralph asked me, “Did you know Willye B. had an even more famous high school classmate.”
No, I said, I did not.
“Ever heard of Morgan Freeman?” Ralph said, laughing.
Of course.
“I was with Morgan one time and I asked him if he ever ran track,” Ralph said, already chuckling about what would come next.
“Morgan said he did not run track in high school because he knew if he ran, he’d have to run against Willye B. White, and Morgan said he didn’t want to lose to a girl.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Early voting proposal killed on last day of Mississippi legislative session
Mississippi will remain one of only three states without no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting.
Senate leaders, on the last day of their regular 2025 session, decided not to send a bill to Gov. Tate Reeves that would have expanded pre-Election Day voting options. The governor has been vocally opposed to early voting in Mississippi, and would likely have vetoed the measure.
The House and Senate this week overwhelmingly voted for legislation that established a watered-down version of early voting. The proposal would have required voters to go to a circuit clerk’s office and verify their identity with a photo ID.
The proposal also listed broad excuses that would have allowed many voters an opportunity to cast early ballots.
The measure passed the House unanimously and the Senate approved it 42-7. However, Sen. Jeff Tate, a Republican from Meridian who strongly opposes early voting, held the bill on a procedural motion.
Senate Elections Chairman Jeremy England chose not to dispose of Tate’s motion on Thursday morning, the last day the Senate was in session. This killed the bill and prevented it from going to the governor.
England, a Republican from Vancleave, told reporters he decided to kill the legislation because he believed some of its language needed tweaking.
The other reality is that Republican Gov. Tate Reeves strongly opposes early voting proposals and even attacked England on social media for advancing the proposal out of the Senate chamber.
England said he received word “through some sources” that Reeves would veto the measure.
“I’m not done working on it, though,” England said.
Although Mississippi does not have no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting, it does have absentee voting.
To vote by absentee, a voter must meet one of around a dozen legal excuses, such as temporarily living outside of their county or being over 65. Mississippi law doesn’t allow people to vote by absentee purely out of convenience or choice.
Several conservative states, such as Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas and Florida, have an in-person early voting system. The Republican National Committee in 2023 urged Republican voters to cast an early ballot in states that have early voting procedures.
Yet some Republican leaders in Mississippi have ardently opposed early voting legislation over concerns that it undermines election security.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi Legislature approves DEI ban after heated debate
Mississippi lawmakers have reached an agreement to ban diversity, equity and inclusion programs and a list of “divisive concepts” from public schools across the state education system, following the lead of numerous other Republican-controlled states and President Donald Trump’s administration.
House and Senate lawmakers approved a compromise bill in votes on Tuesday and Wednesday. It will likely head to Republican Gov. Tate Reeves for his signature after it clears a procedural motion.
The agreement between the Republican-dominated chambers followed hours of heated debate in which Democrats, almost all of whom are Black, excoriated the legislation as a setback in the long struggle to make Mississippi a fairer place for minorities. They also said the bill could bog universities down with costly legal fights and erode academic freedom.
Democratic Rep. Bryant Clark, who seldom addresses the entire House chamber from the podium during debates, rose to speak out against the bill on Tuesday. He is the son of the late Robert Clark, the first Black Mississippian elected to the state Legislature since the 1800s and the first Black Mississippian to serve as speaker pro tempore and preside over the House chamber since Reconstruction.
“We are better than this, and all of you know that we don’t need this with Mississippi history,” Clark said. “We should be the ones that say, ‘listen, we may be from Mississippi, we may have a dark past, but you know what, we’re going to be the first to stand up this time and say there is nothing wrong with DEI.'”
Legislative Republicans argued that the measure — which will apply to all public schools from the K-12 level through universities — will elevate merit in education and remove a list of so-called “divisive concepts” from academic settings. More broadly, conservative critics of DEI say the programs divide people into categories of victims and oppressors and infuse left-wing ideology into campus life.
“We are a diverse state. Nowhere in here are we trying to wipe that out,” said Republican Sen. Tyler McCaughn, one of the bill’s authors. “We’re just trying to change the focus back to that of excellence.”
The House and Senate initially passed proposals that differed in who they would impact, what activities they would regulate and how they aim to reshape the inner workings of the state’s education system. Some House leaders wanted the bill to be “semi-vague” in its language and wanted to create a process for withholding state funds based on complaints that almost anyone could lodge. The Senate wanted to pair a DEI ban with a task force to study inefficiencies in the higher education system, a provision the upper chamber later agreed to scrap.
The concepts that will be rooted out from curricula include the idea that gender identity can be a “subjective sense of self, disconnected from biological reality.” The move reflects another effort to align with the Trump administration, which has declared via executive order that there are only two sexes.
The House and Senate disagreed on how to enforce the measure but ultimately settled on an agreement that would empower students, parents of minor students, faculty members and contractors to sue schools for violating the law.
People could only sue after they go through an internal campus review process and a 25-day period when schools could fix the alleged violation. Republican Rep. Joey Hood, one of the House negotiators, said that was a compromise between the chambers. The House wanted to make it possible for almost anyone to file lawsuits over the DEI ban, while Senate negotiators initially bristled at the idea of fast-tracking internal campus disputes to the legal system.
The House ultimately held firm in its position to create a private cause of action, or the right to sue, but it agreed to give schools the ability to conduct an investigative process and potentially resolve the alleged violation before letting people sue in chancery courts.
“You have to go through the administrative process,” said Republican Sen. Nicole Boyd, one of the bill’s lead authors. “Because the whole idea is that, if there is a violation, the school needs to cure the violation. That’s what the purpose is. It’s not to create litigation, it’s to cure violations.”
If people disagree with the findings from that process, they could also ask the attorney general’s office to sue on their behalf.
Under the new law, Mississippi could withhold state funds from schools that don’t comply. Schools would be required to compile reports on all complaints filed in response to the new law.
Trump promised in his 2024 campaign to eliminate DEI in the federal government. One of the first executive orders he signed did that. Some Mississippi lawmakers introduced bills in the 2024 session to restrict DEI, but the proposals never made it out of committee. With the national headwinds at their backs and several other laws in Republican-led states to use as models, Mississippi lawmakers made plans to introduce anti-DEI legislation.
The policy debate also unfolded amid the early stages of a potential Republican primary matchup in the 2027 governor’s race between State Auditor Shad White and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann. White, who has been one of the state’s loudest advocates for banning DEI, had branded Hosemann in the months before the 2025 session “DEI Delbert,” claiming the Senate leader has stood in the way of DEI restrictions passing the Legislature.
During the first Senate floor debate over the chamber’s DEI legislation during this year’s legislative session, Hosemann seemed to be conscious of these political attacks. He walked over to staff members and asked how many people were watching the debate live on YouTube.
As the DEI debate cleared one of its final hurdles Wednesday afternoon, the House and Senate remained at loggerheads over the state budget amid Republican infighting. It appeared likely the Legislature would end its session Wednesday or Thursday without passing a $7 billion budget to fund state agencies, potentially threatening a government shutdown.
“It is my understanding that we don’t have a budget and will likely leave here without a budget. But this piece of legislation …which I don’t think remedies any of Mississippi’s issues, this has become one of the top priorities that we had to get done,” said Democratic Sen. Rod Hickman. “I just want to say, if we put that much work into everything else we did, Mississippi might be a much better place.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
-

 Mississippi Today3 days ago
Mississippi Today3 days agoPharmacy benefit manager reform likely dead
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days agoTornado watch, severe thunderstorm warnings issued for Oklahoma
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days agoGeorgia road project forcing homeowners out | FOX 5 News
-

 News from the South - West Virginia News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - West Virginia News Feed7 days agoHometown Hero | Restaurant owner serves up hope
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days agoTornado practically rips Bullitt County barn in half with man, several animals inside
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoRepublicans look to maintain majority in Congress ahead of Florida special election
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed5 days agoLife of David Boren memorialized in ceremony attended by hundreds
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed3 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed3 days ago'I think everybody's concerned': Mercedes-Benz plant eyeing impact of imported vehicle tariffs