Mississippi Today
Why so many top candidates are ignoring Mississippi’s worsening hospital crisis

The hospital crisis has emerged as the state’s most dire problem. Yet with Mississippi’s major statewide primary election less than three weeks away, only one candidate for an office that could do anything about it is even acknowledging its existence.
Gov. Tate Reeves, who faces two Republican primary opponents on Aug. 6, would rather voters think about problems that apparently don’t exist in Mississippi like trans athletes and the influence of national liberals on our state’s policies — not the fact that dozens of hospitals are on the brink of closure.
Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann and his Republican primary challenger state Sen. Chris McDaniel appear most focused on out-flanking each other on the right and arguing over who is the truer conservative Republican. Never mind the fact that at least 200,000 working Mississippians cannot afford doctor visits and dying hospitals are underwater having to cover those bills.
Speaker of the House Philip Gunn isn’t running for reelection and has been missing in action the past few weeks. And speaker heir apparent Rep. Jason White, who does have a Republican primary challenger for his House seat early next month, has been a complete non-factor in the 2023 cycle.
Mississippi’s hospital system is failing, and as campaigns really begin to share their ideas and solutions with voters, just one single candidate for high office, Democratic gubernatorial candidate Brandon Presley, has focused meaningful attention on the crisis.
Right now, no Mississippi hospital — large or small, urban or rural, private or public — is immune from potentially debilitating financial concerns. Hospital leaders are having to make life-changing decisions about how they can balance their budgets. They’ve slashed health care services, laid off staff or even closed doors permanently just to make ends meet.
State Health Officer Dr. Daniel Edney put it bluntly a couple weeks ago on a radio program: “No one is knocking it out of the park right now. We have a spectrum of hospitals that literally see their drop-dead date ahead of them if something does not happen.”
Edney, in fact, has been desperately working to sound this alarm for months now, telling the State Board of Health in November 2022 that the crisis was worsening “and no one is coming to the rescue.”
Boy, was that an accurate prophecy. Below are just a few of Mississippi Today’s headlines since Edney issued that warning:
- Vicksburg hospital, evicted by Merit Health, is now closed
- Jackson area’s only inpatient hospice facility closes
- St. Dominic lays off 5.5% of its workforce, halts mental health services
- Health care giant with dozens of facilities in Mississippi announces layoffs
- Memorial Hospital in Gulfport lays off nearly 100 employees
- North Mississippi health system announces layoffs
- In last ditch effort to stay open, Holly Springs hospital ends inpatient care
- ‘The funding just isn’t there’: Yazoo health department reopens just two days a week
- Delta hospital, once projected to close within 6 months, will stay open until next year
- ‘Leaving for greener pastures’: Mississippi’s nurse vacancy rates are at their highest in at least a decade
- Hospitals thought they’d get $450M in extra money this year. They’re actually getting much less.
- A quarter of Mississippi’s rural hospitals could close within three years, report shows
The proverbial walls are closing in on Mississippians. Emergency rooms across the state are constantly full with hours-long wait times. Cash-strapped health care systems are struggling to recruit and retain nurses and doctors, meaning fewer beds are available for people who need them. Ambulance services are struggling to meet demand and respond quickly when dispatched because of hospital bed backups.
So why aren’t our state’s best positioned leaders even mentioning the crisis — let alone offering solutions to it — on the 2023 campaign trail? Because it would be incredibly difficult for them to defend their past inaction on the crisis, which they’ve been warned about over and over and over again.
For several years, both private sector and government appointed health care experts have all but begged Mississippi’s elected officials to do something — anything — to slow the system’s bleeding.
The experts have even presented the politicians with a readymade solution to the hospital crisis: Medicaid expansion. Expansion — not a cure-all fix, but by all accounts a major assist — would bring an estimated $1.61 billion to the state’s health care system in year one. In year two, it would garner $1.64 billion. Projected out over several years, new revenue to the state would never fall below $1 billion per year. In new jobs and revenue created, several studies show, the policy would more than cover the marginal cost the state would have to pay to draw down the billions in federal funds.
READ MORE: FAQ: What is Medicaid expansion, really?
The politicians, however, have leaned on rosy, non-scientific anecdotes or weak, politically charged talking points to ignore the pleas to pass expansion or other programs that would help.
Reeves, the leader of the state’s opposition to Medicaid expansion for more than 10 years, has not mentioned the hospital crisis so far on the 2023 campaign trail without being prompted by reporters. He could not be more dug in on his opposition to expansion.
Meanwhile, his opponent Presley is devoting campaign resources on a clear pitch for expansion as a solution to the hospital crisis. Given Medicaid expansion’s broad popularity with Mississippi voters on top of its other benefits, this focus couldn’t have been a tough decision for Presley.
“Tate Reeves is fiddling while the health care system in Mississippi burns to the ground,” Presley told Mississippi Today earlier this month. “… There are ways to look at the Arkansas model or the Indiana model or models in other states in which we get something done on (Medicaid expansion).”
READ MORE: Former UM chancellor: Gov. Tate Reeves privately acknowledged Medicaid expansion benefits
But then there are the others. Considering the questions their newfound focus on the crisis would raise, the silence from so many top 2023 candidates shouldn’t be all that surprising.
How can these leaders who have ignored the expert cries for years defend leaving at least $10 billion on the table since 2013, when Medicaid expansion was phased in? What about the additional $1.5 billion in each coming year that would help hospitals keep services going and doors open?
How would Hosemann, who at times has expressed openness to some version of expansion, answer questions about why he hasn’t worked in his last four years of immense power to at least start an earnest legislative debate? If he’s worried about not being conservative enough, he should ask the 15 Republican-dominated states that have already expanded how well their health care economies are doing. How on earth would McDaniel justify calling a program that would send billions directly to health care providers “an expansion of the welfare state?”
How would Gunn or White explain to their constituents that they have been sitting on their hands in Jackson on this issue?
And how would Reeves, a self-proclaimed “numbers guy” who focuses so much of his time boasting how “hot” the Mississippi economy is, explain why he’s rejecting a 10-to-1 return on state investment that would stand to save thousands of jobs and create new ones across the state? How is he justifying the hospital crisis when pitching business leaders who may want to move their companies to the state?
At least one major Mississippi hospital leader is apparently asking the same question of him.
“We don’t understand why Tate Reeves doesn’t understand why he needs a healthy workforce,” Delta Health Systems CEO Iris Stacker said just last week while publicly criticizing the governor for refusing to expand Medicaid.
As the hospital crisis worsens and we search for answers to these questions and more, just look at the past records of these leaders. There, you’ll find all the answers you need.
READ MORE: Mississippi leaving more than $1 billion per year on table by rejecting Medicaid expansion
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Meet Willye B. White: A Mississippian we should all celebrate
In an interview years and years ago, the late Willye B. White told me in her warm, soothing Delta voice, “A dream without a plan is just a wish. As a young girl, I had a plan.”
She most definitely did have a plan. And she executed said plan, as we shall see.
And I know what many readers are thinking: “Who the heck was Willye B. White?” That, or: “Willye B. White, where have I heard that name before?”
Well, you might have driven an eight-mile, flat-as-a-pancake stretch of U.S. 49E, between Sidon and Greenwood, and seen the marker that says: “Willye B. White Memorial Highway.” Or you might have visited the Olympic Room at the Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame and seen where White was a five-time participant and two-time medalist in the Summer Olympics as a jumper and a sprinter.
If you don’t know who Willye B. White was, you should. Every Mississippian should. So pour yourself a cup of coffee or a glass of iced tea, follow along and prepare to be inspired.
Willye B. White was born on the last day of 1939 in Money, near Greenwood, and was raised by grandparents. As a child, she picked cotton to help feed her family. When she wasn’t picking cotton, she was running, really fast, and jumping, really high and really long distances.
She began competing in high school track and field meets at the age of 10. At age 11, she scored enough points in a high school meet to win the competition all by herself. At age 16, in 1956, she competed in the Summer Olympics at Melbourne, Australia.
Her plan then was simple. The Olympics, on the other side of the world, would take place in November. “I didn’t know much about the Olympics, but I knew that if I made the team and I went to the Olympics, I wouldn’t have to pick cotton that year. I was all for that.”
Just imagine. You are 16 years old, a high school sophomore, a poor Black girl. You are from Money, Mississippi, and you walk into the stadium at the Melbourne Cricket Grounds to compete before a crowd of more than 100,000 strangers nearly 10,000 miles from your home.
She competed in the long jump. She won the silver medal to become the first-ever American to win a medal in that event. And then she came home to segregated Mississippi, to little or no fanfare. This was the year after Emmett Till, a year younger than White, was brutally murdered just a short distance from where she lived.
“I used to sit in those cotton fields and watch the trains go by,” she once told an interviewer. “I knew they were going to some place different, some place into the hills and out of those cotton fields.”
Her grandfather had fought in France in World War I. “He told me about all the places he saw,” White said. “I always wanted to travel and see the places he talked about.”
Travel, she did. In the late 1950s there were two colleges that offered scholarships to young, Black female track and field athletes. One was Tuskegee in Alabama, the other was Tennessee State in Nashville. White chose Tennessee State, she said, “because it was the farthest away from those cotton fields.”
She was getting started on a track and field career that would take her, by her own count, to 150 different countries across the globe. She was the best female long jumper in the U.S. for two decades. She competed in Olympics in Melbourne, Rome, Tokyo, Mexico City and Munich. She would compete on more than 30 U.S. teams in international events. In 1999, Sports Illustrated named her one of the top 100 female athletes of the 20th century.
Chicago became White’s home for most of adulthood. This was long before Olympic athletes were rich, making millions in endorsements and appearance fees. She needed a job, so she became a nurse. Later on, she became an public health administrator as well as a coach. She created the Willye B. White Foundation to help needy children with health and after school care.
In 1982, at age 42, she returned to Mississippi to be inducted into the Mississippi Sports Hall of Fame and was welcomed back to a reception at the Governor’s Mansion by Gov. William Winter, who introduced her during induction ceremonies. Twenty-six years after she won the silver medal at Melbourne, she called being hosted and celebrated by the governor of her home state “the zenith of her career.”
Willye B. White died of pancreatic cancer in a Chicago hospital in 2007. While working on an obituary/column about her, I talked to the late, great Ralph Boston, the three-time Olympic long jump medalist from Laurel. They were Tennessee State and U.S. Olympic teammates. They shared a healthy respect from one another, and Boston clearly enjoyed talking about White.
At one point, Ralph asked me, “Did you know Willye B. had an even more famous high school classmate.”
No, I said, I did not.
“Ever heard of Morgan Freeman?” Ralph said, laughing.
Of course.
“I was with Morgan one time and I asked him if he ever ran track,” Ralph said, already chuckling about what would come next.
“Morgan said he did not run track in high school because he knew if he ran, he’d have to run against Willye B. White, and Morgan said he didn’t want to lose to a girl.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.![]()
Mississippi Today
Early voting proposal killed on last day of Mississippi legislative session
Mississippi will remain one of only three states without no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting.
Senate leaders, on the last day of their regular 2025 session, decided not to send a bill to Gov. Tate Reeves that would have expanded pre-Election Day voting options. The governor has been vocally opposed to early voting in Mississippi, and would likely have vetoed the measure.
The House and Senate this week overwhelmingly voted for legislation that established a watered-down version of early voting. The proposal would have required voters to go to a circuit clerk’s office and verify their identity with a photo ID.
The proposal also listed broad excuses that would have allowed many voters an opportunity to cast early ballots.
The measure passed the House unanimously and the Senate approved it 42-7. However, Sen. Jeff Tate, a Republican from Meridian who strongly opposes early voting, held the bill on a procedural motion.
Senate Elections Chairman Jeremy England chose not to dispose of Tate’s motion on Thursday morning, the last day the Senate was in session. This killed the bill and prevented it from going to the governor.
England, a Republican from Vancleave, told reporters he decided to kill the legislation because he believed some of its language needed tweaking.
The other reality is that Republican Gov. Tate Reeves strongly opposes early voting proposals and even attacked England on social media for advancing the proposal out of the Senate chamber.
England said he received word “through some sources” that Reeves would veto the measure.
“I’m not done working on it, though,” England said.
Although Mississippi does not have no-excuse early voting or no-excuse absentee voting, it does have absentee voting.
To vote by absentee, a voter must meet one of around a dozen legal excuses, such as temporarily living outside of their county or being over 65. Mississippi law doesn’t allow people to vote by absentee purely out of convenience or choice.
Several conservative states, such as Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas and Florida, have an in-person early voting system. The Republican National Committee in 2023 urged Republican voters to cast an early ballot in states that have early voting procedures.
Yet some Republican leaders in Mississippi have ardently opposed early voting legislation over concerns that it undermines election security.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi Legislature approves DEI ban after heated debate
Mississippi lawmakers have reached an agreement to ban diversity, equity and inclusion programs and a list of “divisive concepts” from public schools across the state education system, following the lead of numerous other Republican-controlled states and President Donald Trump’s administration.
House and Senate lawmakers approved a compromise bill in votes on Tuesday and Wednesday. It will likely head to Republican Gov. Tate Reeves for his signature after it clears a procedural motion.
The agreement between the Republican-dominated chambers followed hours of heated debate in which Democrats, almost all of whom are Black, excoriated the legislation as a setback in the long struggle to make Mississippi a fairer place for minorities. They also said the bill could bog universities down with costly legal fights and erode academic freedom.
Democratic Rep. Bryant Clark, who seldom addresses the entire House chamber from the podium during debates, rose to speak out against the bill on Tuesday. He is the son of the late Robert Clark, the first Black Mississippian elected to the state Legislature since the 1800s and the first Black Mississippian to serve as speaker pro tempore and preside over the House chamber since Reconstruction.
“We are better than this, and all of you know that we don’t need this with Mississippi history,” Clark said. “We should be the ones that say, ‘listen, we may be from Mississippi, we may have a dark past, but you know what, we’re going to be the first to stand up this time and say there is nothing wrong with DEI.'”
Legislative Republicans argued that the measure — which will apply to all public schools from the K-12 level through universities — will elevate merit in education and remove a list of so-called “divisive concepts” from academic settings. More broadly, conservative critics of DEI say the programs divide people into categories of victims and oppressors and infuse left-wing ideology into campus life.
“We are a diverse state. Nowhere in here are we trying to wipe that out,” said Republican Sen. Tyler McCaughn, one of the bill’s authors. “We’re just trying to change the focus back to that of excellence.”
The House and Senate initially passed proposals that differed in who they would impact, what activities they would regulate and how they aim to reshape the inner workings of the state’s education system. Some House leaders wanted the bill to be “semi-vague” in its language and wanted to create a process for withholding state funds based on complaints that almost anyone could lodge. The Senate wanted to pair a DEI ban with a task force to study inefficiencies in the higher education system, a provision the upper chamber later agreed to scrap.
The concepts that will be rooted out from curricula include the idea that gender identity can be a “subjective sense of self, disconnected from biological reality.” The move reflects another effort to align with the Trump administration, which has declared via executive order that there are only two sexes.
The House and Senate disagreed on how to enforce the measure but ultimately settled on an agreement that would empower students, parents of minor students, faculty members and contractors to sue schools for violating the law.
People could only sue after they go through an internal campus review process and a 25-day period when schools could fix the alleged violation. Republican Rep. Joey Hood, one of the House negotiators, said that was a compromise between the chambers. The House wanted to make it possible for almost anyone to file lawsuits over the DEI ban, while Senate negotiators initially bristled at the idea of fast-tracking internal campus disputes to the legal system.
The House ultimately held firm in its position to create a private cause of action, or the right to sue, but it agreed to give schools the ability to conduct an investigative process and potentially resolve the alleged violation before letting people sue in chancery courts.
“You have to go through the administrative process,” said Republican Sen. Nicole Boyd, one of the bill’s lead authors. “Because the whole idea is that, if there is a violation, the school needs to cure the violation. That’s what the purpose is. It’s not to create litigation, it’s to cure violations.”
If people disagree with the findings from that process, they could also ask the attorney general’s office to sue on their behalf.
Under the new law, Mississippi could withhold state funds from schools that don’t comply. Schools would be required to compile reports on all complaints filed in response to the new law.
Trump promised in his 2024 campaign to eliminate DEI in the federal government. One of the first executive orders he signed did that. Some Mississippi lawmakers introduced bills in the 2024 session to restrict DEI, but the proposals never made it out of committee. With the national headwinds at their backs and several other laws in Republican-led states to use as models, Mississippi lawmakers made plans to introduce anti-DEI legislation.
The policy debate also unfolded amid the early stages of a potential Republican primary matchup in the 2027 governor’s race between State Auditor Shad White and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann. White, who has been one of the state’s loudest advocates for banning DEI, had branded Hosemann in the months before the 2025 session “DEI Delbert,” claiming the Senate leader has stood in the way of DEI restrictions passing the Legislature.
During the first Senate floor debate over the chamber’s DEI legislation during this year’s legislative session, Hosemann seemed to be conscious of these political attacks. He walked over to staff members and asked how many people were watching the debate live on YouTube.
As the DEI debate cleared one of its final hurdles Wednesday afternoon, the House and Senate remained at loggerheads over the state budget amid Republican infighting. It appeared likely the Legislature would end its session Wednesday or Thursday without passing a $7 billion budget to fund state agencies, potentially threatening a government shutdown.
“It is my understanding that we don’t have a budget and will likely leave here without a budget. But this piece of legislation …which I don’t think remedies any of Mississippi’s issues, this has become one of the top priorities that we had to get done,” said Democratic Sen. Rod Hickman. “I just want to say, if we put that much work into everything else we did, Mississippi might be a much better place.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
-

 Mississippi Today3 days ago
Mississippi Today3 days agoPharmacy benefit manager reform likely dead
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days ago
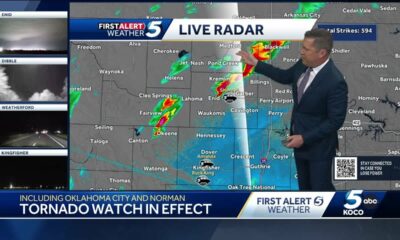
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed6 days agoTornado watch, severe thunderstorm warnings issued for Oklahoma
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days agoGeorgia road project forcing homeowners out | FOX 5 News
-

 News from the South - West Virginia News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - West Virginia News Feed7 days agoHometown Hero | Restaurant owner serves up hope
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed4 days agoTornado practically rips Bullitt County barn in half with man, several animals inside
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed5 days agoLife of David Boren memorialized in ceremony attended by hundreds
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed6 days agoRepublicans look to maintain majority in Congress ahead of Florida special election
-

 News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Texas News Feed7 days agoPopular online food critic surprises Houston-area dessert shop with $50,000 donation