Mississippi Today
New USM President Joe Paul discusses welfare scandal, diversifying students and faculty, and falling enrollment
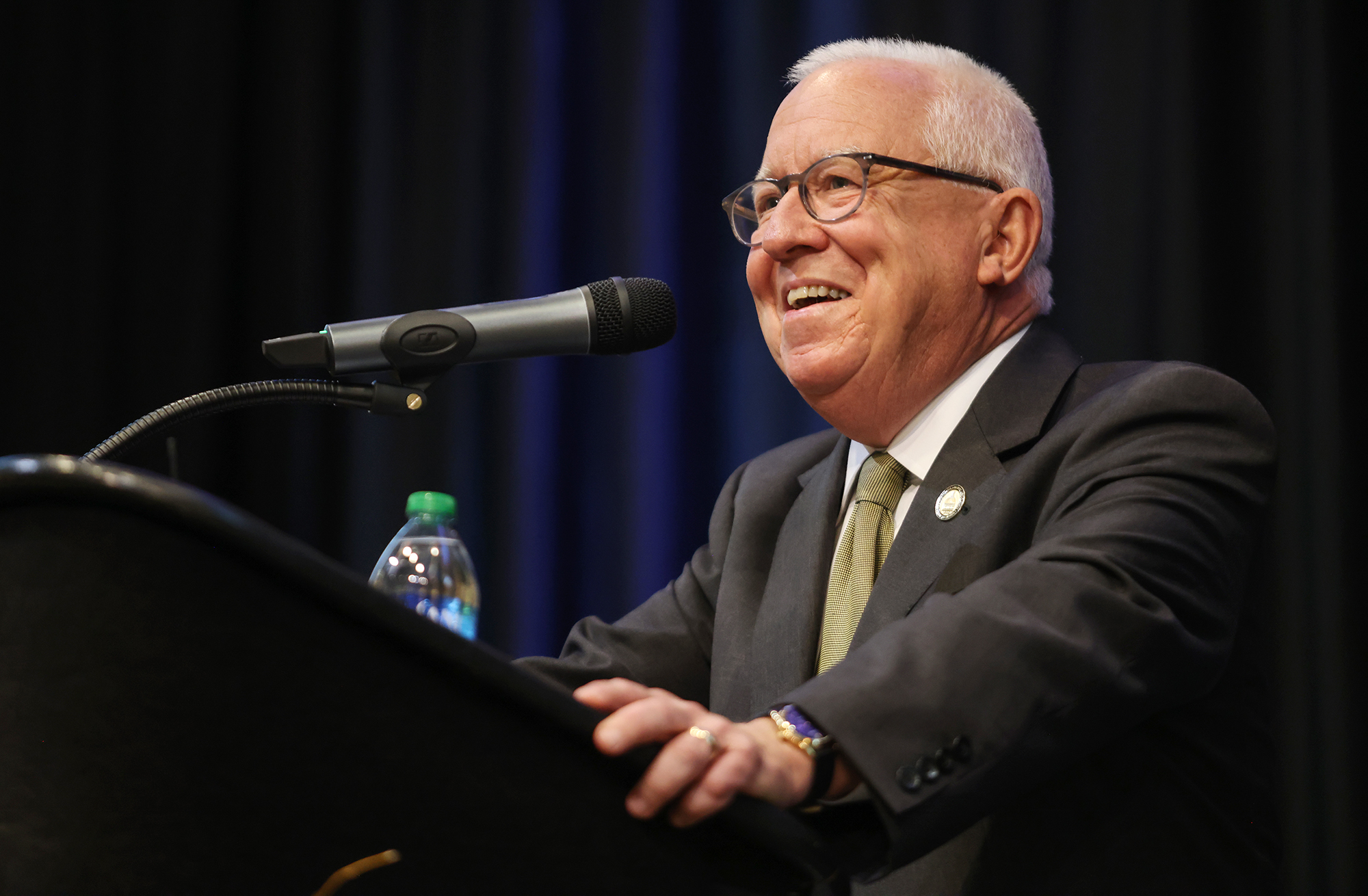

New USM President Joe Paul discusses welfare scandal, diversifying students and faculty, and falling enrollment
New president of University of Southern Mississippi Joe Paul sat down for a 45-minute interview with Mississippi Today on Tuesday.
Paul, who is serving a four-year term with an annual salary of $650,000, discussed his priorities — including enrollment, especially at USM Gulf Park; maintaining the university’s top-tier research status; and fundraising, along with the need to increase the number of diverse students and faculty. He also read a prepared statement about the university’s role in the welfare scandal.
Paul was joined by Jim Coll, the university’s chief communications officer.
This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
Molly Minta: Can you talk about the university’s overall and current financial picture, particularly in the context of declining state appropriations in the last few decades?
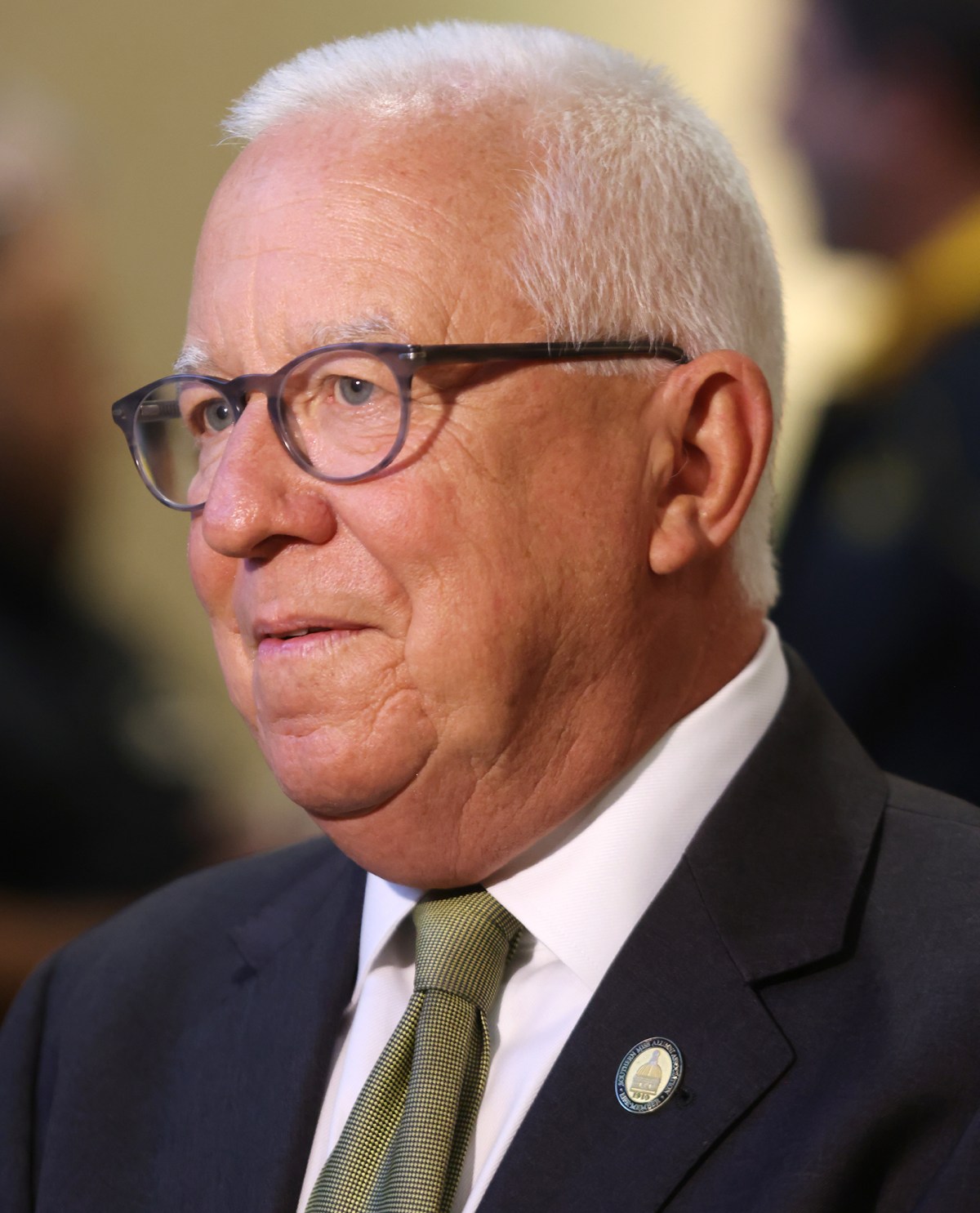

Joe Paul: And more recently, a slight downturn in enrollment. The good news is that the University of Southern Mississippi is in excellent fiscal health. … We have about $150 million in unrestricted reserves. …If a disaster struck, and there were no external funding, we can operate for 155 days, which is well beyond the standard. (Editor’s note: IHL’s recommended minimum is 90 days cash on hand.)
The final thing deals with what we call our debt-ratio coverage. We’ve got about $13 million dollars in annual debt that comes with bonds for construction. Our coverage rate is just below 2.0 and that basically means we have twice as much as we need to assure that we can pay our debts.
Minta: You brought up the slight downturn in enrollment. (Editor’s note: Enrollment declined by 4.4% this fall to 13,526 students, according to IHL). How does that affect the overall financial picture?
Paul: I began in higher education over 40 years ago, and at that time, state appropriations probably covered 70-to-80% of the (budget). . Today that’s almost flipped, so enrollment becomes critical.
Minta: Does it seem like it’s possible to advocate (for) increased funding for higher education from the Legislature? Or is it just a picture of turning to other sources of funding?
Paul: Not to be ambiguous, but I think the answer is both. … We’ve got to continue to advocate for adequate funding to create top-level academic opportunities for Mississippi residents. At the same time, we’ve got to be really creative in terms of budget management. You cannot tuition your way out of a drop in state appropriations or a drop in enrollment. …The way I view student recruitment and enrollment growth is … it’s strategy, it’s processes … how customer friendly you can be is critical. … (It’s also) investment. What are you going to invest in marketing? What are you going to invest in scholarships? What are you going to invest in personnel to do recruitment? The final part is effort.
We were encouraged that in spite of the demographic shift toward fewer high school graduates — and more high school graduates going into vocational and technical programs, which is not a bad thing for the state of Mississippi — that we did have a slight uptick in freshmen this fall. I’m also encouraged — because we really focused on the community colleges this fall — that we’ve got 300 more new transfer students enrolled for spring semester. That’s a double-digit percentage bump for us.
Minta: What I would want to touch on a little more is if you could help people understand the drivers of the enrollment drop? … People seem to feel like there was an institutional failure that had contributed to the enrollment decline. (Is) there an element here where it’s unavoidable given the demographics that there’s going to be an enrollment drop?
Paul: … I don’t spend a lot of time in the rearview mirror in terms of what has happened — except as that might inform us going forward. Another core part of my leadership strategy is that I truly believe that two of the greatest wastes of human energy and leadership are blaming and justifying.
… For us, we’ve got to refocus on South Mississippi. … We’re located in the part of the state where there’s the most people and where there’s the most dynamic growth, right? … There’s no valid reason that students should drive through Hattiesburg to go to school anywhere else in Mississippi — that’s our mantra.
We’ve got to make sure that what we offer is distinctive from other options, whether they’re in state and certainly out of state. … If you want the bells and whistles (of a large university), in terms of the quality of the faculty, being able to engage in research as an undergraduate, state-of-the-art facilities, major college athletics, fraternities and sororities, you name it, and yet you want a bit more personal attention? Southern Miss is a great choice for you.
Minta: Tom Duff, the current IHL board president, (has) talked about what makes the satellite campus on the Gulf Coast, USM Gulf Park, really valuable. … Does increasing enrollment at Gulf Park factor into this overall strategy that you just laid out? What sort of conversations or plans have been started in terms of revitalizing that campus?
Paul: Molly, absolutely it does. It’s not only a mandate for me from the IHL board, but it is critical.
We’re the only dual-campus university in Mississippi, and (the) Mississippi Gulf Coast is a dynamic place. … When you talk about capacity and under-utilization (at Gulf Park), that is clearly a fact. … Let me be clear, my priorities are to grow enrollment overall, which means Hattiesburg, online and Gulf Park. … It’s not about that historical stuff about something we do at Gulf Park might hurt something in Hattiesburg. That is false logic. It’s not a part of what we’re about going forward.
So the overall strategy for growing Gulf Park comes down to this: Coastal academic programs for coastal people for coastal jobs. … What I want to do is focus programs on the Gulf Park campus that will lead to excellent job opportunities on the Mississippi Gulf Coast. … You’re going to have people — we already do in hydrographic science — that would come there from all over the world.
The other thing that we must do is we’ve got to forge a stronger partnership with Mississippi Gulf Coast Community College. That community college is a juggernaut. …. And also for Pearl River Community College. I envision a time soon when Mississippi Gulf Coast Community College faculty can teach classes on our campus and where we, as needed, can go to the Harrison County campus and teach Southern Miss courses. …
Minta: … What is the university’s commitment to keep or increase general education on the coast?
Paul: Because our Gulf Park campus is a non-residential campus, we’ve got to measure what we offer in terms of academic programming by the market demand.
I guess the best short answer is … we’ve got to be really careful to make sure that we’re doing things that are scalable and have a return on investment so that we can grow the campus. If we expended all of our resources on general education programs with very low enrollment, we would not have the resources to expand these programs that are more relevant to the Gulf Coast.
Minta: Last month, the state of Mississippi added USM’s volleyball stadium to its attempt to recoup the misspent welfare funds. Does USM plan to repay all of the improperly allocated welfare funds that have been questioned in the forensic audit? That would include not just the volleyball stadium but things like the $840,000 that was given to a ‘Student Development Program’ that was used to buy speciality performance drinks, popsockets and massages for student athletes?
Paul: Yeah. Molly, as you are well aware, from a legal standpoint it is an incredibly complex situation, right? And because the Southern Miss Athletic Foundation has now been named a party to the suit from DHS, I cannot comment because of pending litigation.
But I do want to say this: I’m deeply troubled by this. All of us are here. And anything that distracts us from our mission to serve the state of Mississippi concerns us gravely. And I’m committed to resolving this situation within legal limits as we move forward toward our goals and will remain relentless in our desire to reach an equitable resolution for all.
Minta: A lot of people were also unsatisfied with the statement on the welfare scandal. Many faculty and alumni … want the university to fully account for its role in the scandal; something like that would include a detailed timeline and who was involved. Is that something USM plans to do?
Paul: … We have complied with every request for information. All of that information is out there and accessible to our faculty and staff. And I understand and appreciate the point of view and have had a lot of conversations with faculty, collectively and individually, about it.
Minta: In terms of complying with every request for information, is that from the state of Mississippi, from reporters, from faculty?
Paul: Yes. (Editor’s note: USM officials have not responded to multiple questions from Mississippi Today about its November statement or the welfare funds it spent on perks for student athletes.)
Minta: Conservative lawmakers in Southern states are increasingly taking aim at tenure by linking the job protection to attacks against critical race theory. In Mississippi, past attempts in the Legislature to ban tenure have died in committee, but faculty want to know how you would respond to an effort from the state Legislature to ban tenure.
Paul: I believe absolutely that both academic freedom and the system of tenure are a cornerstone of what makes public higher education in the United States unique in all the world.
Our professors spend a great amount of their lives preparing themselves to become a PhD and a distinguished scholar and they have to have the unfettered ability to teach as they choose. And as president of Southern Miss, I will always defend that.
Minta: There has been a decline in the number of tenure-track faculty at USM from 2017 to 2021. There’s another view of attack on tenure as simply universities not filling those jobs or filling those jobs with adjunct professors. Faculty would like to know, would the university commit to increasing tenure-track positions?
Paul: I’m not privy to those numbers yet, Molly, and I don’t know if we have them–
Minta: They’re on IHL’s website.
Paul: This is a little bit speculative, because I wasn’t here, right, but it could be that a lot of that shift has to do with temporary budget constraints.
There are few things more important to this university than maintaining and enhancing our Carnegie (R1) designation. And, of course, our SACS accreditation. We cannot maintain and enhance that by creating a pattern of reducing tenure-track positions. … There is no movement afoot here to shift away from tenure-track and toward non-tenured instructors. This is a major research university, and we attract tenure-track professors who are great teachers and incredible scholars.
Can I talk more about the (R1 designation)? It’s prestigious. … But the prestige alone is not the value. … First, we’re a public university paid for by the taxpayers of Mississippi and (R1) designation allows us to create research, discovery, innovation that can lead to enhancing the quality of life and economic development in Mississippi. (R1) designation also allows us to recruit the best and brightest faculty from all over – not just the nation, but the world.
It’s critical that we maintain that (status) and that not only informs that question you had about tenure, but a lot of other questions you may have, such as compensation for graduate students. We’re in the first year of a three-year plan to enhance our graduate assistant stipends. (Editor’s note: The plan would increase stipends to $11,700 by fall 2024).
Minta: Another question about faculty that gets into a broader question about the university. Faculty are overwhelmingly white at USM.
Paul: Yes.
Minta: In 2021, there were just 52 Black faculty and 17 Hispanic faculty compared to 688 White faculty. Those are numbers from IHL.
Black students also make up 27% USM’s student body which is a higher percentage than its peer universities in Mississippi. It’s a higher rate among the predominantly white institutions in the state, but if you look at the overall demographics of … Mississippi, it’s still not equitable. Why aren’t Black students attending USM? Why aren’t Black faculty coming to teach at USM? What can the university better do to serve this community?
Paul: … I need to point out that in many ways, our student body is the most reflective in Mississippi, among research universities, of the population in our state, in terms of African American Mississippians, in terms of other kinds of areas … the ratio of in-state to out-of-state students would be another example.
That’s not to say that we’re good there, Molly, okay? Because my core belief is that as a state institution, we should reflect the population that we serve.
You sort of phrased the question like, what’s the problem? To me, it’s not, ‘what’s the problem?’ It’s, ‘what’s the opportunity?’ … I think the far more challenging, perplexing problem is how do we create a faculty that reflects the demographics of our current student body? That’s not a challenge unique to Southern Miss. … Currently, we are in a search for a new permanent provost and … the first conversation that I want to have with that person is around diversity, equity and inclusion. Specifically, how can we recruit and retain more non-white faculty members at Southern Miss? … We don’t have answers for you today.
… I think traditionally what we’ve done in faculty recruitment is wait till they’re out there and let them come to you. When it comes to diversifying the faculty, my idea would be, why don’t we start to build relationships with a diverse pool of students while they’re pursuing their doctoral degrees at outstanding institutions? Another side of the equation is, what are we doing for diverse faculty members when they get here? How are we making sure that they are welcome?
Minta: Have you looked more at (how to diversify) the student body or more at specific strategies or types of outreach the university should be doing?
Paul: We have an incredibly strong program currently in terms of student life around diversity, equity, and inclusion. … Though the number of high school graduates is (going to be) decreasing in Mississippi, the diversity of those graduates is increasing. They’re more non-white each year, so the opportunity is there. We’re going to be more diverse.
Minta: Is it a matter of making the campus more welcoming or providing more scholarships or financial aid for non-white or Black students specifically?
Pau: It’s all of that. It’s making sure that you’ve got a diverse staff and student life. … Growing the diversity of faculty is a key to it. And it’s making sure (there is) diversity in terms of recruitment staff. Molly, it has to be more than words, you know?
Minta: The average faculty salary at USM during the 2020-21 school year was little over $70,000 and that is significantly less than the SREB average. The average staff member makes a little more than $47,000. How do you plan to meaningfully increase faculty and staff pay, keeping in mind that the percentage-base pay increases that are granted by the Legislature don’t keep pace with inflation or the increase in the cost of health insurance?
Paul: I think we’re about 80% of the SREB average in Mississippi in general.
I am strongly committed to increasing pay for faculty and staff, from professional staff to those hard-working folks that keep this place going every day. I don’t disagree that largely what the Legislature has been able to do — I’m grateful for it and extremely hopeful again this year — is that as they appropriate for increases, at least in our short-run economy, that inflation is outpacing that.
… There is no magic-wand solution to that. One of the things that can enable us to do that is … to create revenue through the increasing number of students that we can then commit to moving faculty salaries toward the SREB average.
Minta: Is there anything I haven’t asked about that you’d like to talk about?
Jim Coll, addressing Paul: Priority-wise, we’ve talked about a couple things, but you haven’t talked about private fundraising.
Paul: Yeah, I mean, I don’t know who I’ve got out there. So, there are a couple things I want to tell you.
I think the role of the president as a leader in higher education is critical. … I want to establish … a sense of being present and accessible to our students, our faculty, our staff, alumni and other constituents. The other side of it is that I absolutely believe that … you’ve got to earn the trust of those that you’ve been given the responsibility to lead. Trust is not given … it has to be earned every day by the relationship between what you say and what you commit to and what you do.
The other (piece) of the main agenda from me … is private philanthropy. One of my goals is to push us well beyond the $150 million goal that we have in our Capital Campaign. We rest at about $132 million now. Since I’ve been here in July, we’ve raised about $8 million. I want to push it well beyond that.
Minta: There was another question I wanted to ask. Last year, the student newspaper ran an article on how international students would like more support, particularly when it comes to finding housing and securing internships and scholarships. Have you been doing anything to address these concerns and if so, what?
Paul: I’m aware of that. I’ve got a working to-do list but, Molly, I’ve not been able to corral the folks yet to have that conversation. I think it’s critically important.
The number of international students ebbs and flows and right now. … But every student that comes to Southern Miss deserves … the full Southern Miss experience, not to be marginalized. And that certainly includes our international students.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Did you miss our previous article…
https://www.biloxinewsevents.com/?p=203911
Mississippi Today
Mississippi Legislature approves DEI ban after heated debate
Mississippi lawmakers have reached an agreement to ban diversity, equity and inclusion programs and a list of “divisive concepts” from public schools across the state education system, following the lead of numerous other Republican-controlled states and President Donald Trump’s administration.
House and Senate lawmakers approved a compromise bill in votes on Tuesday and Wednesday. It will likely head to Republican Gov. Tate Reeves for his signature after it clears a procedural motion.
The agreement between the Republican-dominated chambers followed hours of heated debate in which Democrats, almost all of whom are Black, excoriated the legislation as a setback in the long struggle to make Mississippi a fairer place for minorities. They also said the bill could bog universities down with costly legal fights and erode academic freedom.
Democratic Rep. Bryant Clark, who seldom addresses the entire House chamber from the podium during debates, rose to speak out against the bill on Tuesday. He is the son of the late Robert Clark, the first Black Mississippian elected to the state Legislature since the 1800s and the first Black Mississippian to serve as speaker pro tempore and preside over the House chamber since Reconstruction.
“We are better than this, and all of you know that we don’t need this with Mississippi history,” Clark said. “We should be the ones that say, ‘listen, we may be from Mississippi, we may have a dark past, but you know what, we’re going to be the first to stand up this time and say there is nothing wrong with DEI.'”
Legislative Republicans argued that the measure — which will apply to all public schools from the K-12 level through universities — will elevate merit in education and remove a list of so-called “divisive concepts” from academic settings. More broadly, conservative critics of DEI say the programs divide people into categories of victims and oppressors and infuse left-wing ideology into campus life.
“We are a diverse state. Nowhere in here are we trying to wipe that out,” said Republican Sen. Tyler McCaughn, one of the bill’s authors. “We’re just trying to change the focus back to that of excellence.”
The House and Senate initially passed proposals that differed in who they would impact, what activities they would regulate and how they aim to reshape the inner workings of the state’s education system. Some House leaders wanted the bill to be “semi-vague” in its language and wanted to create a process for withholding state funds based on complaints that almost anyone could lodge. The Senate wanted to pair a DEI ban with a task force to study inefficiencies in the higher education system, a provision the upper chamber later agreed to scrap.
The concepts that will be rooted out from curricula include the idea that gender identity can be a “subjective sense of self, disconnected from biological reality.” The move reflects another effort to align with the Trump administration, which has declared via executive order that there are only two sexes.
The House and Senate disagreed on how to enforce the measure but ultimately settled on an agreement that would empower students, parents of minor students, faculty members and contractors to sue schools for violating the law.
People could only sue after they go through an internal campus review process and a 25-day period when schools could fix the alleged violation. Republican Rep. Joey Hood, one of the House negotiators, said that was a compromise between the chambers. The House wanted to make it possible for almost anyone to file lawsuits over the DEI ban, while Senate negotiators initially bristled at the idea of fast-tracking internal campus disputes to the legal system.
The House ultimately held firm in its position to create a private cause of action, or the right to sue, but it agreed to give schools the ability to conduct an investigative process and potentially resolve the alleged violation before letting people sue in chancery courts.
“You have to go through the administrative process,” said Republican Sen. Nicole Boyd, one of the bill’s lead authors. “Because the whole idea is that, if there is a violation, the school needs to cure the violation. That’s what the purpose is. It’s not to create litigation, it’s to cure violations.”
If people disagree with the findings from that process, they could also ask the attorney general’s office to sue on their behalf.
Under the new law, Mississippi could withhold state funds from schools that don’t comply. Schools would be required to compile reports on all complaints filed in response to the new law.
Trump promised in his 2024 campaign to eliminate DEI in the federal government. One of the first executive orders he signed did that. Some Mississippi lawmakers introduced bills in the 2024 session to restrict DEI, but the proposals never made it out of committee. With the national headwinds at their backs and several other laws in Republican-led states to use as models, Mississippi lawmakers made plans to introduce anti-DEI legislation.
The policy debate also unfolded amid the early stages of a potential Republican primary matchup in the 2027 governor’s race between State Auditor Shad White and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann. White, who has been one of the state’s loudest advocates for banning DEI, had branded Hosemann in the months before the 2025 session “DEI Delbert,” claiming the Senate leader has stood in the way of DEI restrictions passing the Legislature.
During the first Senate floor debate over the chamber’s DEI legislation during this year’s legislative session, Hosemann seemed to be conscious of these political attacks. He walked over to staff members and asked how many people were watching the debate live on YouTube.
As the DEI debate cleared one of its final hurdles Wednesday afternoon, the House and Senate remained at loggerheads over the state budget amid Republican infighting. It appeared likely the Legislature would end its session Wednesday or Thursday without passing a $7 billion budget to fund state agencies, potentially threatening a government shutdown.
“It is my understanding that we don’t have a budget and will likely leave here without a budget. But this piece of legislation …which I don’t think remedies any of Mississippi’s issues, this has become one of the top priorities that we had to get done,” said Democratic Sen. Rod Hickman. “I just want to say, if we put that much work into everything else we did, Mississippi might be a much better place.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
House gives Senate 5 p.m. deadline to come to table, or legislative session ends with no state budget
The House on Wednesday attempted one final time to revive negotiations between it and the Senate over passing a state budget.
Otherwise, the two Republican-led chambers will likely end their session without funding government services for the next fiscal year and potentially jeopardize state agencies.
The House on Wednesday unanimously passed a measure to extend the legislative session and revive budget bills that had died on legislative deadlines last weekend.
House Speaker Jason White said he did not have any prior commitment that the Senate would agree to the proposal, but he wanted to extend one last offer to pass the budget. White, a Republican from West, said if he did not hear from the Senate by 5 p.m. on Wednesday, his chamber would end its regular session.
“The ball is in their court,” White said of the Senate. “Every indication has been that they would not agree to extend the deadlines for purposes of doing the budget. I don’t know why that is. We did it last year, and we’ve done it most years.”
But it did not appear likely Wednesday afternoon that the Senate would comply.
The Mississippi Legislature has not left Jackson without setting at least most of the state budget since 2009, when then Gov. Haley Barbour had to force them back to set one to avoid a government shutdown.
The House measure to extend the session is now before the Senate for consideration. To pass, it would require a two-thirds majority vote of senators. But that might prove impossible. Numerous senators on both sides of the aisle vowed to vote against extending the current session, and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann who oversees the chamber said such an extension likely couldn’t pass.
Senate leadership seemed surprised at the news that the House passed the resolution to negotiate a budget, and several senators earlier on Wednesday made passing references to ending the session without passing a budget.
“We’ll look at it after it passes the full House,” Senate President Pro Tempore Dean Kirby said.
The House and Senate, each having a Republican supermajority, have fought over many issues since the legislative session began early January.
But the battle over a tax overhaul plan, including elimination of the state individual income tax, appeared to cause a major rift. Lawmakers did pass a tax overhaul, which the governor has signed into law, but Senate leaders cried foul over how it passed, with the House seizing on typos in the Senate’s proposal that accidentally resembled the House’s more aggressive elimination plan.
The Senate had urged caution in eliminating the income tax, and had economic growth triggers that would have likely phased in the elimination over many years. But the typos essentially negated the triggers, and the House and governor ran with it.
The two chambers have also recently fought over the budget. White said he communicated directly with Senate leaders that the House would stand firm on not passing a budget late in the session.
But Senate leaders said they had trouble getting the House to meet with them to haggle out the final budget.
On the normally scheduled “conference weekend” with a deadline to agree to a budget last Saturday, the House did not show, taking the weekend off. This angered Hosemann and the Senate. All the budget bills died, requiring a vote to extend the session, or the governor forcing them into a special session.
If the Legislature ends its regular session without adopting a budget, the only option to fund state agencies before their budgets expire on June 30 is for Gov. Tate Reeves to call lawmakers back into a special session later.
“There really isn’t any other option (than the governor calling a special session),” Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann previously said.
If Reeves calls a special session, he gets to set the Legislature’s agenda. A special session call gives an otherwise constitutionally weak Mississippi governor more power over the Legislature.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Amount of federal cuts to health agencies doubles
Cuts to public health and mental health funding in Mississippi have doubled – reaching approximately $238 million – since initial estimates last week, when cancellations to federal grants allocated for COVID-19 pandemic relief were first announced.
Slashed funding to the state’s health department will impact community health workers, planned improvements to the public health laboratory, the agency’s ability to provide COVID-19 vaccinations and preparedness efforts for emerging pathogens, like H5 bird flu.
The grant cancellations, which total $230 million, will not be catastrophic for the agency, State Health Officer Dr. Daniel Edney told members of the Mississippi House Democratic Caucus at the Capitol April 1.
But they will set back the agency, which is still working to recover after the COVID-19 pandemic decimated its workforce and exposed “serious deficiencies” in the agency’s data collection and management systems.
The cuts will have a more significant impact on the state’s economy and agency subgrantees, who carry out public health work on the ground with health department grants, he said.
“The agency is okay. But I’m very worried about all of our partners all over the state,” Edney told lawmakers.
The health department was forced to lay off 17 contract workers as a result of the grant cancellations, though Edney said he aims to rehire them under new contracts.
Other positions funded by health department grants are in jeopardy. Two community health workers at Back Bay Mission, a nonprofit that supports people living in poverty in Biloxi, were laid off as a result of the cuts, according to WLOX. It’s unclear how many more community health workers, who educate and help people access health care, have been impacted statewide.
The department was in the process of purchasing a comprehensive data management system before the cuts and has lost the ability to invest in the Mississippi Public Health Laboratory, he said. The laboratory performs environmental and clinical testing services that aid in the prevention and control of disease.
The agency has worked to reduce its dependence on federal funds, Edney said, which will help it weather the storm. Sixty-six percent of the department’s budget is federally funded.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention pulled back $11.4 billion in funding to state health departments nationwide last week. The funding was originally allocated by Congress for testing and vaccination against the coronavirus as part of COVID-19 relief legislation, and to address health disparities in high-risk and underserved populations. An additional $1 billion from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration was also terminated.
“The COVID-19 pandemic is over, and HHS will no longer waste billions of taxpayer dollars responding to a non-existent pandemic that Americans moved on from years ago,” the Department of Health and Human Services Director of Communications Andrew Nixon said in a statement.
HHS did not respond to questions from Mississippi Today about the cuts in Mississippi.
Democratic attorneys general and governors in 23 states filed a lawsuit against the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Tuesday, arguing that the sudden cancellation of the funding was unlawful and seeking injunctive relief to halt the cuts. Mississippi did not join the suit.
Mental health cuts
The Department of Mental Health received about $7.5 million in cuts to federal grants from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.

Over half of the cuts were to community mental health centers, and supported alcohol and drug treatment services for people who can not afford treatment, housing services for parenting and pregnant women and their children, and prevention services.
The cuts could result in reduced beds at community mental health centers, Phaedre Cole, the director of Life Help and President of Mississippi Association of Community Mental Health Centers, told lawmakers April 1.
Community mental health centers in Mississippi are already struggling to keep their doors open. Four centers in the state have closed since 2012, and a third have an imminent to high risk of closure, Cole told legislators at a hearing last December.
“We are facing a financial crisis that threatens our ability to maintain our mission,” she said Dec. 5.
Cuts to the department will also impact diversion coordinators, who are charged with reducing recidivism of people with serious mental illness to the state’s mental health hospital, a program for first-episode psychosis, youth mental health court funding, school-aged mental health programs and suicide response programs.
The Department of Mental Health hopes to reallocate existing funding from alcohol tax revenue and federal block grant funding to discontinued programs.
The agency posted a list of all the services that have received funding cuts. The State Department of Health plans to post such a list, said spokesperson Greg Flynn.
Health leaders have expressed fear that there could be more funding cuts coming.
“My concern is that this is the beginning and not the end,” said Edney.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
-

 Mississippi Today1 day ago
Mississippi Today1 day agoPharmacy benefit manager reform likely dead
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoSevere storms will impact Alabama this weekend. Damaging winds, hail, and a tornado threat are al…
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days agoUniversity of Alabama student detained by ICE moved to Louisiana
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed4 days agoTornado watch, severe thunderstorm warnings issued for Oklahoma
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days agoA little early morning putting at the PGA Tour Superstore
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days agoYoungkin removes Ellis, appoints Cuccinelli to UVa board | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days agoPeanut farmer wants Florida water agency to swap forest land
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed4 days agoGeorgia road project forcing homeowners out | FOX 5 News