Mississippi Today
Welfare recipient won’t stop fighting for ‘decency and common sense’
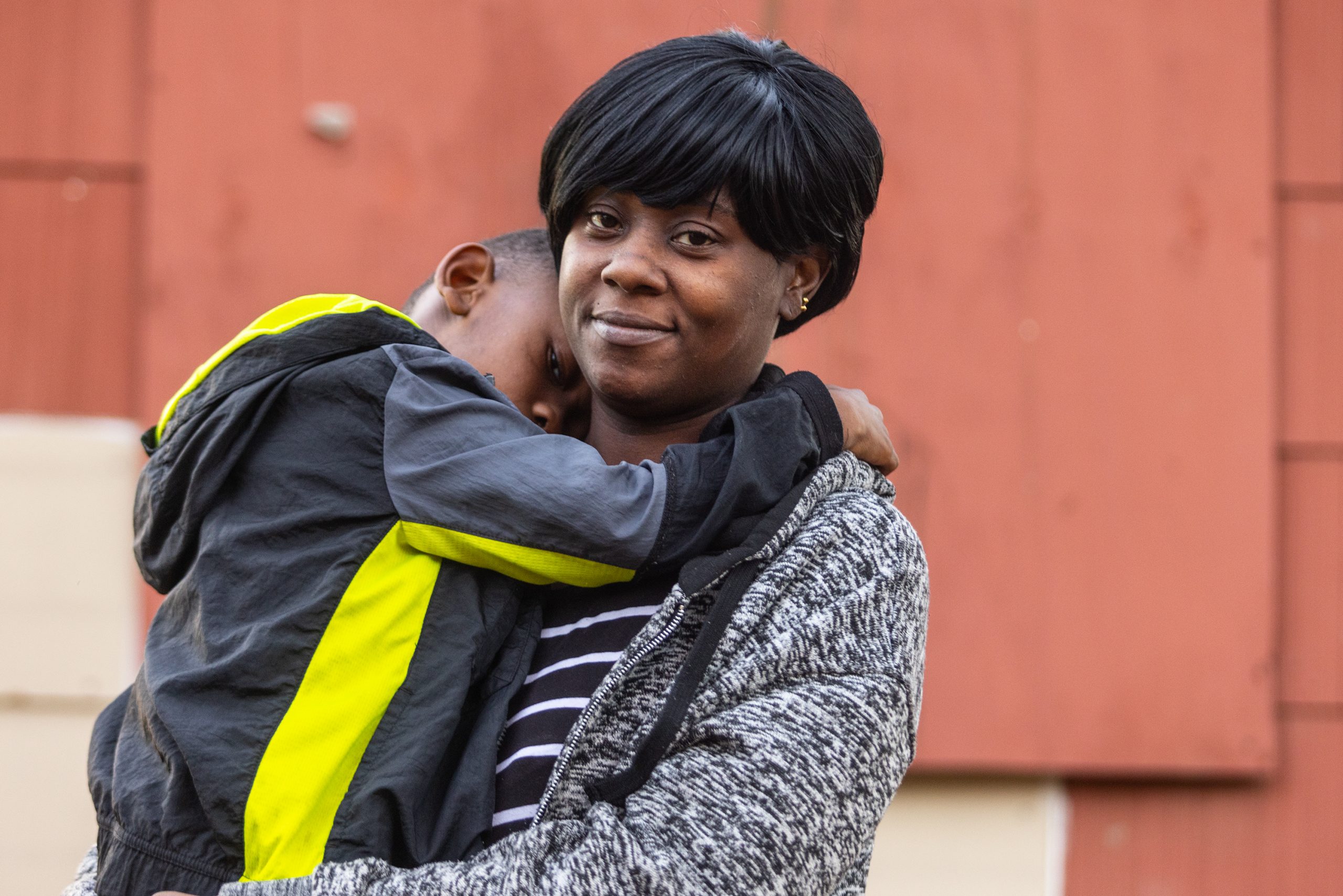

Welfare recipient won’t stop fighting for ‘decency and common sense’
The state of Mississippi isn’t getting anything past Danielle Thomas.
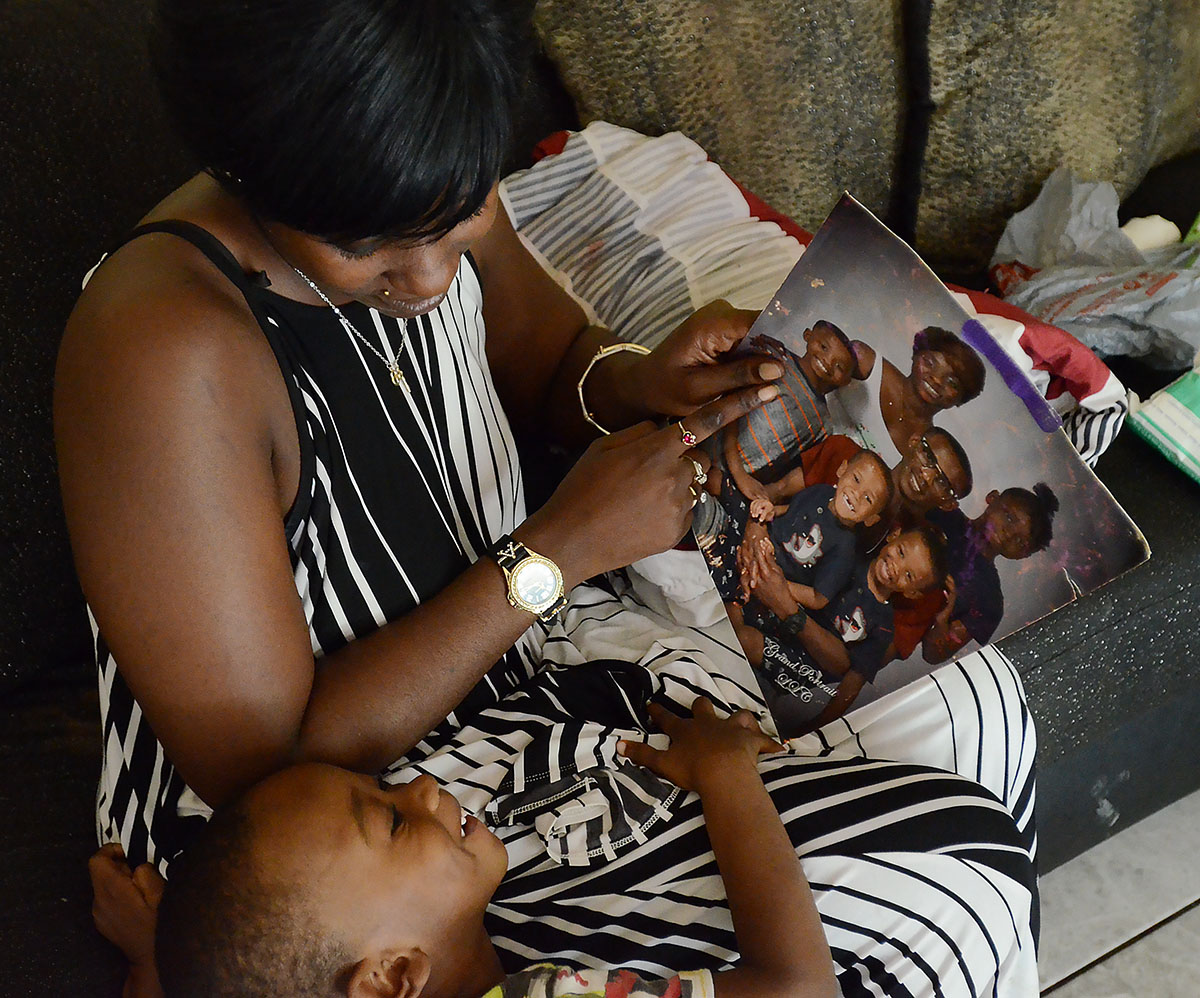
Thomas is a bright, young single mother raising her six kids in south Jackson. Because she lives in poverty, Thomas is also an expert in the convoluted policies and bureaucratic red tape surrounding one of the biggest scandals in state history: the TANF program.
Despite recent attention on the graft and corruption within the state’s Temporary Assistance for Needy Families block grant, Mississippi is still pumping less than 5% of the money directly to mothers like Thomas.
“I really think it’s still them stealing from people, to be honest,” Thomas, 34, said. “I really feel like they feel like a lot of us aren’t smart enough, or they feel like we probably don’t know the system in and out well enough.”
Thomas works part time as a home health aide earning $9.50 an hour, the same wage she started at 10 years ago. When she’s not on the job, she’s feeding and changing her 5-month-old, ferrying her other kids to and from school, cooking meals, fetching medication, tending to boo-boos, monitoring screen time, and trying to keep the shrieking to a tolerable decibel.
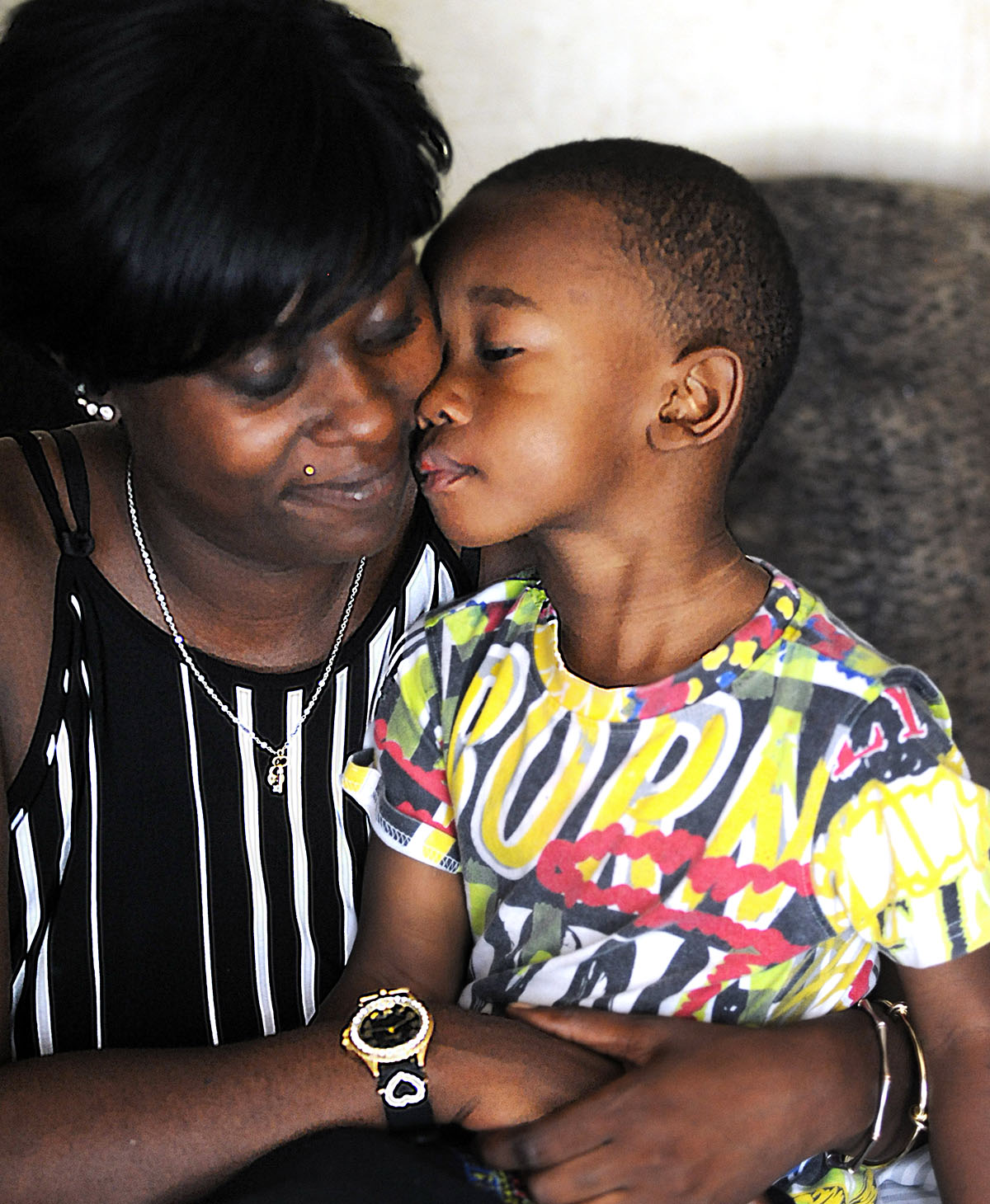

On top of all that, Thomas basically moonlights as the unpaid lawyer, auditor and investigator on her own cases at the Mississippi Department of Human Services and other state service agencies. As most public assistance recipients know, it takes fierce self advocacy to ensure fair treatment within Mississippi’s social safety net.
Only about 1,600 very poor families in Mississippi are successfully jumping through the hoops required to receive the small TANF cash assistance payments each month.
Thomas knows a great deal more about how the TANF program works than the politicians who write the laws that govern the program.
But what happened to Thomas in recent weeks has stumped even the nation’s top policy experts.
In October, Thomas learned that she would be receiving a lump sum of more than $5,000 in back due child support from her ex-husband Larry Young, the father of her four youngest children. The state’s child support office, run by a private contractor, intercepted the money from Young’s child tax credit.
This tax offset process is part of the state’s child support enforcement program that Thomas is required to participate in to keep receiving public benefits. The rationale is, if the state is going to provide taxpayer support to single-parent families, then the noncustodial parents, usually fathers, should be forced to pay up as well.
This is where things get tricky: When the office collects support on behalf of a child receiving TANF, the state then seizes the funds to pay itself back for the welfare payments it issued. Most of that money goes straight back to the federal government.
Thomas said she sees the rationale in this, but at the same time, “I think that’s messed up a lot of co-parenting relationships … it doesn’t help how they think it helps. It kinda actually divides the family a little more.”
Thomas receives assistance from the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, formerly known as food stamps, for all of her children – several hundred dollars a month that comes on a debit card Thomas can only use on qualified items at qualified stores.
But Thomas only receives TANF cash assistance, $118 a month, for each of the two eldest children, not Young’s kids.
This is because of a harsh and little-known rule in Mississippi that if a parent is already on welfare when she gets pregnant and gives birth, that new child is not eligible for TANF benefits. These are sometimes called “capped” children. Just 12 states still have this policy in place, according to a 2020 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities report.
For Thomas, this makes the child support payments for the younger kids all the more crucial.
The $5,000 cash infusion from the tax credit was coming just in time for Christmas. Thomas also planned to use some of the money to replace the radiator fan and valve cover gasket on her 2012 Dodge Durango – long overdue repairs on her only mode of transportation to work and the kids’ schools. Right now, she gets under the hood and manually sets spark to the fan before driving anywhere.
Thomas and her kids survive on the combination of her work income, no more than $13,000 a year, about $900 in monthly Supplemental Security Income, or disability benefits, that Thomas gets for her severe depression and anxiety attacks, and the public assistance. Because Thomas receives disability, she doesn’t receive a TANF payment for herself.
The prospect of a financial cushion provided Thomas some hope, but it was short lived.
In late October, Thomas received the child support payment on her debit card. It was $100.
She called a representative at the child support office, who told her that, according to the computer screen she was looking at, the TANF program had seized the rest.
That’s not how that works, Thomas thought.
“TANF took $5,000 from my kids, but the kids that they took the money from, they don’t receive TANF. They have never received TANF,” Thomas said.
Without the incoming funds, Thomas told her ex she still needed him to help pay for clothes and shoes for the kids. At first, the dad was skeptical that the state had taken the money. The situation caused tension between the parents.
“It makes me feel bad,” Young said. “It’s sad how Mississippi does things, man. Mississippi don’t care about no one, but what they do? Help Brett Favre. Help Phil (Bryant). They don’t help the ones that actually need help.”
Mississippi, which offers some of the lowest wages, strictest public assistance requirements, fewest labor protections and most meager health care of any state is also the most poverty stricken.
But Mississippi politicians have long blamed “fatherlessness” and nonmarital pregnancy for the state’s high poverty rate, ignoring the research that reflects the inverse: that those family outcomes are most often a symptom of poverty – and the feeling that upward mobility is unachievable – rather than the cause of it.
Instead of focusing on evidence-based practices for interrupting systemic poverty, the state has spent hundreds of millions of welfare funds attempting to address fatherhood and teen pregnancy. Along the way, MDHS admits it has gathered no evidence of how these “family stabilization” programs reduced poverty.
Millions through these programs ended up going to the pet projects of former NFL quarterback Brett Favre, other famous athletes and the cronies of state politicians.
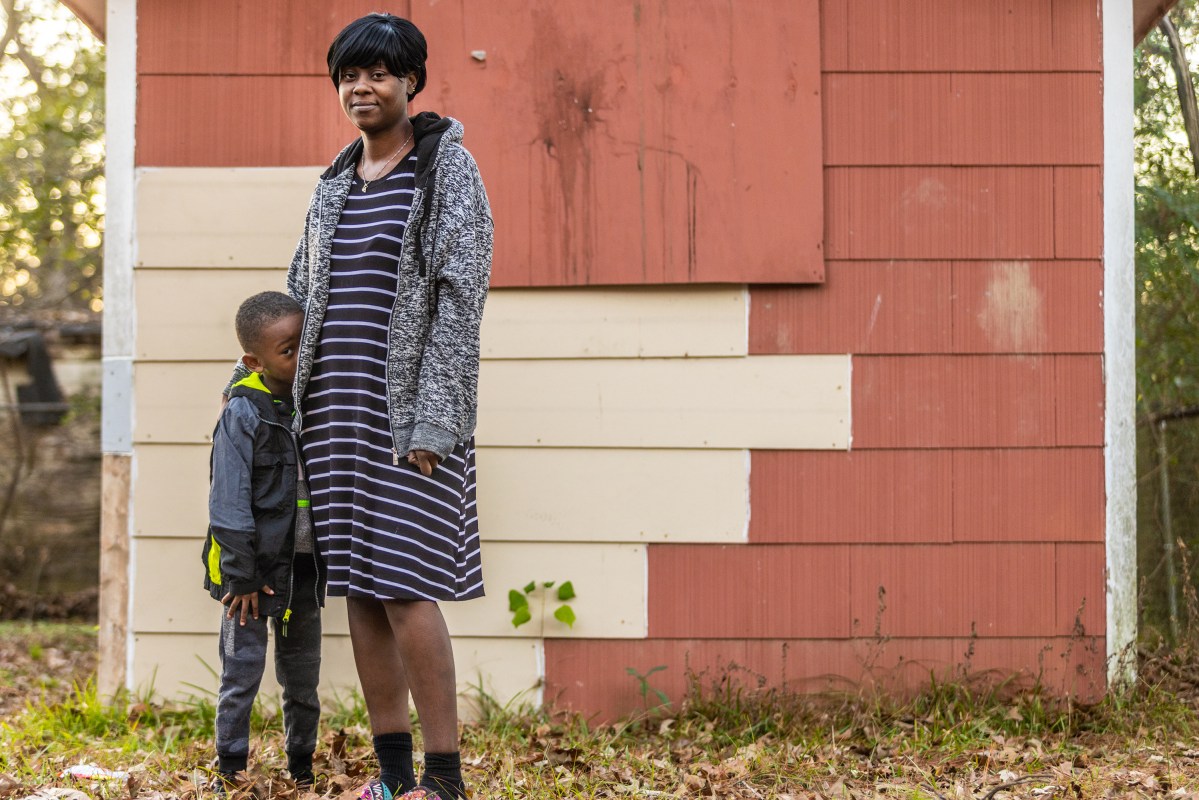
Escaping poverty was always going to be a challenge for Thomas, whose parents split before she could remember. Child Protection Services took Thomas from her mother, who is legally blind and ran an unstable household, when she was 6. She moved with her father to South Carolina until her mom regained custody, and, at 16, Thomas returned to Jackson. She bounced around high schools before dropping out, meeting her first child’s father and becoming a mother.
Thomas secured her GED and has started several higher education programs in the hopes of securing a better paying job, but it seemed like something always got in the way of her finishing. “I start strong, I start motivated, and then I might take a blow from different things and I kind of back out,” she said.
She has prioritized the paying gig that she has versus striving for another because, she said, “I know from experience that if I don’t work, we don’t eat.”
Several years ago, Thomas entered a work program offered through SNAP, the federal food assistance program administered by Mississippi Department of Human Services. It was a 24-week course, she recalled, to learn medical billing and coding – a job in which she could potentially earn $50,000. The program promised to provide her with a certificate at the end.
“During the seventh week, we went in and they told us it was no funds left to be able to continue the program,” Thomas said. “I really felt like it might have been something where they just found a way to reroute the money.”
Like that, the program was over.
During the pandemic, Thomas had to leave her home health job to take care of her kids, who were conducting virtual school at home. She applied for unemployment, which would have provided her an additional $600-a-week, more than she’d ever made and finally a chance to get ahead. But unemployment insurance only covers people who make over a certain amount, and because of her low earnings, the Mississippi Department of Employment Security denied Thomas the benefits.
It appeared a technicality: Thomas didn’t qualify under traditional unemployment insurance rules, but she should have qualified under the special pandemic unemployment program, the purpose of which was to extend benefits to people not typically covered, including part-time workers like herself.
Thomas did her research, appealed the decision, and secured a hearing with the labor office. She even got her employer to corroborate the information on her claim. But after representing herself in the proceeding, she was still denied because she had filed under the traditional unemployment insurance.
Through setback after setback, Thomas doesn’t blame the government for her current situation.
“I’m not a victim because I know the decisions and the choices I have made when it comes to these children and certain things, I’ll take the accountability for. But when it comes to my children … I’d shovel horse manure to make sure my kids eat every night. There’s nothing I wouldn’t do to make sure me and my children have a roof over our head and we have food on the table.”
Then there’s the added stress of raising her children in a neighborhood where gun violence is prevalent. “We’re in an area that’s really crime-ridden. It’s real, real crime-ridden and poverty-ridden,” Thomas said.
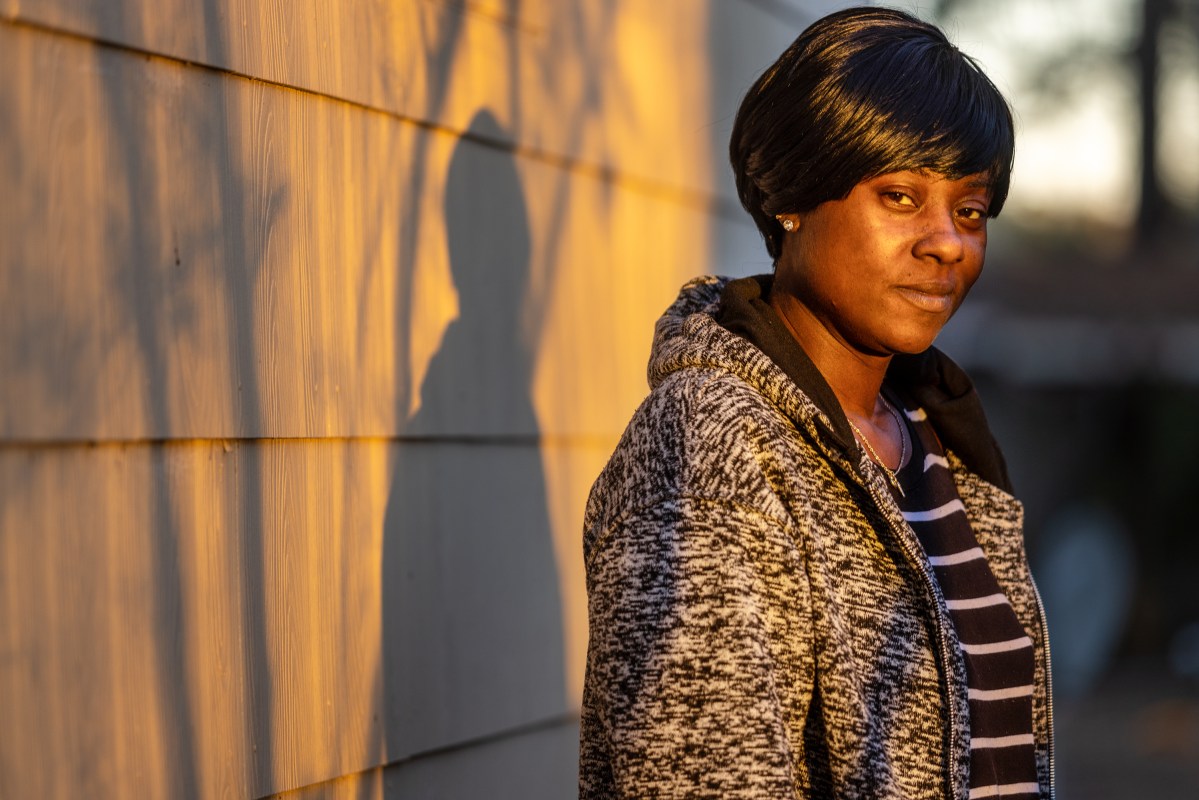

Not too long ago, Thomas’ 9-year-old son found a bag of marijuana on the ground on his way to school. A curious mind, he picked it up and carried it with him to class. When the administration discovered it, Thomas said they almost opened a DHS case, but because she’d been such an attentive parent – attending all parent-teacher conferences and volunteering to bring food for parties – a school administrator vouched for her.
“I’ve been raised in this type of environment … but I don’t wanna repeat cycles. I wanna break generational curses. I don’t want us to be here, but for some reason I feel like I’m stuck, because nothing will come in to allow me to get away from here,” Thomas said.
“Yes, I had all these kids. I made this bed. I have to lay in it,” she said. “But I also know I’m the type of person to where I’m not looking for the government to take care of me and my kids. I can do without, but they also gotta realize the trauma that they have forced upon some of us to where we can’t even live properly. Like, I don’t even like going outside of my home unless I have to.”
In August, State Auditor Shad White, who initially launched the ongoing TANF fraud investigation, released a report demonstrating the cost of “absent fathers” to Mississippi taxpayers. The report focused on how children who grow up in single-parent households are less likely to finish high school, more likely to go to prison and more likely to become teen mothers.
“I’m hoping folks will be informed as taxpayers, but will also realize collectively as a society we need to be sending the message that if you’re man enough to father a child, you ought to be man enough to step up and help raise that child,” White said when the report was released, WXXV reported.

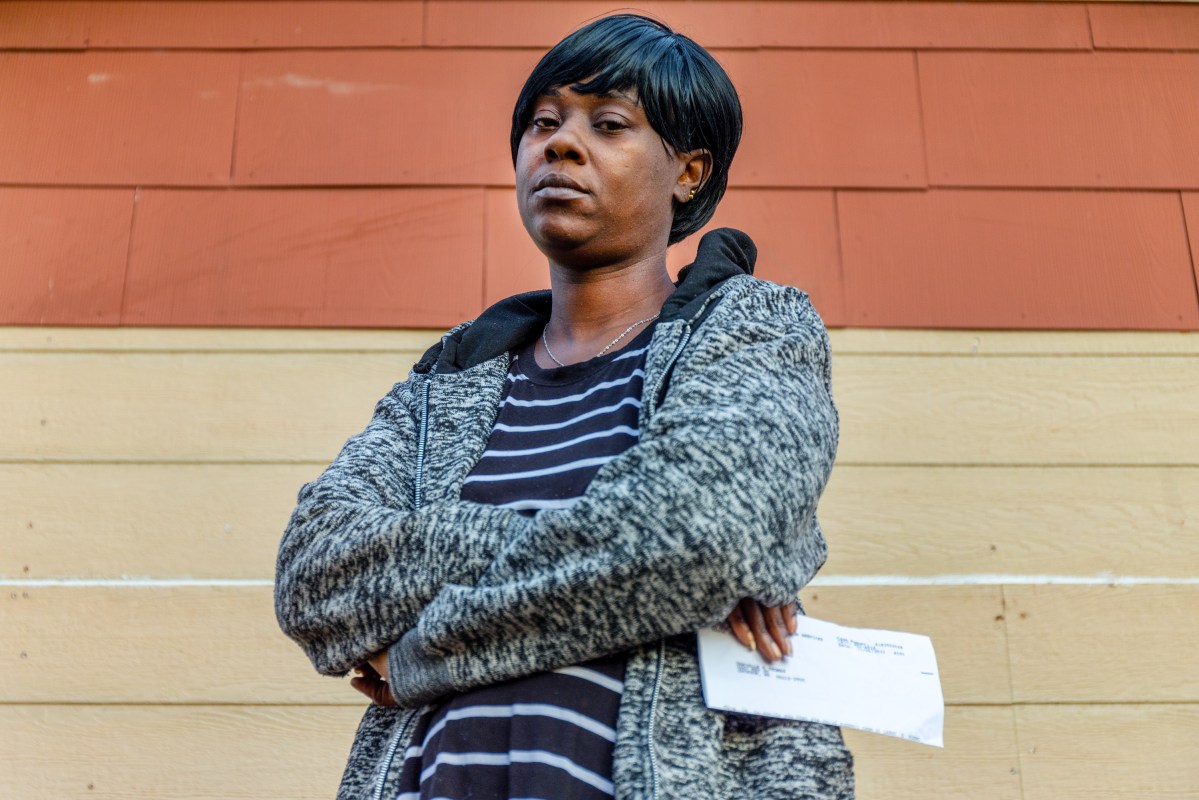
In Young’s case, Mississippi has done nothing to inspire his participation. The state took from him to indirectly support the kids of someone else, while his own kids got nothing.
National policy experts have long advocated against states confiscating the child support payments of poor children to pay back the TANF support they received. They say the practice, which barely makes a difference for states since the money is returned to the feds, keeps families in poverty and harms the relationship between children and their noncustodial parents.
“In this case, it’s even worse: the state is taking money paid by a father for children who the state didn’t even provide assistance to,” said Elizabeth Lower-Basch, deputy director for policy for the Center for Law and Social Policy (CLASP). “While the state may have found a loophole that makes this legal, keeping these funds from Mrs. Thomas and her children is a violation of both decency and common sense.”
Little to no research on this scenario exists. Mississippi’s TANF policy manual doesn’t explicitly address it, according to the reviews of Mississippi Today and two national experts who reviewed the manual at Mississippi Today’s request for this story. It does not come up in exhaustive Q&As published by the federal agency that administers the programs, the Administration for Children & Families under the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. When asked about what happened, the federal office told Mississippi Today that the agency was following Mississippi state law.
The Mississippi Department of Human Services similarly confirmed in an email to Mississippi Today that this is the agency’s policy.It said it could not comment on Thomas’ case specifically.
“While they (capped children) are not considered in the calculation of benefits, these children are still part of the head of household’s TANF case,” the statement reads. “When there are multiple children in the TANF-recipient household with different non-custodial parents, and one of those non-custodial parents makes a child support payment, that payment is applied to the overall household’s TANF recovery balance.”
It’s a miniscule policy distinction but with substantial implications – as is true with much of the state’s social safety net. The Legislature could change it.
But this area of government is often too complicated, too niche to capture the attention of the public or even policy makers. It’s part of the reason so much corruption was able to occur within the program in recent years.
Without a closer analysis, it’s easy to miss the catch-22.
When it behooves the state to exclude the children, in the case of determining who gets monthly benefits, it excludes the children. But when it benefits the state to count the children, such as to seize their child support payments, it counts them.
MDHS said it did not have any data on how many mixed-family households this policy affects.
Thomas questions it plainly: “I don’t see how one parent can be responsible for what another parent owes.”

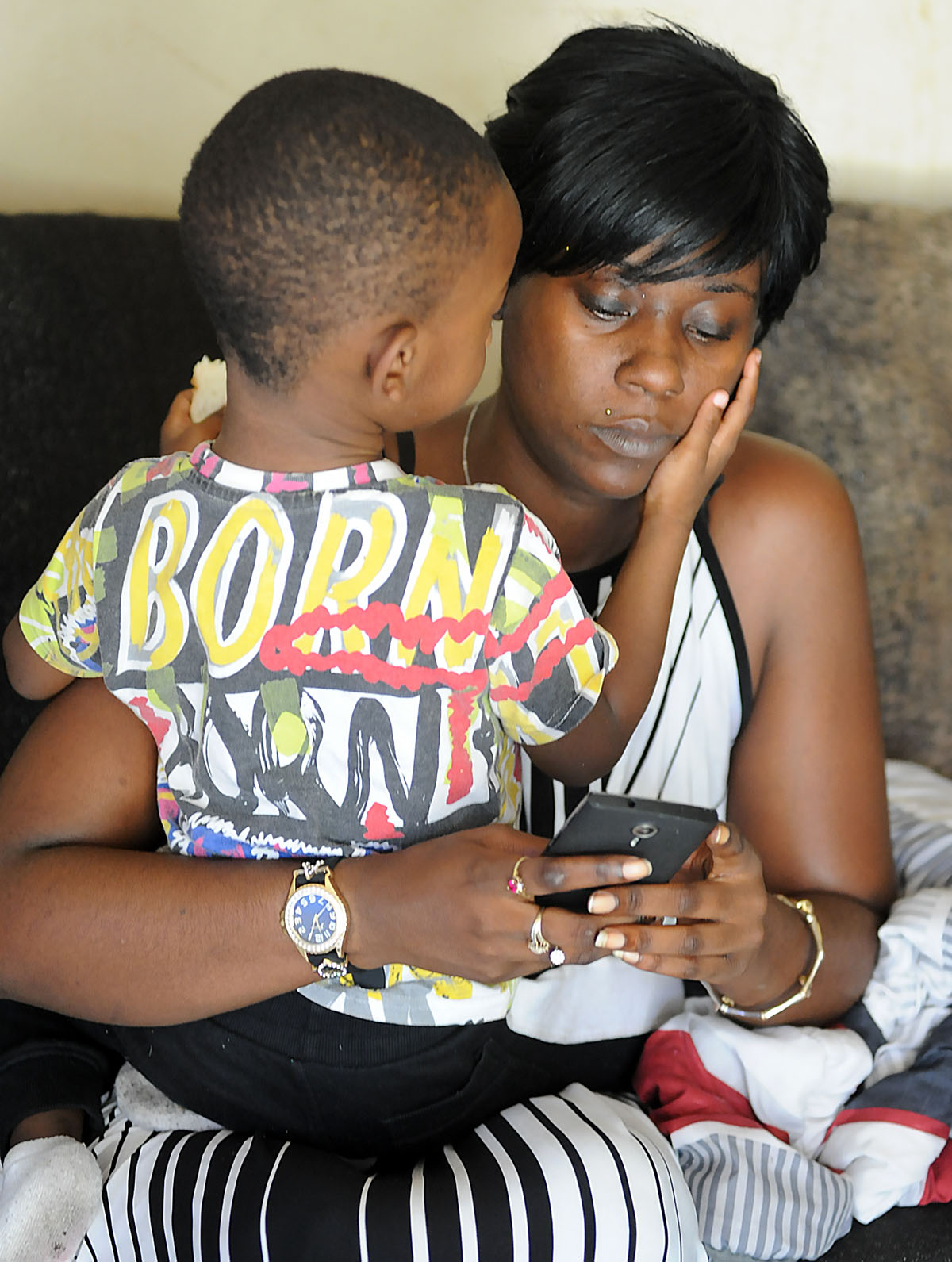
Since the $100 child support payment, Thomas has had countless calls with MDHS, the child support office, and advocates, many of whom told Thomas they’ve never encountered this scenario and that they believed it was a mistake.
When Thomas visited MDHS in person, a supervisor in the office said her TANF case carried an unreimbursed balance of about $17,000 – a mathematical mystery since she’s only received a total of $146-a-month for both children, recently raised to $236-a-month, on and off over the last several years. TANF has a lifetime limit of 60 months. At one point, an MDHS caseworker told Thomas she had been receiving TANF for two children since 2008, before her second child was even born.
“I’ve calculated and added some things up myself and I’m like, you know, ain’t no way,” Thomas said. “… It’s a lot of things I’m not understanding, but I’m really thinking like it is really just (determined by) who reviews your case and files at the time. Like, if you have someone who is reviewing your case who might let some stuff slip through the system.”
Shortly after she began pressing the agency, Thomas found a letter in her mail. It was from the child support office, notifying her that her entire MDHS public assistance case had been closed. This wasn’t true, but it added to her list of issues to resolve. She wondered if her speaking out had triggered this notice.

Several days later, Thomas received another letter. This one targeted her 5-month-old, who had barely begun receiving assistance, and ordered Thomas to add the baby to her child support case. The notice said she had 21 days to visit the office and hand over paperwork proving the child’s father or her entire family would be cut off from assistance altogether.
Following Mississippi’s ban on abortion, which led to the overturning of Roe v. Wade, Mississippi Attorney General Lynn Fitch and others have advocated for more strictly enforcing child support. The policy is advertised as a protection for mothers.
But for Thomas, the state’s meddling has only hurt her.
“They usually don’t contact you this early,” Thomas said after receiving the last letter. “I really feel like once again, this has something to do with me going and talking to people about them.”
With about $12,000 in supposed unreimbursed TANF still hanging over her head, it’s questionable if she’ll ever see a dime of child support from any of the three fathers of her children.
By this point, Thomas was dejected.
“I don’t understand how this system works,” she said in a slow, flat voice. “I’m no longer trying to figure out how it works.”
In fact, Thomas understands better than anyone how the system works. It is working the way it was designed, by wearing down the people it purports to serve.
But then, after talking to a free legal aid office, Thomas learned she could request a formal hearing from the TANF office to challenge the paradoxical policy. It’s scheduled for later this month. She’s already downloaded and started reading the agency’s program manuals from its website.
“I’m actually not going to stop fighting,” Thomas said.
In one of her educational stints, Thomas was studying to become a paralegal. When she thinks about going back to school, that’s the career path she envisions.
If her TANF case is any indicator, she’s a natural.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
IHL deletes the word ‘diversity’ from its policies

The governing board of Mississippi’s public universities voted Thursday to delete the word “diversity” from several policies, including a requirement that the board evaluate university presidents on campus diversity outcomes.
Though the Legislature has not passed a bill targeting diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives in higher education, the Institutions of Higher Learning Board of Trustees approved the changes “in order to ensure continued compliance with state and federal law,” according to the board book.
The move comes on the heels of the re-election of former President Donald Trump and after several universities in Mississippi have renamed their diversity offices. Earlier this year, the IHL board approved changes to the University of Southern Mississippi’s mission and vision statements that removed the words “diverse” and “inclusiveness.”
In an email, John Sewell, IHL’s communications director, did not respond to several questions about the policy changes but wrote that the board’s goal was to “reinforce our commitment to ensuring students have access to the best education possible, supported by world-class faculty and staff.”
“The end goal is to support all students, and to make sure they graduate fully prepared to enter the workforce, hopefully in Mississippi,” Sewell added.
On Thursday, trustees approved the changes without discussion after a first reading by Harold Pizzetta, the associate commissioner for legal affairs and risk management. But Sewell wrote in an email that the board discussed the policy amendments in open session two months ago during its retreat in Meridian, more than an hour away from the board’s normal meeting location in Jackson.
IHL often uses these retreats, which unlike its regular board meetings aren’t livestreamed and are rarely attended by members of the public outside of the occasional reporter, to discuss potentially controversial policy changes.
Last year, the board had a spirited discussion about a policy change that would have increased its oversight of off-campus programs during its retreat at the White House Hotel in Biloxi. In 2022, during a retreat that also took place in Meridian, trustees discussed changing the board’s tenure policies. At both retreats, a Mississippi Today reporter was the only member of the public to witness the discussions.
The changes to IHL’s diversity policy echo a shift, particularly at colleges and universities in conservative states, from concepts like diversity in favor of “access” and “opportunity.” In higher education, the term “diversity, equity and inclusion” has traditionally referred to a range of efforts to comply with civil rights laws and foster a sense of on-campus belonging among minority populations.
But in recent years, conservative politicians have contended that DEI programs are wasteful spending and racist. A bill to ban state funding for DEI in Mississippi died earlier this year, but at least 10 other states have passed laws seeking to end or restrict such initiatives at state agencies, including publicly funded universities, according to ABC News.
In Mississippi, the word “diversity” first appeared in IHL’s policies in 1998. The diversity statement was adopted in 2005 and amended in 2013.
The board’s vote on Thursday turned the diversity statement, which was deleted in its entirety, into a “statement on higher education access and success” according to the board book.
“One of the strengths of Mississippi is the diversity of its people,” the diversity statement read. “This diversity enriches higher education and contributes to the capacity that our students develop for living in a multicultural and interdependent world.”
Significantly, the diversity statement required the IHL board to evaluate the university presidents and the higher learning commissioner on diversity outcomes.
The statement also included system-wide goals — some of which it is unclear if the board has achieved — to increase the enrollment and graduation rates of minority students, employ more underrepresented faculty, staff and administrators, and increase the use of minority-owned contractors and vendors.
Sewell did not respond to questions about if IHL has met those goals or if the board will continue to evaluate presidents on diversity outcomes.
In the new policy, those requirements were replaced with two paragraphs about the importance of respectful dialogue on campus and access to higher education for all Mississippians.
“We encourage all members of the academic community to engage in respectful, meaningful discourse with the aim of promoting critical thinking in the pursuit of knowledge, a deeper understanding of the human condition, and the development of character,” the new policy reads. “All students should be supported in their educational journey through programming and services designed to have a positive effect on their individual academic performance, retention, and graduation.”
Also excised was a policy that listed common characteristics of universities in Mississippi, including “a commitment to ethnic and gender diversity,” among others. Another policy on institutional scholarships was also edited to remove a clause that required such programs to “promote diversity.”
“IHL is committed to higher education access and success among all populations to assist the state of Mississippi in meeting its enrollment and degree completion goals, as well as building a highly-skilled workforce,” the institutional scholarship policy now reads.
The board also approved a change that requires the universities to review their institutional mission statements on an annual basis.
A policy on “planning principles” will continue to include the word “diverse,” and a policy that states the presidential search advisory committees will “be representative in terms of diversity” was left unchanged.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Mississippi Today
Closed St. Dominic’s mental health beds to reopen in December under new management

The shuttered St. Dominic’s mental health unit will reopen under the management of a for-profit, Texas-based company next month.
Oceans Behavioral Hospital Jackson, a 77-bed facility, will provide inpatient behavioral health services to adults and seniors and add intensive outpatient treatment services next year.
“Jackson continuously ranks as one of the cities for our company that shows one of the greatest needs in terms of behavioral health,” Oceans Healthcare CEO Stuart Archer told Mississippi Today at a ribbon cutting ceremony at its location on St. Dominic’s campus Thursday. “…There’s been an outcry for high quality care.”
St. Dominic’s 83-bed mental health unit closed suddenly in June 2023, citing “substantial financial challenges.”
Merit Health Central, which operates a 71-bed psychiatric health hospital unit in Jackson, sued Oceans in March, arguing that the new hospital violated the law by using a workaround to avoid a State Health Department requirement that the hospital spend at least 17% of its gross patient revenue on indigent and charity care.
Without a required threshold for this care, Merit Health Central will shoulder the burden of treating more non-paying patients, the hospital in South Jackson argued.
The suit, which also names St. Dominic’s Hospital and the Mississippi Department of Health as defendants, awaits a ruling from Hinds County Chancery Court Judge Tametrice Hodges-Linzey next year.
The complaint does not bar Oceans from moving forward with its plans to reopen, said Archer.

Oceans operates two other mental health facilities in Mississippi and over 30 other locations in Louisiana, Oklahoma and Texas.
“Oceans is very important to the Coast, to Tupelo, and it’s important right here in this building. It’s part of the state of Mississippi’s response to making sure people receive adequate mental health care in Mississippi,” said Lt. Governor Delbert Hosemann at the Nov. 21 ribbon cutting.
Some community leaders have been critical of the facility.
“Oceans plans to duplicate existing services available to insured patients while ignoring the underserved and indigent population in need,” wrote Hinds County Sheriff Tyree Jones in an Oct. 1 letter provided to Mississippi Today by Merit Health.
Massachusetts-based Webster Equity Partners, a private-equity firm with a number of investments in health care, bought Oceans in 2022. St. Dominic’s is owned by Louisiana-based Catholic nonprofit Franciscan Missionaries of Our Lady Health System.
Oceans first filed a “certificate of need” application to reopen the St. Dominic’s mental health unit in October 2023.
Mississippi’s certificate of need law requires medical facilities to receive approval from the state before opening a new health care center to demonstrate there is a need for its services.
The Department of Health approved the application under the condition that the hospital spend at least 17% of its patient revenue on free or low-cost medical care for low-income individuals – far more than the two percent it proposed.

Oceans projected in its application that the hospital’s profit would equal $2.6 million in its third year, and it would spend $341,103 on charity care.
Merit Health contested the conditional approval, arguing that because its mental health unit provides 22% charity care, Oceans providing less would have a “significant adverse effect” on Merit by diverting more patients without insurance or unable to pay for care to its beds.
Oceans and St. Dominic’s also opposed the state’s charity care condition, arguing that 17% was an unreasonable figure.
But before a public hearing could be held on the matter, Oceans and St. Dominic’s filed for a “change of ownership,” bypassing the certificate of need process entirely. The state approved the application 11 days later.
Merit Health Central then sued Oceans, St. Dominic and the State Department of Health, seeking to nullify the change of ownership.
“The (change of ownership) filing and DOH approval … are nothing more than an ‘end run’ around CON law,” wrote Merit Health in the complaint.
Oceans, St. Dominic’s and the Mississippi Department of Health have filed motions to dismiss the case.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
Mississippi Today
How Mississippi’s Supreme Court Runoff Election Could Impact Criminal Cases

Mississippi voters have dealt defeat to one conservative state Supreme Court justice and forced a moderate justice into a Nov. 26 runoff, with the final outcome possibly making the court more open to considering the rights of criminal defendants.
The nine-member court is largely conservative but justices have recently split in high-profile decisions that sharply affected state politics, including a ruling that shut down citizen-led ballot initiatives in Mississippi and allowed some state control over local criminal cases in its majority-Black capital. The court has also rendered rulings that have made the state increasingly unfavorable to defendants appealing their cases.
“The ability of death row inmates in particular, and inmates in general, to access the courts has been recently curtailed significantly,” Matthew Steffey, a professor at Mississippi College School of Law, told The Marshall Project – Jackson and Bolts following the Nov. 5 election.
Justice Dawn H. Beam joined the majority in those decisions, acquiring a reputation of being hostile to appeals by criminal defendants, and she ran for reelection this fall as the Republican Party’s favored candidate. However, she lost in the state’s 2nd District on Nov. 5 to David P. Sullivan, a defense attorney who has worked as a public defender.
Judicial races in Mississippi are nonpartisan and Sullivan has given few explicit signals about his judicial outlook. He has supported at least some criminal justice reforms and would be the third justice with experience as a defense attorney on this court. Some reformers nationwide have pushed for more professional diversity on the bench.
Even if Sullivan turns out to be more centrist or independent than Beam on criminal law, any overall shift in power on the court depends on the outcome of a runoff election next week.
Two-term Justice Jim Kitchens and challenger Jenifer B. Branning will face each other in the Nov. 26 runoff election after neither won more than 50% of the vote on Nov. 5. The runoff will take place across the 22 counties that make up the Supreme Court’s central district, including Hinds County, home to Jackson. Throughout the campaign, the state GOP targeted Kitchens with attacks, while Branning, a Republican state senator with a conservative voting record, is endorsed by the party.
Kitchens is one of two reliably moderate-to-liberal high court justices. Justices from among an additional group of four sometimes veer away from the majority, as well, but can be more unpredictable, and this group does not vote as a bloc.
Quinn Yeargain, a Michigan State University law professor who closely watches state courts, recently analyzed the court’s voting patterns and found Beam was consistently more conservative than Kitchens in recent cases. Yeargain told The Marshall Project – Jackson and Bolts that conservative and liberal voters often have few signals about how to select a candidate in judicial races. “It’s very hard to label the justices,” they said.
Sullivan — whose father was a Mississippi Supreme Court justice from 1984 to 2000 — called himself a “conservative” throughout his campaign. But he has also touted the value of judicial independence and criticized Beam for campaigning on her endorsement by the state Republican Party.
“I think that rubbed a lot of people the wrong way,” Sullivan told the Sun Herald newspaper, speaking of Beam’s use of the endorsement. “Judicial races are nonpartisan for a reason. A judge’s impartiality could be called into question.”
Sullivan has broad legal experience, but much of his career has focused on private criminal defense while also doing some public defense work. He told The Marshall Project – Jackson and Mississippi Today that he supported a new administrative rule handed down in 2023 by the state Supreme Court to require continuous legal representation for poor criminal defendants from the beginning of their cases. An investigation by The Marshall Project, ProPublica and the Northeast Mississippi Daily Journal last year found, however, that many courts were unready at the time to implement the new representation rules.
During the campaign, Sullivan told The Marshall Project – Jackson and Mississippi Today that more work is needed to improve public defense.
Kitchens has also advocated for public defense reforms during his two terms on the court. He told a committee of legislators last year that the “playing field is far from level” between prosecutors and poor defendants.
On other criminal justice issues, he has sometimes dissented from opinions upholding death sentences. His decisions have scrutinized prosecutorial conduct and inadequate legal representation.
Branning, the Republican senator, has a voting record on criminal justice issues that suggests a harsher approach toward criminal defendants. She has supported higher mandatory minimum sentences and reclassifying misdemeanors as felonies, has opposed expansion of parole and was among only a few lawmakers who voted against legalizing medical marijuana.
She also supported increasing the jurisdiction of a controversial, state-run police force inside the majority-Black city of Jackson as well as increasing state control over many felony cases in Jackson. The Supreme Court unanimously curtailed much state power over these felony cases, but a majority left some control intact, with Kitchens and another judge dissenting.
Branning did not respond to questions from The Marshall Project – Jackson and Mississippi Today during the Nov. 5 campaign about her possible judicial outlook.
Kitchens was a prosecutor and then in private practice before joining the bench. Branning is a practicing attorney who typically handles civil cases.
The winner of the Nov. 26 runoff will join Sullivan on a court that in recent years has been restricting the ability of people who say the legal system has wronged them to seek relief, legal experts told The Marshall Project – Jackson and Bolts this month.
Krissy Nobile, director of the state’s Office of Capital Post-Conviction Counsel, said it’s become “increasingly more difficult to correct a wrongful conviction.” Her office provides legal counsel for indigent people on death row.
She said a number of recent cases showed the barriers the high court has erected for criminal defendants appealing their convictions, and demonstrated indifference to civil rights violations. Kitchens disagreed with the majority, in full or in part, in all but one of the appeals, which the court unanimously denied.
In a case earlier this year, the Court ruled to monetarily fine an incarcerated person for filing any future post-conviction relief petitions that lacked merit. Kitchens joined a dissenting opinion condemning the fine. In another, the court denied a man who argued that his lawyers were ineffective and that they did not challenge prosecutorial misconduct or false forensic evidence presented by a medical examiner with a checkered past. The court’s majority denied the motion, and in the process, overturned a precedent that allowed ineffective counsel as an adequate reason to give a case another look in some types of appeals. Kitchens dissented, along with two other justices.
“For decades in Mississippi, the Court held that it would correct errors if there was a violation (of) a person’s fundamental rights,” Nobile said. But she added this has changed considerably. Now, if you land a terrible lawyer who rushes your case, “You are out of luck,” she said, “even if your core constitutional rights have been clearly violated.”
For the court’s majority, Nobile added, “The legal technicalities now trump a person’s constitutional rights.”

The runoff is the nation’s final supreme court race of the year. Thirty-two states held elections for their high courts earlier this year, resulting in a muddled picture, with liberals and conservatives each gaining ground in different places, Bolts reports.
Mississippi’s runoff outcome will heavily depend on turnout and the composition of the electorate. In the Supreme Court’s central district, voters split narrowly between Democrat Kamala Harris and Republican Donald Trump in the presidential election on Nov. 5, but the runoff is just two days before Thanksgiving and will likely see a large dropoff in turnout. Branning received 42% of the vote in the first round, and Kitchens received 36%, with three other candidates making up the rest.
There will also be a runoff the same day in the Gulf Coast area between Amy Lassiter St. Pé and Jennifer Schloegel for an open seat on the state Court of Appeals. The Court of Appeals hears both criminal and civil cases that have been appealed from lower courts. The Mississippi Supreme Court can hear cases directly on appeal or can assign cases to the Court of Appeals.
Observers agreed that against the national legal backdrop, neither a Kitchens victory nor a Branning victory would lead to a seismic change since neither outcome would flip the court’s conservative lean. Still, a modest shift could impact some of the most controversial cases, such as a rare 5-4 decision that upheld the death sentence in Willie Manning’s case.
A Kitchens win, coupled with Sullivan’s upset earlier this month, would deal the Republican Party rare setbacks in a state where it has been dominant and could put moderate forces in a position to grow their numbers further in future elections.
“You might end up with a normal conservative court,” law professor Yeargain said, “instead of one of the most conservative courts in the country.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
-

 Our Mississippi Home7 days ago
Our Mississippi Home7 days agoCreate Art from Molten Metal: Southern Miss Sculpture to Host Annual Interactive Iron Pour
-

 Local News6 days ago
Local News6 days agoCelebrate the holidays in Ocean Springs with free, festive activities for the family
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed6 days ago'Hunting for females' | First day of trial in Laken Riley murder reveals evidence not seen yet
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed7 days agoFirst woman installed as commanding officer of NAS Pensacola
-

 Kaiser Health News4 days ago
Kaiser Health News4 days agoA Closely Watched Trial Over Idaho’s Near-Total Abortion Ban Continues Tuesday
-

 Mississippi Today6 days ago
Mississippi Today6 days agoOn this day in 1972
-
 News from the South - Alabama News Feed2 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed2 days agoTrial underway for Sheila Agee, the mother accused in deadly Home Depot shooting
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed2 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed2 days agoAlabama's weather forecast is getting colder, and a widespread frost and freeze is likely by the …


























