Mississippi Today
Mississippi prisons may soon exceed capacity

Mississippi prisons may soon exceed capacity
Mississippi — the world’s leader in imprisoning people — will soon skyrocket past its capacity to hold them all.
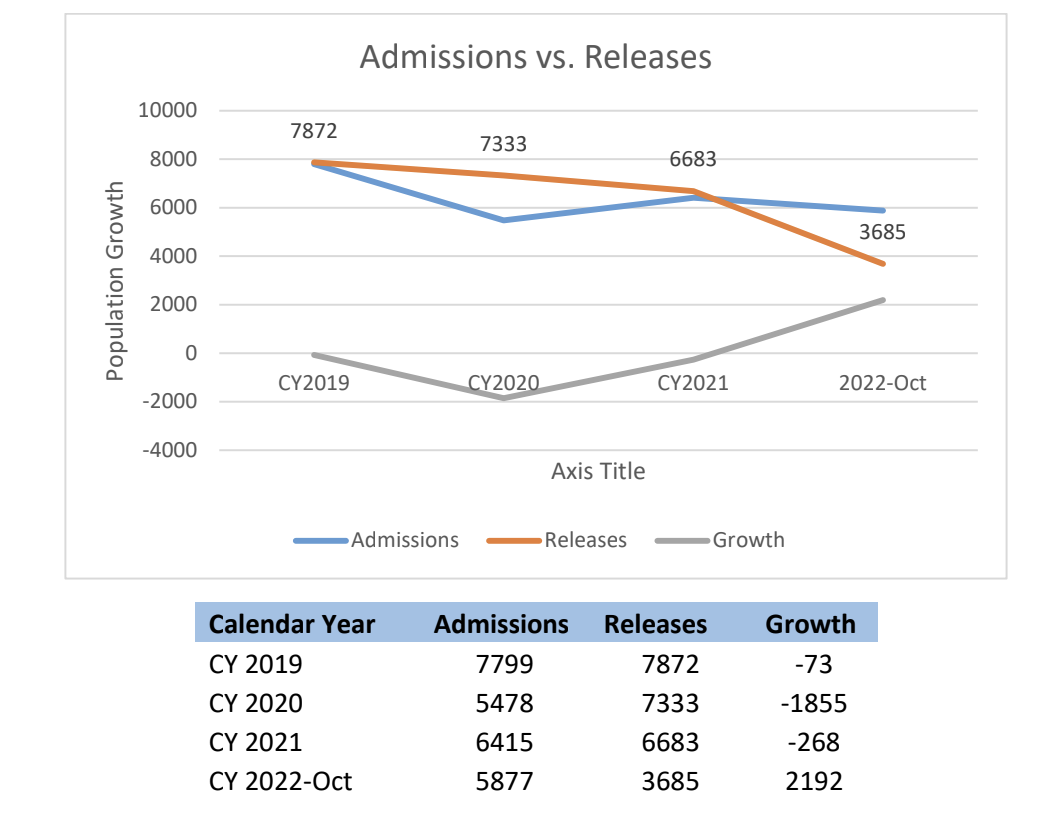
In just 10 months, the state’s prison population has exploded, rising almost twice as fast as inflation. If this rate persists, the Mississippi Department of Corrections would exceed its listed capacity of 20,443 over the next several months.
Eldon Vail, an inspector of Mississippi prisons in recent years, called the alarming rate “pouring gasoline on a top of a fire that is already raging.”
Between 1993 and 2013, the state’s prison population more than quadrupled, thanks largely to mandatory minimum sentences, with the population peaking in the past decade at more than 23,000. That prompted a push for reforms that included House Bill 585, which then Republican Gov. Phil Bryant signed into law in 2014.
In the years since, reforms and an aggressive Parole Board reduced the number of inmates. By 2016, Mississippi had fallen into third place in per capita imprisonment, trailing Louisiana and Oklahoma.
Five years later, additional reform took place with the passage of the Mississippi Earned Parole Eligibility Act, which gave thousands more inmates the opportunity to go before the Parole Board. By Feb. 7, the prison population had fallen to 16,499, the lowest level in two decades.
That fall mirrored the nation, which saw the prison population decline more than 16% in all states but one between 2019 and 2021, according to the Vera Institute of Justice. (The lone holdout? Alaska, which rose 3.6%.)
But under the leadership of new Parole Board Chairman Jeffrey Belk, that trend has reversed itself.
Ten months later, Mississippi’s prison population now exceeds 19,000 in what the Corrections and Criminal Justice Oversight Task Force calls “unprecedented growth.” If this growth continues at the same rate through 2023, that population would surpass 22,500 for the first time since 2010.
If Mississippi hits that number, taxpayers would be forced to pay $111 million more a year than they were paying in 2020 before the population hike, based on the per-day cost figured by the state’s legislative watchdog, Performance Evaluation and Expenditure Review. That’s more than enough to fund the state Department of Health, the governor’s office and a dozen other state agencies.
“While other states are reducing their prison populations, Mississippi is backsliding, thanks in large part to the actions of the Parole Board,” said Cliff Johnson, director of the MacArthur Justice Center at the University of Mississippi School of Law. “It’s demoralizing. It’s infuriating. And it’s terrible corrections policy.”
The population increase has come, despite the decline in Mississippians sentenced to prison, going from 4,270 in 2018 to 3,189 over the past year, according to the task force’s report.
In an interview, Belk told MCIR that the Parole Board is “not a numbers-driven board.”
Some people want the board to “just blindly parole people and not care if they come back,” he said. “We’re not going to do that.”
For his part, Corrections Commissioner Burl Cain said he isn’t worried about MDOC surpassing capacity, because his agency is creating 660 new spaces inside Mississippi prisons. That includes a move of all female inmates from Central Mississippi Correctional Facility in Pearl to the Delta Correctional Facility in Greenwood.
To curb the rise in prison population, he’s banking on better drug rehabilitation and job training programs to reduce recidivism.
About three-fourths of those behind bars in Mississippi battle drug or alcohol problems or both. Cain said a robust rehabilitation program is now available to 2,700 different inmates.
While serving as superintendent of the Louisiana Penitentiary at Angola, he established a job training program that resulted in a three-year recidivism rate of 9.4% for those who finished the program compared with 34% for the average inmate, according to the Louisiana Commission on Law Enforcement.
He hopes to replicate that success in Mississippi, where the three-year recidivism rate is about 33% and the five-year rate is 77%, according to the 2022 World Population Review.
So far, “we have about 170 inmates in the program,” with more to come, he said.
Most of the instructors, who are inmates, earn 25 to 30 cents an hour, or about $52 a month, he said. “It gives them a little bit of independence, and it’s really good for morale.”
MDOC’s work release program plays a companion role in this. “We have 23 out of 25 inmates in jobs making $15 an hour,” he said. “They’re not going to come back.”
Senior U.S. District Judge Keith Starrett of Hattiesburg, who chairs Mississippi’s Reentry Council, praised Cain for providing job training, moral training and job certification. “Reducing recidivism saves lives, money, families and communities,” he said.
House Bill 585 sought to reduce prison overcrowding, which the Pew Foundation estimated would save Mississippi $266 million over a decade.
But the lawmakers’ promise to use those savings for corrections programming never took place, Starrett said. “The Legislature looks out for a lot of folks, but prisons and programs that reduce recidivism are way down on their list of priorities.”
The weak link is the follow-up in programming for those leaving prison, he said. “Let’s say somebody is successful in getting drug treatment, getting a GED and getting a job, but the first week on the job, they cuss at their boss and get fired.”
Now the work goes away, “and they get discouraged and start stealing or selling drugs,” he said. “You’ve got to have support, supervision and encouragement.”
The ultimate goal of both law enforcement and corrections is community safety, and the way to make the community safer is to reduce recidivism, he said. “Of those in prison, 98% are coming back into the community. What’s important is what kind of people they are when they come back. You don’t want them coming home and breaking in your mama’s house.”
Hinds County District Attorney Jody Owens II — who worked with the then-governor and lawmakers of both parties to help pass House Bill 585 — questioned the rise in inmates. “Are we safer because we are incarcerating more people?” he asked.
Former Chairman Steve Pickett said his Parole Board had a parole rate of about 60%. That is, six out of 10 inmates eligible for parole were able to go free. Belk puts his board’s rate at about 40%.
In contrast to the past board, the current one regularly sets off parole hearings for inmates for years, sometimes as much as seven years before they’re eligible again.
Belk cited the case of 80-year-old woman Evelun Smith, who has been in prison 31 years. He said she had come up for a parole hearing every six months. This time, the Parole Board set her off five years.
“She was not ‘parole-able,’” Belk said. “She didn’t know the heinousness of her crime.”
In 1991, Smith and her boyfriend, Phillip Beard, were given life sentences for their roles in stabbing to death a 28-year-old woman, Dedra McGill of Brookhaven, who had “snitched” on Beard, according to the McComb Enterprise-Journal. Smith testified that Beard had been plotting to kill McGill before she spoke to a grand jury investigating Beard’s drug dealings.
Smith is also serving a 20-year sentence for armed robbery for the couple using McGill’s car to drive them to Louisiana to dump McGill’s mutilated and burned body.
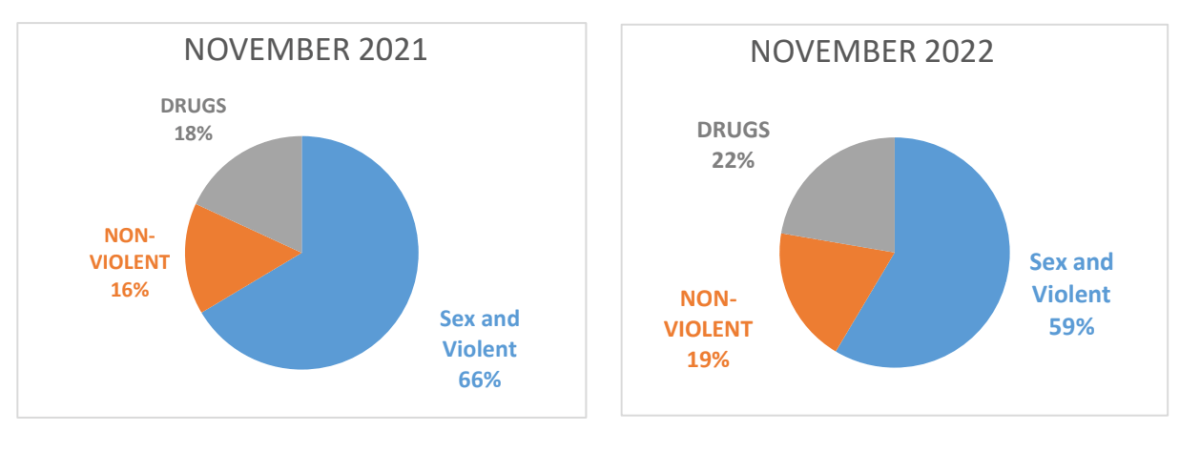
In addition to the current board granting fewer paroles, Mississippi judges are giving longer sentences, according to the task force report. The average sentence in 2018 was 7.7 years; now it’s 8.9 years. The number of those imprisoned for drug offenses has risen from 38.8% in 2018 to 47.3% over the past six months.
State Public Defender André de Gruy said he doesn’t think anyone, including the Parole Board, “knows what they are doing regarding case plans or presumptive parole. They have never followed 585 on presumptive parole.”
The state’s presumptive parole law allows MDOC to release inmates without a parole hearing if they satisfy their case plans.
“Under this program, we tell people exactly what is expected of them when they enter prison, and we reward them when they meet those expectations,” Johnson said. “Our Republican-led Legislature wisely passed the law almost a decade ago, and it has never worked like it is supposed to.”
In a 2021 report, PEER, the state lawmakers’ watchdog, concluded that the Parole Board conducted 274 unnecessary hearings for offenders who qualified for this presumptive parole.
Belk said that was PEER’s “nice way of saying they [the Parole Board and MDOC] weren’t doing it.”
He and Cain are now working to make presumptive parole a reality. That will start with creating a case plan, which will capture education levels, job skills and needs, such as alcohol or drug addictions, when an inmate enters prison, Belk said.
That plan will detail programs for the inmate to take part in, such as getting a GED, developing job skills or taking part in a recovery program, he said. If inmates complete those plans, “there’s no reason why the majority of those can’t be paroled,” he said.
If an inmate rejects chances to improve, it’s better for that inmate to wait, Belk said. “Call it tough love. Sometimes the best thing to do is not parole.”
In fact, he said, some inmates have asked the board to revoke their parole so that they could get six months of intensive drug and alcohol treatment at Walnut Grove Correctional Facility.
Ashley Lukens, president of Mississippi Dreams Prisoner Advocacy, said one major problem is inmates often can’t take classes and programs because of shortages in both correctional officers and case managers.
Since Belk took over as chairman, the Parole Board has increased the number of parole revocations from 1,949 in 2018 to an estimated 2,496 for 2022; the percentage of time served by inmates has risen from 53.5% in 2021 to 60.1% in the last quarter.
To stem this tide, de Gruy suggested the board and judges better utilize Technical Violation Centers. “A lot of people are going to prison for failure to pay fines, fees and assessments. It’s unconstitutional to send someone to prison who can’t pay.”
There needs to be reinvestment, including housing, transportation to jobs for those paroled and improvements in mental health, he said. “We need to relieve the financial burdens because 80% of people entering at arrest can’t afford a lawyer. We then add more and more financial burdens at every step of the process.”
Beyond these issues, there is the question of how many more inmates the Mississippi Department of Corrections can handle.
At the State Penitentiary at Parchman, the department has had to add bunks in order to have enough beds for inmates to sleep. Inmates in Unit 30 told MCIR they now have 104 people, but only three showers, six urinals, five toilets and five sinks.
All this is happening at the same time the department is struggling to hire and retain correctional officers, despite pay raises in recent years. MDOC officials say one of the biggest problems has been retention.
In 2014, the department had 1,591 correctional officers, according to the state Personnel Board. Today, that number is less than 1,000, even though the state is now operating two additional prisons: Walnut Grove Correctional Facility and Marshall County Correctional Facility.
Pickett, who chaired the Parole Board between 2013 and 2021, called the current correctional officer-to-inmate ratio “dangerously low.” So are the case manager numbers, he said.
“We have to accept our failure to invest in good criminal justice public policy,” he said. “We can’t keep pushing the failures back onto local police and county jails and expecting a different outcome.”
Cain said he hopes to solve this shortage through a pay raise for starting correctional officers, beginning Jan. 1. It’s a raise the Personnel Board has already approved.
Will the new pay raise succeed where the old ones failed? For years, starting officers earned $24,900 before the pay rose to $27,149. After Cain arrived in 2020, he convinced lawmakers to boost the starting salary, which is now $36,720. Despite that, MDOC continues to struggle with retaining workers. Cain hopes the newest raise to $40,248 does the trick.
Vail said in recent years, he has witnessed staffing levels so low inside Parchman and East Mississippi Correctional Facility that there wasn’t even a single officer to watch units holding prisoners of 100 or more.
“When that is the case, the vacuum of power and control is ceded to the prisoner population in the form of gangs,” said Vail, who served as corrections secretary for the state of Washington.
In an April report, Justice Department officials criticized “gross understaffing” at Parchman and “uncontrolled gang activity,” which leads to “an environment rife with weapons, drugs, gang violence and extortion. … MDOC officials have long known about these unsafe prison conditions, but have continually failed to correct the conditions.”
In recent months, Parchman has seen a new wave of violence.
On Sept. 26, inmate Richard Weems, who was serving 25 years for armed robbery and 25 years for kidnapping out of Madison County, was killed by blunt force trauma to his head.
Two weeks later, inmate Markeith Williams, who was serving a 25-year sentence for armed robbery out of Grenada County, was stabbed to death in Parchman’s Unit 29, which has a long history of violence, including the killings of three inmates in a 2019-2020 riot.
Despite having the highest incarceration rate in the nation, Mississippi spends less per inmate than any other state.
“Lack of adequate funding is the primary reason for the extraordinary levels of violence and death in the Mississippi Department of Corrections,” Vail said.
Whatever momentum there might have been to parole more people from prison may have been undone by the case of Frederick Bell, whom the Parole Board voted to release under supervision after he served 31 years behind bars for the 1991 killing of a 21-year-old clerk during a store robbery. He also pleaded guilty to killing a 20-year-old man in Memphis.
Bell committed the crimes when he was 19, and now he serves as a mentor, teacher and pastor behind bars.
In August, the Parole Board concluded that he had been rehabilitated and voted to free him, but when criticism followed, the board reversed its decision — just hours before he was slated to walk out the doors of Parchman prison.
Brandon Jones, director of political campaigns for the Southern Poverty Law Center, criticized Mississippi’s “terrible thicket of sentencing laws,” which include “one of the most unforgiving habitual offender arrangements in the world.”
This means thousands of Mississippians held behind bars have “no path to parole at all,” he said. “There needs to be more reasonable paths to parole and a Parole Board that sees the value in second chances.”
Email Jerry.Mitchell@MississippiCIR.org. You can follow him on Facebook, Twitter or Instagram.
This story was produced by the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting, a nonprofit news organization that is exposing wrongdoing, educating and empowering Mississippians, and raising up the next generation of investigative reporters. Sign up for our newsletter.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Mississippi Legislature approves DEI ban after heated debate
Mississippi lawmakers have reached an agreement to ban diversity, equity and inclusion programs and a list of “divisive concepts” from public schools across the state education system, following the lead of numerous other Republican-controlled states and President Donald Trump’s administration.
House and Senate lawmakers approved a compromise bill in votes on Tuesday and Wednesday. It will likely head to Republican Gov. Tate Reeves for his signature after it clears a procedural motion.
The agreement between the Republican-dominated chambers followed hours of heated debate in which Democrats, almost all of whom are Black, excoriated the legislation as a setback in the long struggle to make Mississippi a fairer place for minorities. They also said the bill could bog universities down with costly legal fights and erode academic freedom.
Democratic Rep. Bryant Clark, who seldom addresses the entire House chamber from the podium during debates, rose to speak out against the bill on Tuesday. He is the son of the late Robert Clark, the first Black Mississippian elected to the state Legislature since the 1800s and the first Black Mississippian to serve as speaker pro tempore and preside over the House chamber since Reconstruction.
“We are better than this, and all of you know that we don’t need this with Mississippi history,” Clark said. “We should be the ones that say, ‘listen, we may be from Mississippi, we may have a dark past, but you know what, we’re going to be the first to stand up this time and say there is nothing wrong with DEI.'”
Legislative Republicans argued that the measure — which will apply to all public schools from the K-12 level through universities — will elevate merit in education and remove a list of so-called “divisive concepts” from academic settings. More broadly, conservative critics of DEI say the programs divide people into categories of victims and oppressors and infuse left-wing ideology into campus life.
“We are a diverse state. Nowhere in here are we trying to wipe that out,” said Republican Sen. Tyler McCaughn, one of the bill’s authors. “We’re just trying to change the focus back to that of excellence.”
The House and Senate initially passed proposals that differed in who they would impact, what activities they would regulate and how they aim to reshape the inner workings of the state’s education system. Some House leaders wanted the bill to be “semi-vague” in its language and wanted to create a process for withholding state funds based on complaints that almost anyone could lodge. The Senate wanted to pair a DEI ban with a task force to study inefficiencies in the higher education system, a provision the upper chamber later agreed to scrap.
The concepts that will be rooted out from curricula include the idea that gender identity can be a “subjective sense of self, disconnected from biological reality.” The move reflects another effort to align with the Trump administration, which has declared via executive order that there are only two sexes.
The House and Senate disagreed on how to enforce the measure but ultimately settled on an agreement that would empower students, parents of minor students, faculty members and contractors to sue schools for violating the law.
People could only sue after they go through an internal campus review process and a 25-day period when schools could fix the alleged violation. Republican Rep. Joey Hood, one of the House negotiators, said that was a compromise between the chambers. The House wanted to make it possible for almost anyone to file lawsuits over the DEI ban, while Senate negotiators initially bristled at the idea of fast-tracking internal campus disputes to the legal system.
The House ultimately held firm in its position to create a private cause of action, or the right to sue, but it agreed to give schools the ability to conduct an investigative process and potentially resolve the alleged violation before letting people sue in chancery courts.
“You have to go through the administrative process,” said Republican Sen. Nicole Boyd, one of the bill’s lead authors. “Because the whole idea is that, if there is a violation, the school needs to cure the violation. That’s what the purpose is. It’s not to create litigation, it’s to cure violations.”
If people disagree with the findings from that process, they could also ask the attorney general’s office to sue on their behalf.
Under the new law, Mississippi could withhold state funds from schools that don’t comply. Schools would be required to compile reports on all complaints filed in response to the new law.
Trump promised in his 2024 campaign to eliminate DEI in the federal government. One of the first executive orders he signed did that. Some Mississippi lawmakers introduced bills in the 2024 session to restrict DEI, but the proposals never made it out of committee. With the national headwinds at their backs and several other laws in Republican-led states to use as models, Mississippi lawmakers made plans to introduce anti-DEI legislation.
The policy debate also unfolded amid the early stages of a potential Republican primary matchup in the 2027 governor’s race between State Auditor Shad White and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann. White, who has been one of the state’s loudest advocates for banning DEI, had branded Hosemann in the months before the 2025 session “DEI Delbert,” claiming the Senate leader has stood in the way of DEI restrictions passing the Legislature.
During the first Senate floor debate over the chamber’s DEI legislation during this year’s legislative session, Hosemann seemed to be conscious of these political attacks. He walked over to staff members and asked how many people were watching the debate live on YouTube.
As the DEI debate cleared one of its final hurdles Wednesday afternoon, the House and Senate remained at loggerheads over the state budget amid Republican infighting. It appeared likely the Legislature would end its session Wednesday or Thursday without passing a $7 billion budget to fund state agencies, potentially threatening a government shutdown.
“It is my understanding that we don’t have a budget and will likely leave here without a budget. But this piece of legislation …which I don’t think remedies any of Mississippi’s issues, this has become one of the top priorities that we had to get done,” said Democratic Sen. Rod Hickman. “I just want to say, if we put that much work into everything else we did, Mississippi might be a much better place.”
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
House gives Senate 5 p.m. deadline to come to table, or legislative session ends with no state budget
The House on Wednesday attempted one final time to revive negotiations between it and the Senate over passing a state budget.
Otherwise, the two Republican-led chambers will likely end their session without funding government services for the next fiscal year and potentially jeopardize state agencies.
The House on Wednesday unanimously passed a measure to extend the legislative session and revive budget bills that had died on legislative deadlines last weekend.
House Speaker Jason White said he did not have any prior commitment that the Senate would agree to the proposal, but he wanted to extend one last offer to pass the budget. White, a Republican from West, said if he did not hear from the Senate by 5 p.m. on Wednesday, his chamber would end its regular session.
“The ball is in their court,” White said of the Senate. “Every indication has been that they would not agree to extend the deadlines for purposes of doing the budget. I don’t know why that is. We did it last year, and we’ve done it most years.”
But it did not appear likely Wednesday afternoon that the Senate would comply.
The Mississippi Legislature has not left Jackson without setting at least most of the state budget since 2009, when then Gov. Haley Barbour had to force them back to set one to avoid a government shutdown.
The House measure to extend the session is now before the Senate for consideration. To pass, it would require a two-thirds majority vote of senators. But that might prove impossible. Numerous senators on both sides of the aisle vowed to vote against extending the current session, and Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann who oversees the chamber said such an extension likely couldn’t pass.
Senate leadership seemed surprised at the news that the House passed the resolution to negotiate a budget, and several senators earlier on Wednesday made passing references to ending the session without passing a budget.
“We’ll look at it after it passes the full House,” Senate President Pro Tempore Dean Kirby said.
The House and Senate, each having a Republican supermajority, have fought over many issues since the legislative session began early January.
But the battle over a tax overhaul plan, including elimination of the state individual income tax, appeared to cause a major rift. Lawmakers did pass a tax overhaul, which the governor has signed into law, but Senate leaders cried foul over how it passed, with the House seizing on typos in the Senate’s proposal that accidentally resembled the House’s more aggressive elimination plan.
The Senate had urged caution in eliminating the income tax, and had economic growth triggers that would have likely phased in the elimination over many years. But the typos essentially negated the triggers, and the House and governor ran with it.
The two chambers have also recently fought over the budget. White said he communicated directly with Senate leaders that the House would stand firm on not passing a budget late in the session.
But Senate leaders said they had trouble getting the House to meet with them to haggle out the final budget.
On the normally scheduled “conference weekend” with a deadline to agree to a budget last Saturday, the House did not show, taking the weekend off. This angered Hosemann and the Senate. All the budget bills died, requiring a vote to extend the session, or the governor forcing them into a special session.
If the Legislature ends its regular session without adopting a budget, the only option to fund state agencies before their budgets expire on June 30 is for Gov. Tate Reeves to call lawmakers back into a special session later.
“There really isn’t any other option (than the governor calling a special session),” Lt. Gov. Delbert Hosemann previously said.
If Reeves calls a special session, he gets to set the Legislature’s agenda. A special session call gives an otherwise constitutionally weak Mississippi governor more power over the Legislature.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Mississippi Today
Amount of federal cuts to health agencies doubles
Cuts to public health and mental health funding in Mississippi have doubled – reaching approximately $238 million – since initial estimates last week, when cancellations to federal grants allocated for COVID-19 pandemic relief were first announced.
Slashed funding to the state’s health department will impact community health workers, planned improvements to the public health laboratory, the agency’s ability to provide COVID-19 vaccinations and preparedness efforts for emerging pathogens, like H5 bird flu.
The grant cancellations, which total $230 million, will not be catastrophic for the agency, State Health Officer Dr. Daniel Edney told members of the Mississippi House Democratic Caucus at the Capitol April 1.
But they will set back the agency, which is still working to recover after the COVID-19 pandemic decimated its workforce and exposed “serious deficiencies” in the agency’s data collection and management systems.
The cuts will have a more significant impact on the state’s economy and agency subgrantees, who carry out public health work on the ground with health department grants, he said.
“The agency is okay. But I’m very worried about all of our partners all over the state,” Edney told lawmakers.
The health department was forced to lay off 17 contract workers as a result of the grant cancellations, though Edney said he aims to rehire them under new contracts.
Other positions funded by health department grants are in jeopardy. Two community health workers at Back Bay Mission, a nonprofit that supports people living in poverty in Biloxi, were laid off as a result of the cuts, according to WLOX. It’s unclear how many more community health workers, who educate and help people access health care, have been impacted statewide.
The department was in the process of purchasing a comprehensive data management system before the cuts and has lost the ability to invest in the Mississippi Public Health Laboratory, he said. The laboratory performs environmental and clinical testing services that aid in the prevention and control of disease.
The agency has worked to reduce its dependence on federal funds, Edney said, which will help it weather the storm. Sixty-six percent of the department’s budget is federally funded.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention pulled back $11.4 billion in funding to state health departments nationwide last week. The funding was originally allocated by Congress for testing and vaccination against the coronavirus as part of COVID-19 relief legislation, and to address health disparities in high-risk and underserved populations. An additional $1 billion from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration was also terminated.
“The COVID-19 pandemic is over, and HHS will no longer waste billions of taxpayer dollars responding to a non-existent pandemic that Americans moved on from years ago,” the Department of Health and Human Services Director of Communications Andrew Nixon said in a statement.
HHS did not respond to questions from Mississippi Today about the cuts in Mississippi.
Democratic attorneys general and governors in 23 states filed a lawsuit against the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Tuesday, arguing that the sudden cancellation of the funding was unlawful and seeking injunctive relief to halt the cuts. Mississippi did not join the suit.
Mental health cuts
The Department of Mental Health received about $7.5 million in cuts to federal grants from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.

Over half of the cuts were to community mental health centers, and supported alcohol and drug treatment services for people who can not afford treatment, housing services for parenting and pregnant women and their children, and prevention services.
The cuts could result in reduced beds at community mental health centers, Phaedre Cole, the director of Life Help and President of Mississippi Association of Community Mental Health Centers, told lawmakers April 1.
Community mental health centers in Mississippi are already struggling to keep their doors open. Four centers in the state have closed since 2012, and a third have an imminent to high risk of closure, Cole told legislators at a hearing last December.
“We are facing a financial crisis that threatens our ability to maintain our mission,” she said Dec. 5.
Cuts to the department will also impact diversion coordinators, who are charged with reducing recidivism of people with serious mental illness to the state’s mental health hospital, a program for first-episode psychosis, youth mental health court funding, school-aged mental health programs and suicide response programs.
The Department of Mental Health hopes to reallocate existing funding from alcohol tax revenue and federal block grant funding to discontinued programs.
The agency posted a list of all the services that have received funding cuts. The State Department of Health plans to post such a list, said spokesperson Greg Flynn.
Health leaders have expressed fear that there could be more funding cuts coming.
“My concern is that this is the beginning and not the end,” said Edney.
This article first appeared on Mississippi Today and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.![]()
-

 Mississippi Today1 day ago
Mississippi Today1 day agoPharmacy benefit manager reform likely dead
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed6 days agoSevere storms will impact Alabama this weekend. Damaging winds, hail, and a tornado threat are al…
-

 News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days ago
News from the South - Alabama News Feed5 days agoUniversity of Alabama student detained by ICE moved to Louisiana
-

 News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Oklahoma News Feed4 days agoTornado watch, severe thunderstorm warnings issued for Oklahoma
-

 News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Kentucky News Feed6 days agoA little early morning putting at the PGA Tour Superstore
-

 News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days ago
News from the South - Virginia News Feed6 days agoYoungkin removes Ellis, appoints Cuccinelli to UVa board | Virginia
-

 News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days ago
News from the South - Florida News Feed7 days agoPeanut farmer wants Florida water agency to swap forest land
-

 News from the South - Georgia News Feed4 days ago
News from the South - Georgia News Feed4 days agoGeorgia road project forcing homeowners out | FOX 5 News